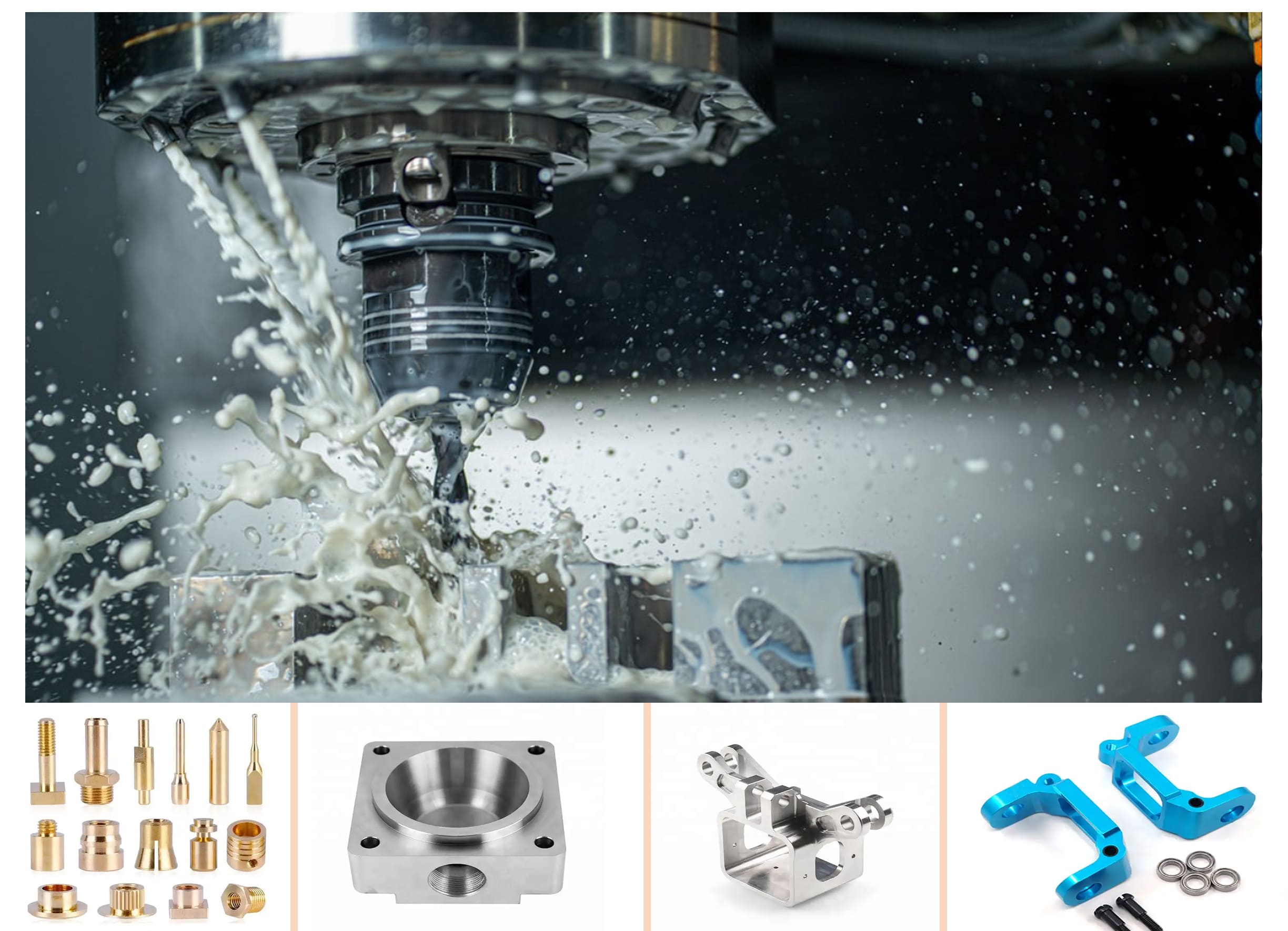
In the ever-evolving realm of contemporary manufacturing and engineering, the adoption of cutting-edge technologies is essential to attain precision, efficiency, and tailored solutions.
Among these technologies, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) stands out as a pivotal player. Covering a diverse range of services, CNC engineering encapsulates various facets, such as CNC machining, programming, and precision engineering.
