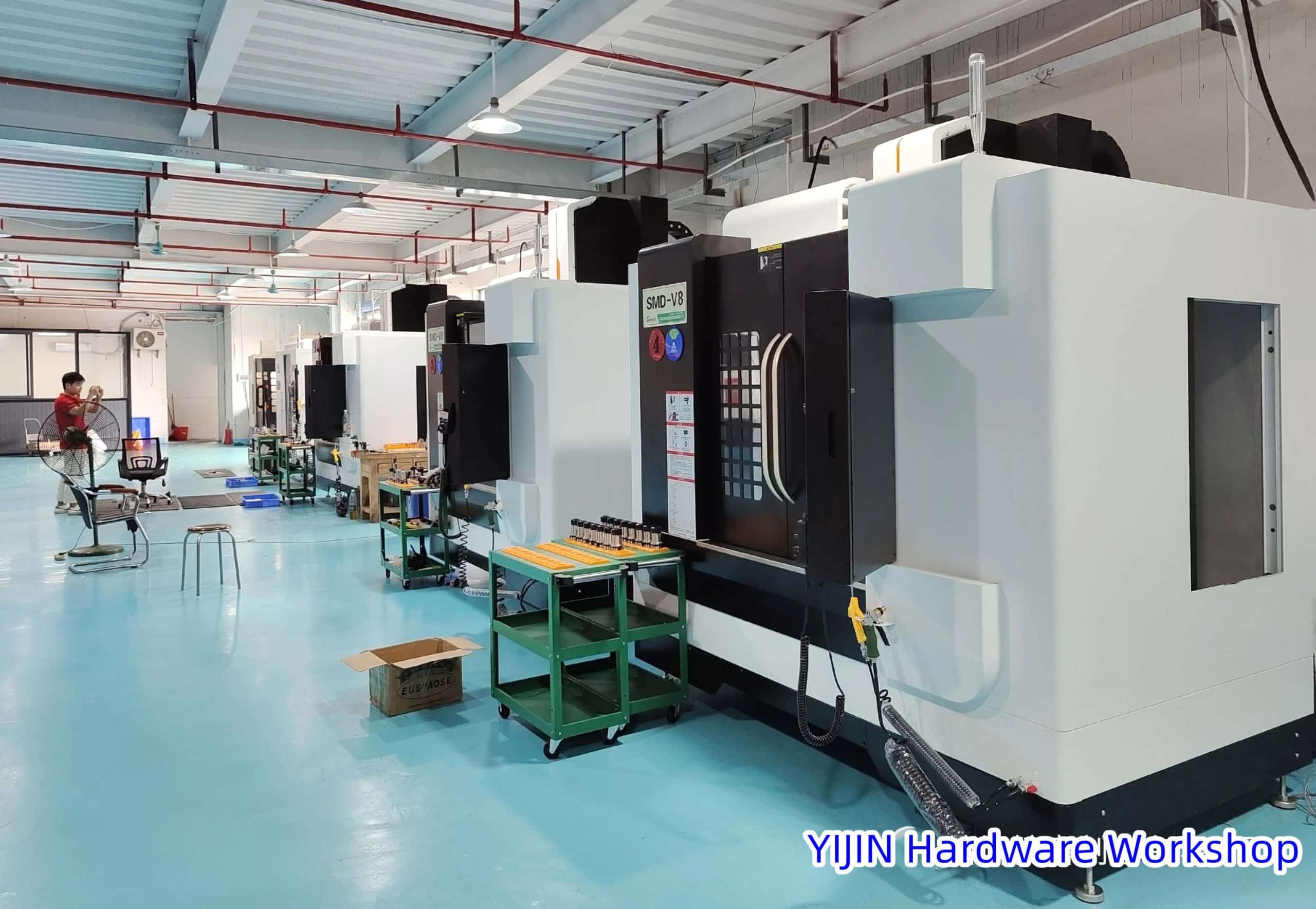
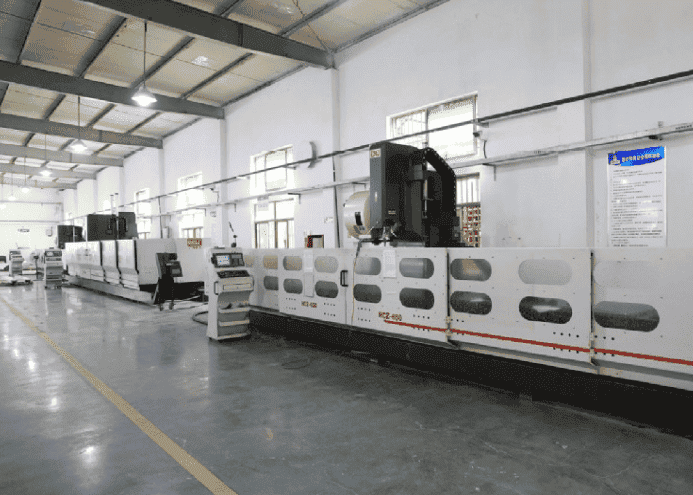
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining involves the use of computerized systems to control machine tools, providing automated precision in the manufacturing process.
