I. Introduction
In the modern world, using cutting-edge materials and precision production techniques has become essential to innovation and advancement.
Among these materials, aluminium stands out for its exceptional combination of strength, lightness, and versatility.
From the aerospace and automotive industries to consumer electronics and robotics, aluminium CNC (Computer Numerical Control) parts play a pivotal role in shaping the products we interact with on a daily basis.
When considering the sourcing of aluminium CNC parts, one destination that consistently emerges as a leader in this field in China.
With its robust manufacturing infrastructure, technological prowess, and cost-effective production capabilities, China has solidified its position as a global hub for aluminium CNC part fabrication.

This introduction aims to explore the importance of sourcing aluminium CNC parts from China, delving into the key factors that make China an attractive and strategic choice for businesses and industries across the world.
From intricate components requiring high precision to larger structural elements demanding durability, aluminium CNC parts manufactured in China offer a spectrum of advantages.
This includes not only the assurance of top-notch quality but also the potential for cost savings, streamlined production processes, and access to a vast pool of skilled labor and cutting-edge machinery.
Furthermore, China’s dedication to research and development ensures that manufacturers remain at the forefront of technological advancements, consistently refining their techniques to meet evolving industry standards.
II. Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
In the quest to secure reliable and high-quality aluminium CNC parts suppliers, conducting comprehensive research and evaluation is paramount.
This section outlines two fundamental approaches to identifying potential suppliers: online research and referrals from industry professionals.
Additionally, we delve into the essential process of evaluating supplier credibility and reputation.

A. Conducting Online Research:
- Utilizing Search Engines and Directories: Use Google and other search engines to your advantage to start your supplier hunt. Use specific keywords such as “aluminium CNC parts suppliers” or “aluminium machining manufacturers.” Online industrial directories, such as Thomasnet, Global Sources, and Alibaba, provide comprehensive databases of suppliers, enabling you to filter and narrow down your options.
- Navigating Supplier Websites: Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, explore their official websites. Look for detailed information about their manufacturing capabilities, range of products, quality certifications, and past projects. A well-designed and informative website can reflect the professionalism of the supplier.
- Contacting Suppliers: Reach out to the shortlisted suppliers through their provided contact information. Initiate communication to inquire about their services, production capacity, lead times, and any other pertinent details.
B. Referrals from Industry Professionals:
- Networking and Industry Events: Attend industry conferences, trade shows, and events related to aluminium manufacturing or CNC machining. These events give attendees the chance to network with industry experts who may be able to identify trustworthy vendors based on their personal experiences.
- Colleague and Expert Recommendations: Engage with colleagues, industry experts, and mentors who have familiarity with aluminium CNC parts sourcing.
C. Evaluating Supplier Credibility and Reputation:
- Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Look up internet testimonials and reviews from customers. A supplier’s service quality, communication style, and product dependability can be learned a great deal by reading about previous customers’ experiences with that source.
- Certifications and Quality Standards: Scrutinize the supplier’s certifications, such as ISO 9001, which signify adherence to rigorous quality management systems. These certifications demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to producing consistent and high-quality products.
- Past Projects and Case Studies: Look for case studies or examples of past projects that the supplier has successfully executed. This offers a glimpse into their capabilities and expertise in producing aluminium CNC parts.
- Transparent Communication: Evaluate the supplier’s ability to respond to your inquiries and their clarity and readiness to do so. A supplier that communicates effectively and transparently is more likely to be reliable and accommodating.
- Online Presence and Social Media: Explore the supplier’s online presence, including their social media profiles. Active and informative online engagement can reflect a commitment to professionalism and customer engagement.
III. Assessing Supplier Capability
After identifying potential suppliers for aluminium CNC parts, the next crucial step is to assess their capability to meet your specific manufacturing requirements.
This assessment involves scrutinizing their experience, equipment, facilities, quality control measures, and certifications.
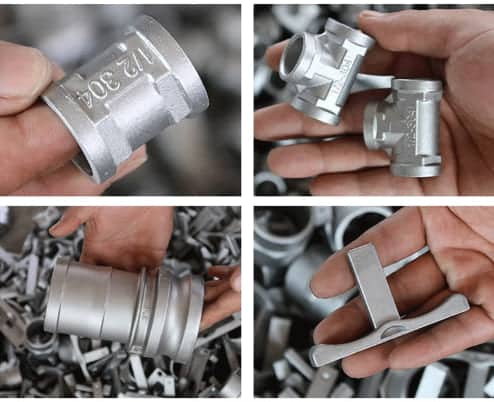

A. Verifying Experience in Manufacturing Aluminium CNC Parts:
- Industry Expertise: Inquire about the supplier’s experience in manufacturing aluminium CNC parts. Ask for details about their involvement in projects similar to yours. Experience in your specific industry or application demonstrates their understanding of your needs.