This article delves into the realm of CNC engineering services, shedding light on the various facets that make it an integral part of contemporary manufacturing processes.
A. Definition of CNC Engineering Services
CNC engineering services comprise a diverse array of specialized solutions designed to harness the capabilities of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology.
Fundamentally, CNC integrates computerized systems to oversee the movement and functions of machining tools, converting raw materials into meticulously crafted components.
Beyond the fundamental machining processes, these services encompass programming, prototyping, and a myriad of additional engineering activities.
In essence, CNC engineering services represent a fusion of computer science, engineering expertise, and manufacturing prowess, with the primary goal of achieving unparalleled precision, repeatability, and efficiency in the production of components and parts.
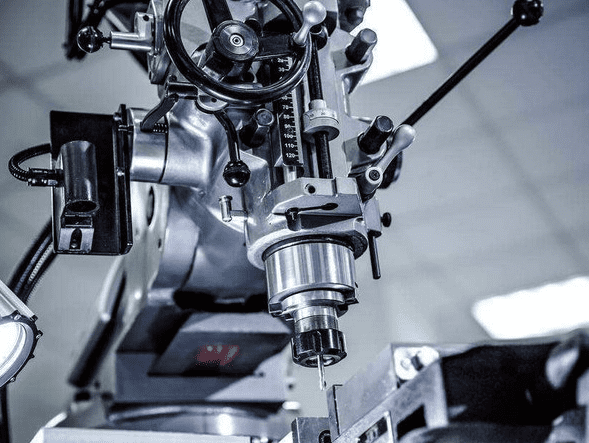
B. Overview of CNC Technology in Engineering and Manufacturing
CNC technology stands as a transformative force in the realms of engineering and manufacturing. Through the substitution of conventional manual practices with computerized control systems, CNC introduces heightened precision and automation across diverse processes.
This segment offers a comprehensive perspective on the evolutionary journey of CNC technology, delineating its essential features and functionalities.
Evolution of CNC:
The origins of CNC can be traced to the mid-20th century, marked by the initial emergence of numerical control systems in machine tools.
As time has progressed, developments in computing power, software algorithms, and machine design have propelled CNC technology to become a fundamental cornerstone of contemporary manufacturing.
Key Components of CNC Technology:
- Computer Programming: CNC machines are controlled through coded instructions, often generated using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software.
- Precision Machining: CNC machines execute precise movements, translating digital designs into physical components with minimal margin for error.
- Automation: The automation feature of CNC technology improves efficiency by decreasing manual involvement, boosting production speeds, and reducing the chances of errors.
Applications Across Industries:
CNC technology transcends specific sectors, finding applications across diverse industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics.
Its adaptability has established it as an essential tool for crafting intricate and tailored components that meet the most rigorous specifications.
Types of CNC Engineering Services
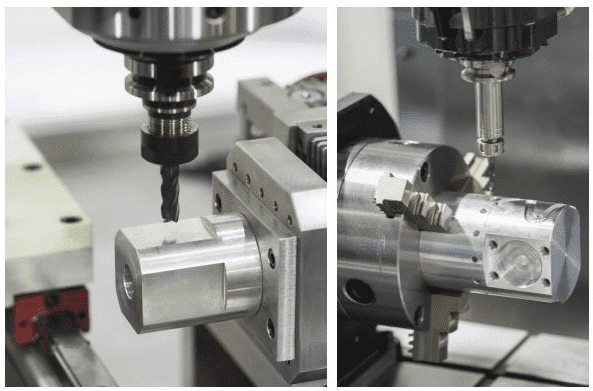
A. CNC Machining Services
CNC machining stands as a cornerstone in the world of manufacturing, where computer-controlled machines carry out precise operations on materials such as metal, plastic, and wood.
This section explores the intricacies of CNC machining, providing insights into its applications across diverse industries.
Fundamentals of CNC Machining
CNC machining represents a paradigm shift from traditional manual machining processes. At its core, CNC machining involves the use of computerized systems to control machining tools, translating digital designs into tangible, high-precision components.
The process typically includes milling, turning, drilling, and other techniques, all orchestrated with meticulous accuracy through coded instructions.
Key Components of CNC Machining
Computer Programming:
- CNC machines operate based on coded instructions, often generated using advanced Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. This programming phase dictates the tool’s movements, speeds, and operations, ensuring a seamless translation of digital designs into physical reality.
