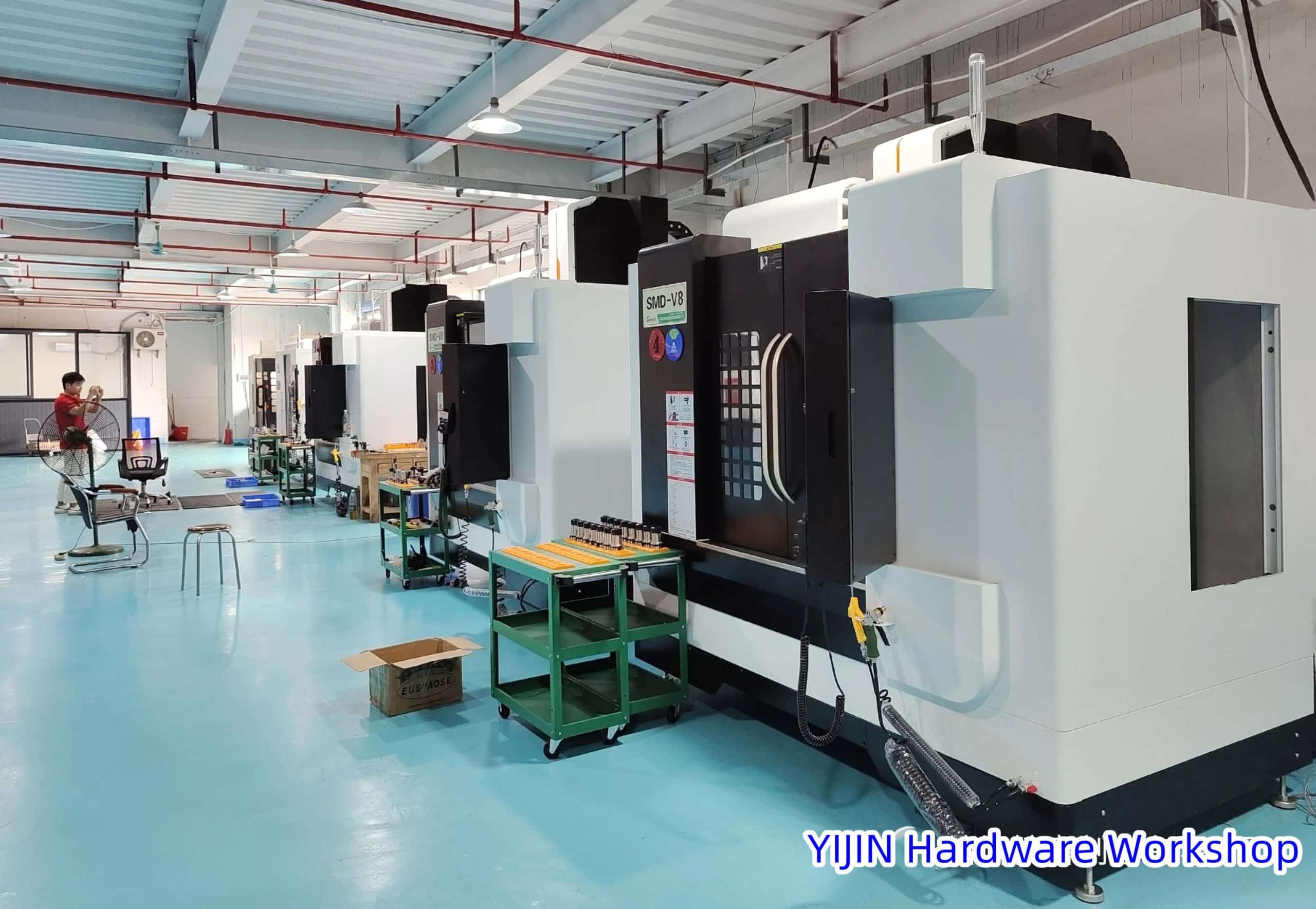
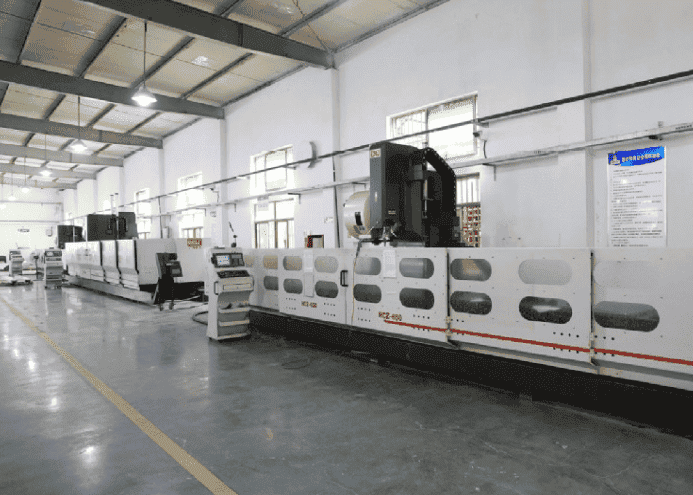
Computer-aided design (CAD) is an ingenious digital technology that serves as a design chameleon, shifting the way design is done in numerous fields. It’s the transformation of artistic creation into pixelated perfection.