- References and Case Studies: Request references from previous clients who have ordered similar aluminium CNC parts. Review case studies or success stories to gauge the supplier’s track record.
B. Evaluating Equipment and Facilities:
- State-of-the-Art Equipment: Assess the supplier’s equipment and machinery. State-of-the-art CNC machines and related tools are indicative of their commitment to precision manufacturing.
- Technological Advancements: Inquire about the technology they employ for CNC machining. Superior results are more likely to be delivered by suppliers who keep up with the most recent developments.
- Production Capacity: Check to see if the provider can handle the volume of your output. This includes considering their available workforce and shifts if your order requires a significant quantity.
C. Assessing Quality Control Measures and Certifications:
- Quality Management Systems (QMS): Investigate the supplier’s quality control measures and systems. A Quality Management System, such as ISO 9001 certification shows that the supplier is dedicated to providing consistent quality.
- Quality Control Processes: Learn about their quality control processes throughout the production lifecycle. This includes inspection, testing, and validation procedures to ensure the parts meet your specifications.
- Certifications and Compliance: Check for industry-specific certifications that pertain to aluminium CNC parts.
- Traceability: Inquire about their ability to provide traceability for the materials used in your parts. Traceability shows that supplier’s transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain process.
D. Additional Considerations:
- Customization and Flexibility: Evaluate the supplier’s willingness and ability to accommodate customization and design changes. A flexible supplier can better align with your evolving project needs.
- Prototyping and Samples: Request prototypes or samples to assess their manufacturing quality and precision.
- Location and Logistics: Consider the supplier’s geographic location in relation to your business.
IV. Communication and Negotiation
Establishing effective communication channels and engaging in successful negotiation play pivotal roles in ensuring a smooth partnership with aluminium CNC parts suppliers.
This section outlines key strategies for effective communication and negotiation throughout the supplier engagement process.

A. Establishing Effective Communication Channels:
- Clear Points of Contact: Identify key contacts on both sides for efficient communication. Having designated representatives for queries, updates, and concerns avoids confusion.
- Preferred Communication Methods: Determine the preferred communication methods—email, phone calls, video conferences, or project management platforms. This aligns with the preferences of both parties.
- Regular Updates: Plan regular updates on the status of the project, its milestones, and any potential problems. Transparent and consistent updates foster trust and keep both parties informed.
- Open Dialogue: Encourage an environment of open dialogue. Address questions, concerns, and potential challenges promptly to prevent misunderstandings and delays.
B. Discussing Requirements, Specifications, and Customization:
- Detailed Requirements: Provide suppliers with comprehensive details about your aluminium CNC part requirements. This includes dimensions, tolerances, materials, finishes, and any other specific features.
- Specifications Clarification: Discuss specifications to ensure mutual understanding. Visual aids like diagrams or technical drawings can aid in conveying intricate details accurately.
- Customization Options: If your project requires customization or specific modifications, discuss these options with the supplier. Clearly articulate your customization needs and inquire about feasibility.
- Design Feedback: Engage in constructive design discussions. Suppliers’ insights into manufacturability and potential design improvements can enhance the final product.
C. Negotiating Pricing, Terms, and Conditions:
- Initial Quotes: Request detailed quotes that itemize costs, including material, machining, finishing, tooling, and shipping. Analyze these quotes to understand the cost breakdown.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare quotes from multiple suppliers based on factors like quality, lead times, and additional services. Consider the overall value rather than solely focusing on the lowest price.
- Volume Consideration: Discuss pricing adjustments based on order volume. Suppliers might offer discounts for larger quantities, which can influence your decision.
- Payment Terms: Negotiate payment terms that align with your financial capabilities. Common terms include advance payments, milestone payments, and final payments upon delivery.
- Delivery Timeline: Define a clear timeline for production, quality control, and delivery. Negotiate realistic lead times to accommodate your project schedule.
- Terms and Conditions: Carefully review and negotiate terms and conditions related to warranties, returns, intellectual property, and any potential issues that might arise.
D. Building Win-Win Relationships:
- Collaborative Approach: Approach negotiation as a collaborative effort to achieve mutual benefit. Seek solutions that meet both parties’ objectives.