CNC machines, ranging from mills to lathes, execute programmed instructions to shape raw materials with accuracy.
In contrast, manual machining relies on the hands-on expertise of machinists who directly control machine tools.
This traditional approach requires skill and craftsmanship as machinists interpret blueprints, set up machines, and guide cutting tools to shape workpieces.
CNC machining and manual machining—each possessing its unique characteristics.
As we embark on this journey, we recognize the paramount importance of considering cost factors in the realm of machining, where decisions have far-reaching implications for businesses and manufacturers.
Overall Cost Analysis
A. Comparison of Overall Costs
CNC Machining:
The initial investment in CNC machining includes the cost of sophisticated machines and the need for skilled programmers. However, automated precision and efficiency often result in reduced labor costs over time.
Manual Machining:
Manual machining, while requiring less initial investment, incurs ongoing labor costs due to the hands-on involvement of skilled machinists. The artisanal approach may result in longer production times, impacting overall expenses.
B. Factors to Consider
Equipment Costs:
- CNC: High upfront costs for machines and programming.
- Manual: Lower initial investment in equipment.
Operating Costs:
- CNC: Reduced labor costs due to automation.
- Manual: Higher labor costs but potentially lower operational expenses.
Maintenance Expenses:
- CNC: Regular maintenance is essential for the complex machinery.
- Manual: Maintenance is typically simpler but may require more frequent adjustments.
C. Evaluation of Cost-Effectiveness
Determining cost-effectiveness hinges on the specific needs or projects at hand:
- High-Volume Production:
CNC machining often proves more cost-effective for large-scale production due to its automation, precision, and reduced per-unit labor costs.
- Prototyping and Small Runs:
Manual machining can be cost-effective for prototyping and small production runs, especially when rapid adjustments and artisanal craftsmanship are critical.
Material and Complexity Considerations:
The choice between CNC and manual machining depends on the material types and the complexity of the project. CNC excels with intricate designs and diverse materials, while manual machining showcases adaptability.

Equipment Investment Comparison
A. Comparison of Upfront Costs
1. CNC Machines:
- CNC machining commands a higher upfront investment due to the complexity and precision of automated systems. The initial costs encompass the machine itself, sophisticated control systems, and programming infrastructure.
2. Manual Machine Tools:
- In contrast, manual machine tools generally incur lower upfront costs. The simplicity of these machines, coupled with the reliance on skilled machinists for manual control, contributes to a more accessible entry point for businesses.
B. Examination of Purchasing or Acquiring Costs
1. CNC Machines:
- Acquiring CNC machines extends beyond the initial purchase to encompass software costs for programming and the employment of skilled personnel. Training expenses may also factor into the overall acquisition costs.
2. Manual Machine Tools:
- Purchasing costs for manual machine tools are typically more straightforward. Initial investments primarily focus on acquiring the necessary machines, with considerations for tooling and accessories.
C. Discussion of Price Range and Considerations for Different Machines
1. CNC Machines:
- The price range for CNC machines can vary widely based on factors such as size, capabilities, and the level of automation. High-precision CNC mills, multi-axis lathes, or advanced routers may fall on the higher end of the spectrum.