Precision Machining:
- The hallmark of CNC machining lies in its ability to execute movements with microscopic precision. This ensures that the final components meet exact specifications, crucial in industries with stringent tolerances.
Automation:
- Automation is a pivotal feature that distinguishes CNC machining. By reducing manual intervention, not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes errors, contributing to the consistent quality of the end products.
Applications Across Diverse Industries
CNC machining’s versatility transcends industry boundaries, finding applications in various sectors that demand precision, reliability, and scalability.
Aerospace Industry:
- In aerospace, where components must adhere to strict standards, CNC machining ensures the fabrication of intricate parts with utmost precision, contributing to the overall safety and performance of aircraft
Automotive Manufacturing:
- The automotive sector leverages CNC machining for the production of complex engine components, custom parts, and intricate body elements. This results in enhanced performance, fuel efficiency, and design flexibility.
Medical Device Production:
- In medical manufacturing, CNC machining is instrumental in crafting precise and intricate components for medical devices, implants, and surgical instruments. The technology’s accuracy is paramount in this field.
Electronics and Consumer Goods:
- The electronics industry relies on CNC machining for the production of intricate components for devices such as smartphones, laptops, and other consumer electronics. CNC ensures the fine details crucial for these applications.
Custom Prototyping:
- Beyond mass production, CNC machining plays a vital role in prototyping. This allows for the swift and accurate fabrication of prototypes, enabling designers and engineers to test and refine their concepts before full-scale production.
B. CNC Programming Solutions
Behind the seamless operation of CNC machines lies the art of CNC programming. This segment unravels the significance of CNC programming in achieving accuracy and consistency in engineering tasks, offering a closer look at the role it plays in the broader CNC engineering spectrum.
The Role of CNC Programming
Precision at its Core:
- At the heart of CNC programming lies the pursuit of precision. CNC machines are only as accurate as the instructions they receive, and CNC programming is the language that dictates every nuanced movement and operation.
Digital Blueprint:
- CNC programming starts with the creation of a digital blueprint, often designed using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This blueprint serves as the guidebook for the machining process, specifying the dimensions, toolpaths, and intricacies of the final product.
Achieving Consistency
Eliminating Variability:
- CNC programming eliminates the variability introduced by manual operations. Every iteration of a task is executed with exacting precision, ensuring consistency across multiple components or products.
Repeatable Excellence:
- The repeatability inherent in CNC programming is a game-changer. Once a program is perfected, it can be rerun countless times with identical results, setting a new standard for consistency in manufacturing.
The Broad Impact on CNC Engineering
Versatility Across Processes:
- CNC programming is not confined to a singular process; it extends its influence across various CNC engineering services, from milling and turning to intricate drilling operations. Its versatility makes it a linchpin in the broader CNC engineering spectrum.
Enhancing Efficiency:
- Efficiency in CNC engineering is a direct byproduct of meticulous programming. By optimizing toolpaths, minimizing unnecessary movements, and strategically planning operations, CNC programming contributes to streamlined processes and reduced production times.
Challenges and Innovations in CNC Programming
Complexity and Mastery:
- CNC programming, while powerful, demands a high level of expertise. The complexity of translating design intent into a precise set of instructions requires skilled programmers who understand not only the machining process but also the intricacies of the CNC machine being used.
Advancements in CAM Software:
- Continuous innovations in Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software contribute to the evolution of CNC programming. Modern CAM tools offer intuitive interfaces, simulation capabilities, and optimization algorithms, empowering programmers to create more efficient and error-free programs.

C. Precision Engineering Services
Precision engineering forms the bedrock of CNC processes, ensuring that intricate components and parts meet exact specifications.
Here, we delve into the world of precision engineering, elucidating its definition, scope, and crucial role in the success of CNC engineering services.
Defining Precision Engineering
Precision Unveiled:
- Precision engineering is the art and science of crafting components and parts with meticulous accuracy, often reaching into the microscopic realm. It involves a systematic approach to ensure that every dimension, tolerance, and finish meets stringent specifications.
Interplay of Disciplines:
- Precision engineering is an interdisciplinary field, amalgamating principles from mechanical engineering, metrology, materials science, and design. This collaborative approach aims to achieve perfection in the production of complex components.