At its core, CAD offers a digital canvas where designers can draft intricate 2D or 3D models of objects, buildings, or systems. But it’s not just a digital doodle.
These models aren’t just pictures; they are sophisticated data repositories of geometry that permit millimeter-precise measurements, swift alterations, and simulations.
CAD isn’t picky about where it lends its magic – it finds a comfortable home in various domains, including:
- Engineering: CAD engineers create digital marvels – like detailed mechanical parts & complex architectural structures. They can predict how materials interact, simulate stresses, and make sure things fit seamlessly.
- Architecture: CAD has become the blueprint of modern architects. It allows them to dream in three dimensions, shaping skyscrapers or cozy cottages with unparalleled precision.
- Manufacturing: In the manufacturing world, CAD shortens the product development journey. It produces lifelike prototypes, enabling engineers to test their ideas and eliminate errors early on.
- Fashion and Apparel: Even the fashion industry has surrendered to CAD’s charm. Fashion designers harness their power for pattern creation, garment design, and endless fabric experiments.
Learn More: Precision Machined Parts Design Services
How Does Computer-Aided Design Work?
CAD is not just a digital canvas; it’s a multidimensional toolkit. It weaves its magic through a well-choreographed dance of digital design:
- Design Creation: The journey begins with the creation of a digital sketch or 3D model, depending on the designer’s vision.
- Modeling: The CAD stage is where creativity meets precision. Designers manipulate the digital object, altering its size, shape, and properties, often to a fraction of a millimeter.
- Analysis: Engineers and architects use CAD for what’s known as the ‘what-if’ game. They simulate how designs will perform under different circumstances, predicting behavior under stress, thermal fluctuations, or fluid dynamics.
- Documentation: CAD software wears the hat of an impeccable documentarian, producing detailed and accurate documentation for every aspect of the design, from blueprints to assembly instructions.
- Collaboration: CAD is also a master facilitator of teamwork. It allows multiple team members to collaborate easily, sharing, reviewing, and refining designs in real time.
- Prototyping: CAD-generated models become real through 3D printing or CNC machining, serving as prototypes to test and fine-tune designs before full-scale production.
Types of CAD
CAD comes in an assortment of flavors, each tailored to a specific craving:
- 2D CAD: A plain yet powerful tool for creating 2D drawings, ideal for floor plans, electrical circuits, and technical schematics. Think of AutoCAD as the poster child for 2D CAD.
- 3D CAD: It’s all about the third dimension. Designers revel in creating 3D models of objects and structures. Think of SolidWorks and CATIA as the heavyweights in the 3D CAD arena.
- Parametric CAD: Parametric CAD turns the design process into a mathematical equation. Design elements are connected to parameters, simplifying modifications. Autodesk Inventor is a prime example.
- BIM (Building Information Modeling): BIM is the kingpin in the architecture and construction realm. It’s all about creating smart 3D models loaded with data on building components, materials, and construction processes.
- CAD for Electronics: Electronics wizards work their magic with specialized CAD software like Eagle and KiCad. It’s all about PCB layouts and schematics.
- Graphic Design CAD: Graphic designers wield Adobe Illustrator and CorelDRAW for 2D graphic design, illustration, and layout.

Who Uses CAD?
- Architects and Civil Engineers: The masters of structures and landscapes, architects and civil engineers rely on CAD to conjure blueprints and 3D marvels for buildings and infrastructure. With CAD, visualizing becomes a reality.