2. Manual Machine Tools:
- The price range for manual machine tools is generally more accessible, with variations based on the type of machines needed. Basic milling machines, lathes, and grinders may have lower acquisition costs compared to their CNC counterparts.
Considerations for Different Machines:
- Businesses need to carefully consider the specific needs of their projects. For high-precision, large-scale production, CNC machines offer unparalleled advantages. However, for smaller-scale operations, prototyping, or applications requiring adaptability and craftsmanship, manual machine tools may prove more cost-effective.

Cost per Part Analysis
A.Comparison of Cost Breakdown
1. Labor Costs:
- CNC: Automation reduces direct labor costs, but skilled personnel are needed for programming and overseeing operations.
- Manual: Higher labor costs due to hands-on involvement and the expertise of machinists.
2. Material Costs:
- Costs associated with raw materials are generally similar for both CNC and manual machining processes.
3. Tooling Expenses:
- CNC: Tooling expenses may include specialized tools and equipment, impacting the overall cost per part.
- Manual: Tooling expenses are typically lower, but may vary based on the complexity of the project.
4. Productivity Rates:
- CNC machines generally boast higher productivity rates, leading to reduced cycle times and increased efficiency.
- Manual machining may have longer cycle times, impacting overall productivity rates.
B. Evaluation of Cost-Effectiveness
The evaluation of cost-effectiveness hinges on specific production requirements:
- For high-volume, standardized production with tight tolerances, CNC machining may offer a more cost-effective solution.
- For smaller production runs, prototyping, or projects requiring adaptability and craftsmanship, manual machining may be the more cost-efficient option.
Efficiency and Labor Cost Comparison
A. Comparison of Efficiency and Productivity
1. CNC Machining:
- CNC machining excels in efficiency, boasting automated precision that leads to reduced cycle times and enhanced productivity. Machines can operate continuously, minimizing downtime between tasks.
2. Manual Machining:
- Manual machining, while embodying skilled craftsmanship, may exhibit longer cycle times due to hands-on operations. Setup times and adjustments are typically more time-consuming compared to CNC.
B. Analysis of Cycle Times, Setup Times, and Labor Costs
1. Cycle Times:
- CNC: Shorter cycle times due to automated and programmed operations.
- Manual: Longer cycle times as machinists manually control the tools and adjust settings.
2. Setup Times:
- CNC: Setup times are generally quicker, as automated systems streamline the preparation process.
- Manual: Setup times can be more extensive, requiring manual adjustments and tool changes.
3. Labor Costs:
- CNC: Automation leads to reduced labor costs per part, although skilled operators are still essential for programming and oversight.
- Manual: Higher labor costs due to the skilled involvement of machinists throughout the process.
C. Evaluation of Cost Advantages of Automation and Faster Machining Speeds in CNC Machining
The evaluation of cost advantages leans toward CNC machining:
Automation Benefits: CNC machining’s automated precision minimizes errors and enhances repeatability, contributing to cost savings in the long run.
Faster Machining Speeds: The quicker cycle times and continuous operation in CNC machining result in increased overall productivity, translating to potential cost advantages for high-volume production.

Cost of Adaptability
A. Assessment of Costs Involved in Adapting CNC Machines or Manual Machine Tools
1. CNC Machines:
- Adapting CNC machines for different tasks may incur costs related to reprogramming, tool changes, and potential hardware modifications. The initial investment in versatile CNC equipment may mitigate some adaptation costs.
2. Manual Machine Tools:
- The adaptability of manual machines relies heavily on the skills of machinists. While these machines offer inherent versatility, the costs associated with skilled labor and potential adjustments should be considered.
B. Consideration of Setup Costs, Reprogramming Expenses, and Tooling Changes
1. CNC Machines:
- Setup Costs: CNC machines often require less setup time, contributing to cost savings.
- Reprogramming Expenses: Adapting CNC machines involves reprogramming costs, especially for complex tasks.
- Tooling Changes: Changing tools in CNC machining may incur costs associated with specialized tooling.
2. Manual Machine Tools:
- Setup Costs: Manual machine setups may be more time-consuming, impacting overall costs.