The Scope of Precision Engineering in CNC
Intricate Components Demand Precision:
- CNC engineering services heavily rely on precision engineering, especially in the crafting of intricate components. From aerospace components with tight tolerances to medical devices requiring flawless precision, CNC processes guided by precision engineering fulfill diverse industry needs.
Machining Excellence:
- Precision engineering in CNC extends to machining processes, ensuring that CNC machines execute movements with minimal margin for error. This includes controlling variables such as toolpaths, speeds and feeds to achieve the desired precision in material removal.
The Crucial Role in CNC Engineering Success
Enhancing CNC Efficiency:
- Precision engineering serves as the backbone of CNC services, enhancing efficiency by minimizing deviations from design intent. Every cut, every rotation, and every operation is orchestrated with precision, contributing to streamlined and error-free manufacturing.
Meeting Rigorous Specifications:
- CNC engineering often caters to industries with stringent specifications, such as aerospace and medical. Precision engineering ensures that components not only meet but exceed these specifications, fostering reliability and performance in the final product.
Innovations in Precision Engineering for CNC
Advanced Materials and Techniques:
- The world of precision engineering continually evolves with advancements in materials and machining techniques. Innovations in materials with enhanced properties and the integration of novel manufacturing methods contribute to pushing the boundaries of precision.
Digital Precision:
- Digital technologies, including 3D scanning and metrology, complement precision engineering in CNC. These tools enable the accurate measurement and verification of machined components, closing the loop for achieving digital precision in the physical realm.

Specialized Tasks within CNC Engineering
A. Custom Part Manufacturing
1. Tailoring Parts to Specific Requirements
Custom part manufacturing is a cornerstone of CNC engineering services, offering the ability to tailor components to exact specifications.
This process involves the meticulous crafting of parts based on unique design requirements, ensuring a precise fit for specific applications.
CNC technology facilitates the production of complex and one-of-a-kind components that may be challenging or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
2. Advantages of Customization
The advantages of custom part manufacturing are multifaceted. Firstly, it allows for the creation of components that perfectly align with the needs of a particular project, contributing to enhanced performance and functionality.
Additionally, customization can lead to material and weight optimizations, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency.
The flexibility inherent in custom part manufacturing ensures that industries with diverse and unique demands can find tailored solutions that meet their exact specifications.
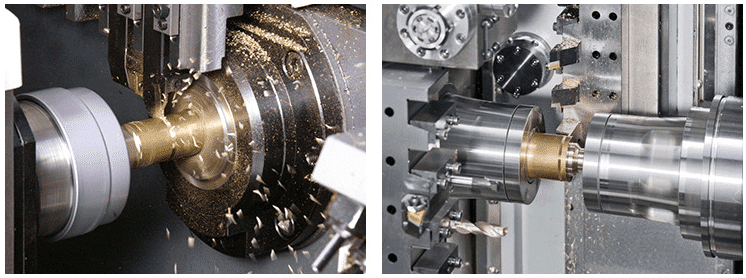
B. CNC Prototyping
1. Prototyping in CNC Processes
CNC prototyping is a pivotal phase in product development that leverages the precision and efficiency of CNC technology.
During this stage, a scaled-down version or a prototype of the final product is created, allowing for testing, validation, and refinement before full-scale production.
CNC prototyping offers a realistic representation of the end product, enabling designers and engineers to assess its form, function, and performance.
2. Rapid Prototyping Benefits
Rapid prototyping, facilitated by CNC technology, provides several key advantages in the product development lifecycle.
The speed at which CNC machines can transform digital designs into physical prototypes accelerates the iteration process, allowing for quicker design improvements.
This agility not only reduces time-to-market but also minimizes development costs by identifying and addressing issues early in the design phase.
CNC prototyping fosters innovation and creativity by enabling designers to experiment with various iterations rapidly.
Professionals and Companies Offering CNC Engineering Services
A. Finding CNC Engineering Professionals
1. Skills and Qualifications
The quest for skilled CNC engineering professionals commences by recognizing the vital skills and qualifications imperative for success in this domain.
Essential skills encompass proficiency in CNC programming, a comprehensive grasp of machining processes, and the capability to interpret intricate engineering drawings.
Strong foundations in mathematics, meticulous attention to detail, and adept problem-solving abilities are equally indispensable.
Qualifications may involve degrees in mechanical engineering, manufacturing, or related fields, further complemented by practical hands-on experience with CNC systems.