- Flexibility: Maintain flexibility during negotiations. It can be necessary to make concessions in order to get to a deal that meets your needs and the supplier’s capabilities.
- Long-Term Perspective: Consider the potential for a long-term partnership. Building a strong supplier relationship can lead to favorable terms, consistent quality, and smoother collaboration.
V. Samples and Prototypes
The stage of obtaining samples and prototypes from potential aluminium CNC parts suppliers is a pivotal point in the supplier evaluation process.
This step allows you to physically assess the quality, precision, and compatibility of the parts with your project’s requirements.
Here, we delve into the importance of requesting samples or prototypes and the subsequent process of providing feedback and requesting necessary revisions.

A. Requesting Samples or Prototypes:
- Quality Assessment: Requesting samples or prototypes enables you to assess the actual quality of the aluminium CNC parts.
- Precision Evaluation: By closely inspecting the samples, you can gauge the precision and accuracy of the machining.
- Material and Finish: Examine the materials used and the finish applied to the samples. This assessment ensures that the chosen materials are suitable for your project and that the finish aligns with your aesthetics and functional requirements.
- Functionality Testing: If feasible, conduct functionality testing with the prototypes. Check how the parts perform in real-world conditions and whether they fulfill their intended purpose.
B. Providing Feedback and Requesting Revisions:
- Clear Feedback: Provide detailed feedback on the samples or prototypes. Clearly articulate any concerns, deviations from specifications, or areas that need improvement. Use annotated diagrams or notes to highlight specific points.
- Quantitative and Qualitative Feedback: Provide both quantitative and qualitative feedback. While precise measurements are important, also express subjective observations about the overall look, feel, and functionality of the parts.
- Revision Requests: If you identify areas that require improvement, communicate your revision requests to the supplier.
- Open Dialogue: Engage in open communication with the supplier regarding your feedback and revision requests. Establish a collaborative approach to finding solutions that enhance the quality of the parts.
- Iterative Process: Recognize that the prototyping process is frequently iterative. It may take several rounds of revisions to achieve the desired quality and compatibility with your project.
C. Balancing Feedback and Supplier Expertise:
- Leveraging Supplier Expertise: While your feedback is crucial, also consider the supplier’s expertise. They might offer insights and suggestions for improvements based on their manufacturing experience.
- Collaborative Approach: Approaching the process of editing and feedback collectively. Work together with the supplier to find solutions that meet both parties’ objectives.
- Alignment with Requirements: Throughout the feedback and revision process, ensure that the samples or prototypes align with your project’s requirements, functionality, and design intent.
VI. Manufacturing and Production
As you move forward with your chosen aluminium CNC parts supplier, the manufacturing and production phase becomes the focal point of your collaboration.
This phase involves finalizing order details, monitoring production progress, and ensuring that the resulting parts adhere to your quality standards.
The main considerations and actions throughout the manufacturing and production phase are examined in this section.
A. Finalizing Order Details and Specification:
- Detailed Order Confirmation: Provide the supplier with a comprehensive order confirmation that includes all finalized details—dimensions, quantities, materials, finishes, and any customization instructions.
- Technical Drawings: Furnish the supplier with accurate technical drawings or 3D models that outline your design specifications. Clear and detailed documentation helps minimize errors during production.
- Quality Requirements: Reiterate your quality requirements and expectations, emphasizing the importance of adhering to industry standards and the agreed-upon specifications.
B. Monitoring Production Progress and Timeline:
- Regular Updates: Maintain a communication channel with the supplier to receive regular updates on the progress of production. Inquire about milestones reached and any potential delays.
- Real-time Tracking: If applicable, consider using project management tools or software that allow you to track production progress in real-time. This transparency enhances accountability.
- Proactive Communication: If you anticipate changes in project timelines or if unforeseen challenges arise, communicate promptly with the supplier to discuss potential solutions.
C. Ensuring Adherence to Quality Standards:
- Quality Control Measures: Verify that the supplier is implementing the agreed-upon quality control measures. This includes inspection, testing, and validation procedures.
- On-site Inspections: If feasible, conduct on-site inspections or audits to verify that the production process aligns with your quality standards and specifications.
- Quality Assurance Protocols: Confirm that the supplier is following quality assurance protocols, such as ISO certifications or industry-specific standards applicable to aluminium CNC parts.
D. Addressing Issues and Modifications:
- Immediate Communication: If you identify any issues or deviations from the agreed-upon specifications, communicate with the supplier promptly. Addressing issues early can prevent further complications.