- Reprogramming Expenses: Manual machines rely on machinists’ expertise, potentially minimizing reprogramming costs.
- Tooling Changes: Changing tools in manual machining is a more straightforward process, often resulting in lower associated costs.
C. Examination of Cost Implications for Different Machining Operations
High-Precision Tasks: CNC machines may prove more cost-effective for tasks requiring high precision due to their automated and programmable nature.
Versatility and Customization: Manual machining can be more cost-effective for projects demanding adaptability, customization, and intricate craftsmanship.
Cost of Maintenance and Repairs
A. Evaluation of Maintenance and Repair Costs
1. CNC Machines:
- Maintenance costs for CNC machines involve regular checks of both mechanical and electronic components. Repairs may include addressing issues with control systems, motors, or other complex components, potentially requiring specialized technicians.
2. Manual Machine Tools:
- Maintenance costs for manual machines typically involve routine checks of mechanical components. Repairs may include adjustments to manual controls, replacement of worn-out parts, and general upkeep. Skilled machinists can often handle routine maintenance.
B. Discussion of Frequency of Maintenance, Costs of Spare Parts, and Need for Specialized Technical Expertise
1. CNC Machines:
- Frequency of Maintenance: CNC machines may require more frequent maintenance due to the intricate nature of electronic components.
- Costs of Spare Parts: Replacement parts for CNC machines can be more expensive, especially for specialized components.
- Specialized Technical Expertise: CNC machines often demand specialized technical expertise for both maintenance and repairs.
2. Manual Machine Tools:
- Frequency of Maintenance: Manual machines may require less frequent maintenance, with checks focusing on mechanical adjustments.
- Costs of Spare Parts: Replacement parts for manual machines are generally more accessible and cost-effective.
- Need for Specialized Technical Expertise: Skilled machinists can often handle routine maintenance and minor repairs without the need for highly specialized expertise.
C. Consideration of Long-Term Cost Implications for Each Type of Equipment
CNC machines may have higher upfront maintenance costs and a need for specialized technical expertise, potentially impacting long-term expenses.
Manual machine tools, while requiring skilled labor for maintenance, may offer cost advantages in terms of accessible spare parts and potentially lower long-term maintenance costs.

Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points Regarding Cost Comparisons
In the realm of machining, the decision between CNC and manual machining hinges on a careful analysis of costs and associated factors. Key points to consider include:
- Upfront Investment: CNC machining often requires a higher initial investment due to the complexity of automated systems, while manual machining offers a more accessible entry point.
- Labor Costs: CNC machining tends to reduce labor costs per part through automation, whereas manual machining relies on skilled machinists, potentially leading to higher labor expenses.
- Maintenance and Repairs: CNC machines may incur higher maintenance and repair costs, especially requiring specialized technical expertise. Manual machines, with simpler mechanics, may offer more cost-effective maintenance.
- Adaptability: Adapting CNC machines involves costs related to reprogramming and potential modifications, while the adaptability of manual machines relies on the skills of machinists.
- Efficiency: CNC machining excels in efficiency, boasting automated precision and reduced cycle times, while manual machining, with hands-on control, may exhibit longer cycle times.
B. Consideration of Other Factors Beyond Cost
Beyond cost considerations, several factors may influence the choice between CNC and manual machining:
- Precision and Automation: CNC machining is preferable for tasks demanding high precision and automation, especially in large-scale production.
- Craftsmanship and Adaptability: Manual machining shines in applications requiring craftsmanship, adaptability, and the ability to handle diverse materials and project requirements.
- Project Complexity: The complexity of the project at hand, including material types, intricacy of designs, and production volumes, plays a pivotal role in choosing the most suitable machining method.
- Technological Innovation: CNC machining aligns with the trajectory of technological advancement, offering cutting-edge solutions for modern manufacturing needs.
In conclusion, the decision between CNC and manual machining is multifaceted, extending beyond cost considerations. A nuanced understanding of project requirements, desired outcomes, and the intrinsic qualities of each machining method ensures a strategic choice that maximizes efficiency, craftsmanship, and long-term success in the dynamic landscape of manufacturing.
 Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569
Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569