2. How to Choose the Right Professionals
Selecting the right CNC engineering professionals involves a meticulous evaluation process. Consider their expertise in specific CNC technologies, the industries they have served, and the complexity of projects they have handled.
Assessing client reviews and testimonials can provide insights into their track record and client satisfaction. Additionally, evaluating their communication skills, project management capabilities, and adherence to timelines ensures a seamless collaboration.
B. CNC Manufacturing Companies
1. Profiles of Leading Companies
Several CNC manufacturing companies stand out for their expertise, innovation, and contributions to the field.
Yijin Solution is renowned for its precision machining capabilities, specializing in aerospace components. They excel in CNC programming solutions, offering tailored services for diverse industries.
It is a leader in custom part manufacturing, with a track record of delivering high-quality components for automotive applications.
Exploring the profiles of such leading companies provides valuable insights into their strengths and areas of specialization.
Ready to experience precision like never before? Take the first step towards excellence.
Connect with us for CNC Turning Services that redefine industry standards.
Elevate your manufacturing game – start your journey with us today.
2. Services Offered by CNC Engineering Firms
CNC engineering firms typically offer a comprehensive suite of services to cater to the diverse needs of their clients.
These services may include CNC machining, precision engineering, CNC programming, custom part manufacturing, and prototyping.
Understanding the breadth of services offered by CNC engineering firms is crucial for aligning their expertise with specific project requirements.
Companies that embrace the latest advancements in CNC technology and offer turnkey solutions often stand out as preferred partners for complex engineering projects.
As industries continue to embrace CNC technology for its precision and efficiency, the selection of qualified professionals and reputable CNC manufacturing companies becomes paramount.
This exploration of finding professionals and companies within the CNC engineering domain provides a foundation for making informed decisions and fostering successful collaborations.
Applications and Benefits of CNC Engineering Services
A. Benefits of CNC Engineering
1. Precision and Accuracy
One of the primary benefits of CNC engineering services is the unparalleled precision and accuracy they bring to manufacturing processes.
Computer Numerical Control ensures that machining operations are executed with microscopic precision, eliminating the variations introduced by manual methods.
This precision is especially crucial in industries such as aerospace and medicine, where exact measurements and tolerances are non-negotiable.
2. Increased Efficiency
CNC engineering services significantly enhance manufacturing efficiency by minimizing manual intervention and streamlining processes.
The automation aspect of CNC technology allows for continuous and consistent operation, leading to faster production cycles. Reduced downtime, enhanced repeatability, and the ability to run operations 24/7 contribute to a substantial increase in overall efficiency, making CNC an ideal choice for high-volume production.
B. Costs of CNC Machining
1. Factors Influencing Costs
While the benefits of CNC engineering are evident, understanding the factors that influence costs is crucial for effective project management.
- Material Costs: The type and quality of materials used directly impact costs. Exotic or high-grade materials may result in higher expenses.
- Machine Complexity: The intricacy of the machining process, including the number of axes involved, tool changes, and programming complexity, can influence costs.
- Project Volume: Economies of scale come into play, with larger production volumes often leading to reduced costs per unit.
- Tooling and Setup: Initial setup costs, including tooling and fixturing, can contribute to the overall expenses.
2. Cost-effectiveness of CNC Engineering Services
Despite the initial setup costs, CNC engineering services are often highly cost-effective in the long run.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automation minimizes the need for extensive manual labor, reducing labor costs and the risk of human errors.
- Efficient Material Utilization: CNC machines optimize material usage, minimizing waste and contributing to cost savings.
- Faster Time-to-Market: The precision and efficiency of CNC processes translate to quicker production cycles, reducing time-to-market and potentially lowering overall project costs.
The benefits of precision, increased efficiency, and the cost-effectiveness of CNC engineering services make them a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Understanding the intricacies of cost factors ensures that businesses can harness the power of CNC technology while optimizing their budgetary considerations.