- Collaborative Solutions: Engage with the supplier to find collaborative solutions to any production challenges. A problem-solving approach fosters a productive partnership.
- Revisions and Modifications: If modifications are necessary during the production process, ensure that they align with your project’s goals and that the supplier implements them accurately.
E. Quality Assurance and Final Inspection:
- Final Inspection: Prior to shipping, request a final inspection of the parts to verify their quality, precision, and adherence to specifications. This step ensures that the delivered parts meet your expectations.
- Quality Checklist: Provide the supplier with a quality checklist that outlines the specific criteria the parts must meet. This checklist aids in the final inspection process.
- Alignment with Requirements: Before accepting the parts, ensure that they align with the initially communicated requirements, specifications, and quality standards.
VIII. Packaging and Shipping
The packaging and shipping phase is the final leg of your collaboration with aluminium CNC parts suppliers.
This phase encompasses discussions about packaging requirements, confirming shipping methods, and ensuring the timely and safe delivery of your ordered parts.
Here, we delve into the essential steps and considerations for a successful packaging and shipping process.
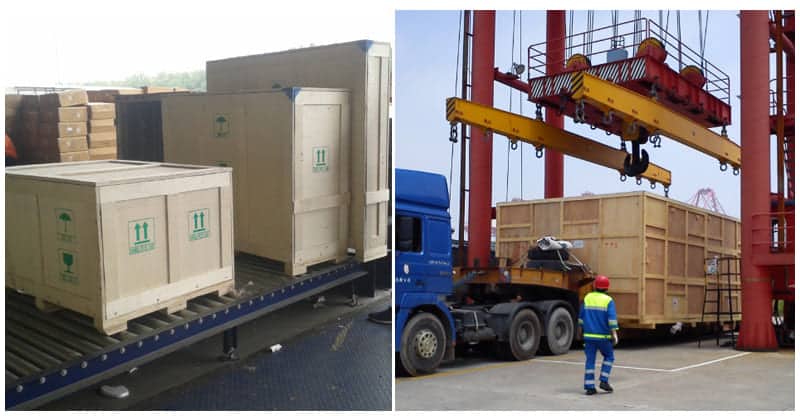

A. Discussing Packaging Requirements and Preferences:
- Protection and Safety: Clearly communicate your expectations regarding the packaging of the parts. Emphasize the need for secure and protective packaging to prevent damage during transit.
- Specific Requirements: Discuss any specific packaging requirements based on the nature of the parts. Delicate or sensitive parts might require additional cushioning or protective measures.
- Labelling and Identification: Address the need for accurate labelling and proper identification of the packages. This facilitates easy handling and tracking throughout the shipping process.
B. Confirming Shipping Methods and Logistics Arrangements:
- Shipping Options: Discuss available shipping methods with the supplier. Choose a delivery option that fits with the schedule of your project by taking into account elements like speed, cost, and dependability.
- International Shipping Considerations: If applicable, confirm that the supplier is experienced in international shipping and that they are aware of customs requirements and regulations.
- Documentation: Ensure that all necessary shipping documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and customs declarations, are accurately completed and attached to the shipments.
C. Tracking Shipment and Ensuring Timely Delivery:
- Tracking Information: Obtain tracking information as soon as the parts are shipped. This enables you to keep track of the shipment’s progress and plan for its arrival.
- Timely Communication: If there are any unexpected delays or issues with the shipment, promptly communicate with the supplier and shipping provider to address the situation.
- Contingency Planning: While rare, consider having a contingency plan in case of significant shipping delays. Discuss potential solutions with the supplier in advance.
D. Receiving and Inspecting the Shipment:
- Timely Arrival: Ensure that the shipment arrives within the expected timeframe. This is crucial if you have project timelines or production schedules dependent on the delivered parts.
- Visual Inspection: As soon as the packages are delivered, perform a visual assessment of the packages. Look for any signs of damage to the packaging that might indicate potential damage to the parts.
- Part Count and Quality: Verify that the number of parts received matches the order quantity.
E. Feedback and Continuous Improvement:
- Feedback Loop: If you encounter any issues related to packaging, shipping, or the quality of received parts, provide feedback to the supplier. This information aids in continuous improvement.
- Suggested Improvements: If you have suggestions for improving the packaging or shipping process based on your experience, share these insights with the supplier.
IX. Payment and Legal Considerations
Navigating the payment and legal aspects of your collaboration with aluminium CNC parts suppliers is crucial to ensure a smooth and legally compliant partnership.