- Mechanical Engineers: The mechanical world bows to CAD’s prowess. Engineers crafting machines, automotive parts, and complex systems harness CAD to streamline design, ensuring prototypes materialize without hitches.
- Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Electrical and electronics engineers employ CAD wizardry in the design of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electrical systems. It unravels complex wiring diagrams and guarantees a snug component fit.
- Industrial Designers: Industrial designers summon CAD to weave product prototypes, fiddle with aesthetics, and scrutinize ergonomics. This is before the manufacturing alchemy commences.
- Aerospace and Automotive Engineers: The sky and road conquerors, aerospace and automotive engineers, rely on CAD to perfect aerodynamics, safety, and overall performance.
- Environmental Engineers: When nature meets engineering, CAD plays a pivotal role. It designs eco-friendly water treatment plants and green waste management systems that safeguard our planet.
- Fashion Designers: In the world of fashion, CAD helps designers conjure digital prototypes of apparel and accessories, weaving the threads of creativity into practical elegance.
- Interior Designers: Inside spaces are no less challenging. Interior designers harness CAD to craft visions of room layouts, placing furniture and decor with finesse.
- Gaming and Animation Professionals: CAD isn’t limited to the tangible world. It fuels the creation of 3D models, environments, and animated characters in the gaming and animation domains, enhancing the realms of fantasy.

CAD benefits
The magic of CAD extends far beyond industries and professions, offering a treasure chest of benefits:
- Precision and Accuracy: CAD’s precision wields the power to virtually eliminate errors, sparing you the torment of rework.
- Efficiency: The design process accelerates, allowing rapid experimentation and adjustments, unleashing the true power of your creativity.
- Visualization: CAD doesn’t stop at 2D. Its 3D modeling capabilities empower you to visualize your creations like never before.
- Collaboration: CAD isn’t a lone wizard’s tool. Its collaborative features enchant team members, fostering real-time communication across vast distances.
- Cost Reduction: CAD reveals design flaws before they metamorphose into costly issues. It’s your trusted financial advisor in the design journey.
- Documentation: Detailed documentation appears as if by magic, including bills of materials and assembly instructions, simplifying the manufacturing process.
- Customization: CAD’s spellbook is filled with customization magic, ensuring your designs align perfectly with project and client demands.
- Data Storage and Retrieval: Your designs are safeguarded and easily retrieved for future projects or tweaks, as CAD becomes your archive of digital blueprints.
- Simulation and Analysis: CAD software may integrate tools for simulations and analysis. For example, in engineering, CAD can be used to analyze stresses and strains in a structure, or in product design, it can simulate the behavior of a product under different conditions.
10 Tips to Improve Your CAD Designs for CNC Machining
[row]
[col span=”1″ span__sm=”12″]
[/col]
[col span=”10″ span__sm=”12″]
[ux_video url=”https://youtu.be/GN8xzsZFRLM”]
[/col]
[col span=”1″ span__sm=”12″]
[/col]
[/row]
Examples of CAD software
- AutoCAD: A revered presence in the CAD world, it offers both 2D and 3D design capabilities, cherished by architects, engineers, and constructors.
- SolidWorks: The mechanical, SolidWorks is a 3D CAD maestro used for industrial and mechanical design.
- CATIA: A gem of aerospace and automotive engineers, this software specializes in complex design and simulation.
- Revit: Architects and structural engineers hold Revit close to their hearts. It’s the talisman of Building Information Modeling (BIM).
- Eagle: The elixir for PCB design and electronics engineers, Eagle breathes life into electrical systems.
- Fusion 360: This cloud-enabled design marvel serves product designers, offering a seamless experience with modeling and simulation.
- Blender: In the land of gaming and animation, Blender is a potent potion, conjuring 3D models, animations, and visual effects.
- Tinkercad: The friendly wizard for beginners and educators, Tinkercad takes the complexity out of 3D printing with its browser-based charms.
Learn More: Top 10 CAD/CAM Software For CNC
Conclusion
CAD technology is a unique and indispensable technology, consistently pushing the boundaries of design and engineering.
From creating digital skyscrapers to enhancing the precision of microscopic medical devices, CAD plays a pivotal role in shaping our world.
Whether you’re an architect dreaming of the next iconic structure or a gamer exploring immersive digital realms, CAD is the unseen hand that shapes your vision into reality.
It’s where the future meets the present in a symphony of pixels and precision.
 Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569
Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569