Advanced CNC Engineering Solutions
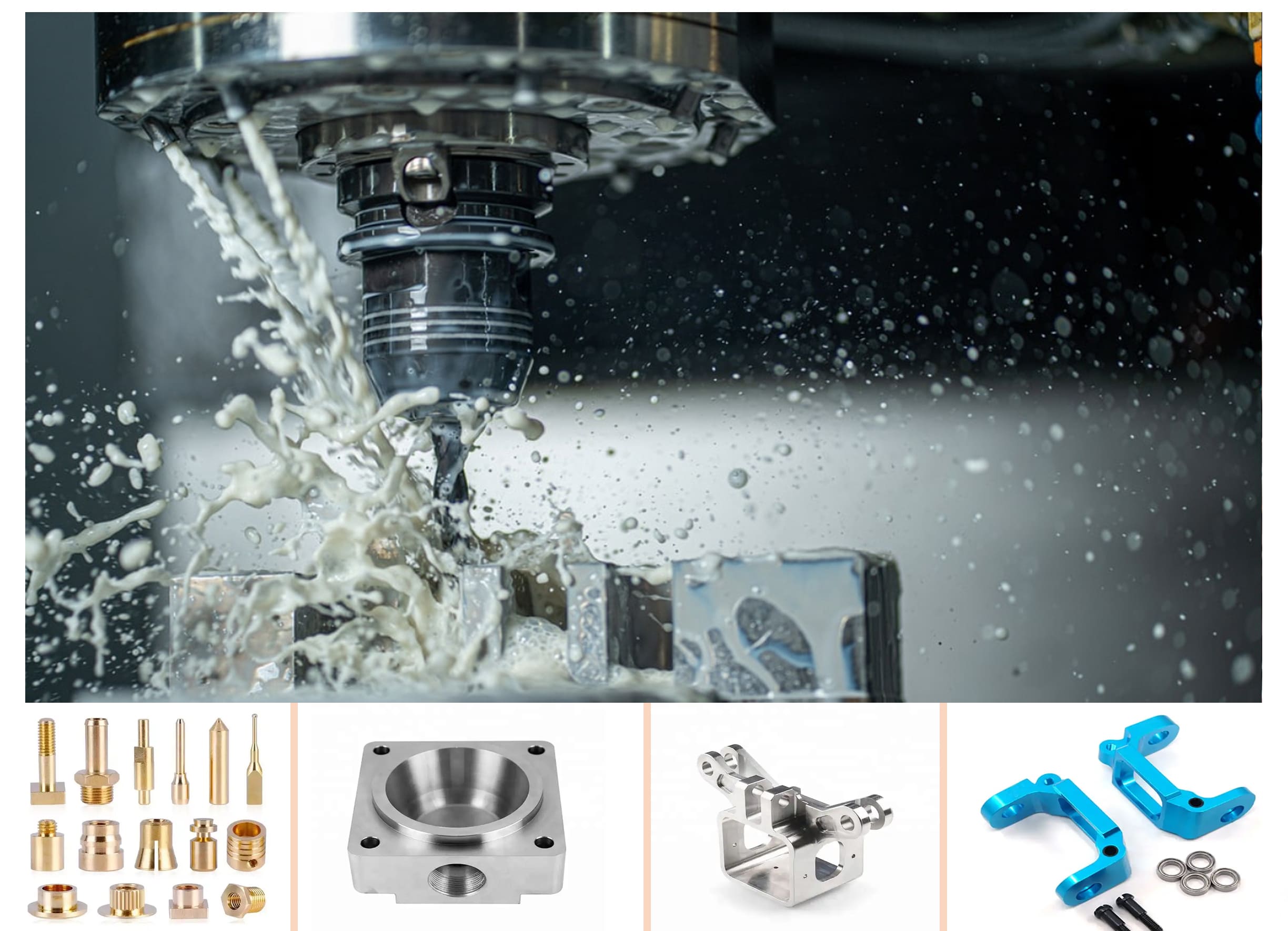
A. CNC Fabrication Services
1. Overview of CNC Fabrication
CNC fabrication services represent a pinnacle of precision and versatility in manufacturing. This advanced form of CNC engineering extends beyond traditional machining, encompassing a wide range of processes such as cutting, bending, and assembling materials with the utmost accuracy.
CNC fabrication relies on computerized controls to guide intricate movements, resulting in the creation of complex and finely detailed components.
2. Applications in Modern Manufacturing
The applications of CNC fabrication services are expansive, touching various industries at the forefront of modern manufacturing.
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: CNC-controlled machines excel in shaping and cutting sheet metals with high precision, crucial in industries ranging from automotive to electronics.