This phase involves discussions about payment terms, compliance with regulations, and a thorough review of contracts and agreements.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to managing payment and legal considerations effectively.

A. Discussing Payment Terms and Options:
- Payment Schedule: Clearly outline the agreed-upon payment schedule with the supplier. This includes advance payments, milestone payments, and final payments upon successful delivery.
- Payment Methods: Discuss preferred payment methods, such as bank transfers, PayPal, or other secure and internationally recognized methods. Ensure that the chosen method is convenient for both parties.
- Currency: Determine the currency in which payments will be made. This can have implications for currency exchange rates and international transactions.
- Late Payment Terms: Specify the conditions and fines for late payments, if any. This encourages timely payment and maintains a professional relationship.
B. Ensuring Compliance with Legal Requirements and Regulation:
- Import and Export Regulations: Ensure that you and the supplier are compliant with any import and export regulations relevant to your industry and region. This includes customs duties, tariffs, and restrictions.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Discuss intellectual property rights and protection measures, especially if your project involves proprietary designs or technologies.
- Data Privacy and Security: If sharing sensitive information with the supplier, ensure that data privacy and security measures are in place to protect your confidential information.
C. Reviewing Contracts and Agreements Carefully:
- Comprehensive Contracts: Draft or review contracts and agreements that encompass all aspects of your collaboration.
- Legal Assistance: To make sure the agreement is valid and safeguards your interests, think about getting legal counsel. You can avoid dangers and complicated provisions with the assistance of a legal expert.
- Dispute Resolution: Clearly outline dispute resolution procedures in the contract. This could involve negotiation, mediation, or arbitration to address conflicts without resorting to legal action.
D. Building Mutual Trust and Transparency:
- Honest Communication: Foster open and honest communication with the supplier throughout the payment and legal process. Address any concerns or questions promptly to prevent misunderstandings.
- Transparency: Be truthful about your goals, restrictions, and any difficulties you anticipate. This promotes a collaborative and problem-solving approach.
- Long-Term Relationship: Consider the potential for a long-term partnership. Building trust and transparency lay the foundation for a strong and enduring supplier relationship.
E. Records and Documentation:
- Document Everything: Maintain thorough records of all payment transactions, communication, contracts, and agreements. These records are valuable in case any disputes arise.
- Backup Documentation: Keep copies of invoices, receipts, and any documentation related to payment and legal agreements. These serve as evidence in case of disputes or audits.
X. After-Sales Support and Feedback
The process of working with aluminium CNC parts suppliers doesn’t end with the completion of a single order.
Establishing a system for after-sales support, providing feedback, and nurturing a long-term relationship are crucial for ongoing success.
This final phase focuses on maintaining a positive partnership and ensuring continuous improvement.

A. Establishing a System for Post-Sales Support and Communication:
- Contact Points: Maintain open lines of communication with the supplier even after the completion of the order. Designate specific contact points for any post-sales inquiries or issues.
- Addressing Concerns: If any concerns arise after receiving the parts, reach out to the supplier promptly. An efficient post-sales support team resolves problems quickly and cooperatively.
- Technical Support: Establish whether the supplier offers technical support for questions related to the parts, their installation, or maintenance.
B. Providing Feedback and Reviews to Suppliers:
- Constructive Feedback: Share feedback with the supplier regarding your experience working together.
- Reviews and Testimonials: If the supplier’s services exceeded your expectations, consider providing them with positive reviews or testimonials. This contributes to their reputation and fosters goodwill.
- Feedback Loop: Encourage the supplier to seek your feedback on their performance as well. A feedback loop allows both parties to learn from each other’s experiences.
C. Maintaining a Long-Term Relationship:
- Regular Updates: Keep the supplier informed about your upcoming projects and potential orders. This ongoing dialogue helps them anticipate your needs and allocate resources accordingly.
- Preferred Supplier: If your experience with the supplier has been consistently positive, consider designating them as a preferred supplier for future projects.
- Negotiation for Future Orders: As you continue your collaboration, you can negotiate more favorable terms based on your established relationship and past successful orders.
XI. Conclusion
In the pursuit of sourcing aluminium CNC parts effectively, a strategic approach encompassing multiple phases is crucial.
From thorough supplier research and assessment to clear communication, negotiation, and diligent quality control, every step plays a pivotal role.
Establishing a strong partnership doesn’t end with the delivery of parts; ongoing feedback, support, and collaboration contribute to a sustainable relationship.
By adhering to these strategies, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminium CNC parts and drive successful projects forward.
 Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569
Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569