- Welding and Assembly: CNC fabrication ensures precise welding and assembly processes, contributing to the construction of robust structures in sectors like construction and aerospace.
- Custom Prototyping: The ability to fabricate intricate prototypes swiftly and accurately enhances the product development cycle, enabling innovation and iteration.
B. CNC Design and Engineering
1. Integrating Design with CNC Processes
The synergy between design and CNC processes is a hallmark of advanced engineering solutions. CNC technology seamlessly integrates with Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems, allowing for the direct translation of digital designs into tangible products.
This integration streamlines the manufacturing workflow, eliminating potential discrepancies and ensuring that the final product faithfully represents the initial design.
2. Importance of Engineering in CNC Projects
The nucleus of prosperous CNC projects resides in engineering proficiency. The precision and intricacy facilitated by CNC technology demand an in-depth comprehension of materials, structural integrity, and manufacturing processes.
The pivotal role of CNC design and engineering teams comes to the forefront as they optimize designs for efficient production, meticulously select appropriate materials, and guarantee that the final product adheres to the utmost standards of quality and functionality.
Advanced CNC engineering solutions, such as CNC fabrication services and the seamless integration of design with manufacturing processes, represent the forefront of technological innovation.
These sophisticated applications not only enhance precision and efficiency but also underscore the crucial role of engineering expertise in realizing the full potential of CNC technology.

Future Trends and Innovations in CNC Engineering
A. Automation in CNC
1. Trends in CNC Automation
The integration of automation into CNC processes is an unfolding trend that promises to revolutionize manufacturing and engineering.
- Dynamic Control Mechanisms: CNC machines featuring dynamic control systems possess the capability to adjust parameters in real time, leveraging live data to optimize performance and minimize errors.
- Machine Learning Integration: The incorporation of machine learning algorithms allows CNC systems to learn and adapt to evolving production scenarios, further enhancing efficiency and precision.
- Collaborative Robotics: The rise of collaborative robots, or cobots, working in tandem with CNC machines is streamlining tasks that require a human touch, marking a leap forward in automation versatility.
2. Impact on Engineering Processes
The increasing automation in CNC engineering has profound implications for the industry’s operational landscape.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation minimizes manual intervention, enabling continuous production cycles and significantly reducing downtime.
- Precision Optimization: Adaptive control and machine learning contribute to heightened precision, ensuring that CNC processes adapt to variables in real time, resulting in superior accuracy.
- Enhancing Expertise: As automation handles routine tasks, it empowers skilled engineers to concentrate on intricate problem-solving, creative endeavors, and strategic decision-making.
B. Turnkey CNC Solutions
1. Comprehensive CNC Engineering Solutions
Turnkey CNC solutions are emerging as a holistic approach to CNC engineering, offering end-to-end services that go beyond traditional machining.
- Design to Production Integration: Turnkey solutions seamlessly integrate the entire manufacturing process, from initial design concepts to the final production stages.
- Supply Chain Integration: Comprehensive solutions encompass supply chain management, ensuring a smooth flow of materials and components throughout the manufacturing journey.
- Ensuring Quality Standards: Turnkey CNC solutions frequently incorporate rigorous quality control measures, guaranteeing that the final products adhere to the most stringent industry standards.
2. Meeting Diverse Industry Needs
As industries continue to diversify, the demand for turnkey CNC solutions is rising, driven by their ability to cater to a wide array of industry needs.
- Tailoring to Industry Needs: Turnkey solutions exhibit adaptability to meet the distinct requirements of various sectors, spanning automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and consumer electronics.
- Flexibility and Scalability: These solutions offer flexibility in adapting to varying production volumes and scalable services that align with the evolving needs of businesses.
The future of CNC engineering holds promising developments with the increasing role of automation and the emergence of turnkey solutions.
These trends not only enhance efficiency and precision but also signify a shift toward more integrated and comprehensive approaches to meet the evolving demands of diverse industries.
Conclusion:
The types of CNC engineering services further highlight its versatility. CNC machining, programming, and precision engineering services offer tailored solutions for diverse industry needs.
Custom part manufacturing, a core component of CNC engineering, allows for the creation of components tailored to specific requirements, optimizing performance and efficiency.
CNC prototyping, facilitated by CNC technology, accelerates the product development lifecycle, reducing time-to-market and fostering innovation.
 Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569
Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569




