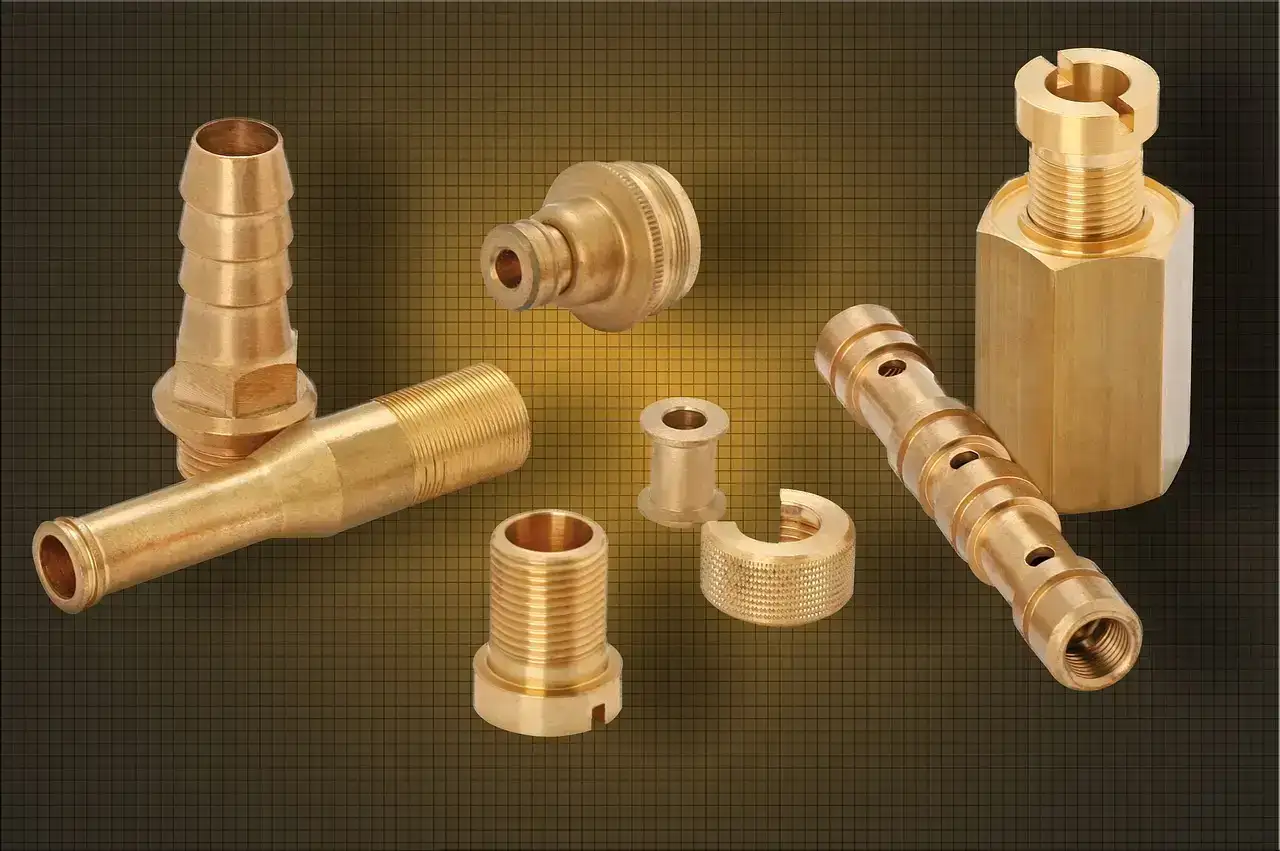
Brass CNC machining is significant for making custom brass parts. Due to its precise properties, manufacturers use brass in many industries like automotive, electronics, and medical instruments. Further, the brass composition is predominantly copper and zinc and incorporates metals like magnesium, iron, and lead. The presence of lead makes brass simple to use for CNC machining. So, these characteristics make brass metal awesome for precise and productive machining processes.
Moreover, this procedure utilizes a PC-controlled machine to make accurate designs and shapes in brass. So, in this web article, we will dig into the unique properties of brass, grades of brass, and their applications in different fields. We will ask various questions: What properties make brass excellent for CNC brass machining? What are the commonly used brass grades for brass CNC machining? It will give valuable information not only for businesses who are looking to use brass in their next project. Let’s start without further ado!
What is Brass CNC Machining?
CNC machining of brass includes a subtractive assembly approach using CNC machine tools, such as carbide inserts and mechanized controls. These devices work to wipe out layers of material from a metal workpiece. The rate at which material is eliminated relies upon the shaft speed. This method empowers the creation of metal parts with upgraded accuracy and tight tolerance.
Also Read:
What Properties Of Brass Make It Suitable For CNC Machining?
Brass has unique properties that make it ideal for various applications. So, in this section, we will explain the properties of brass.
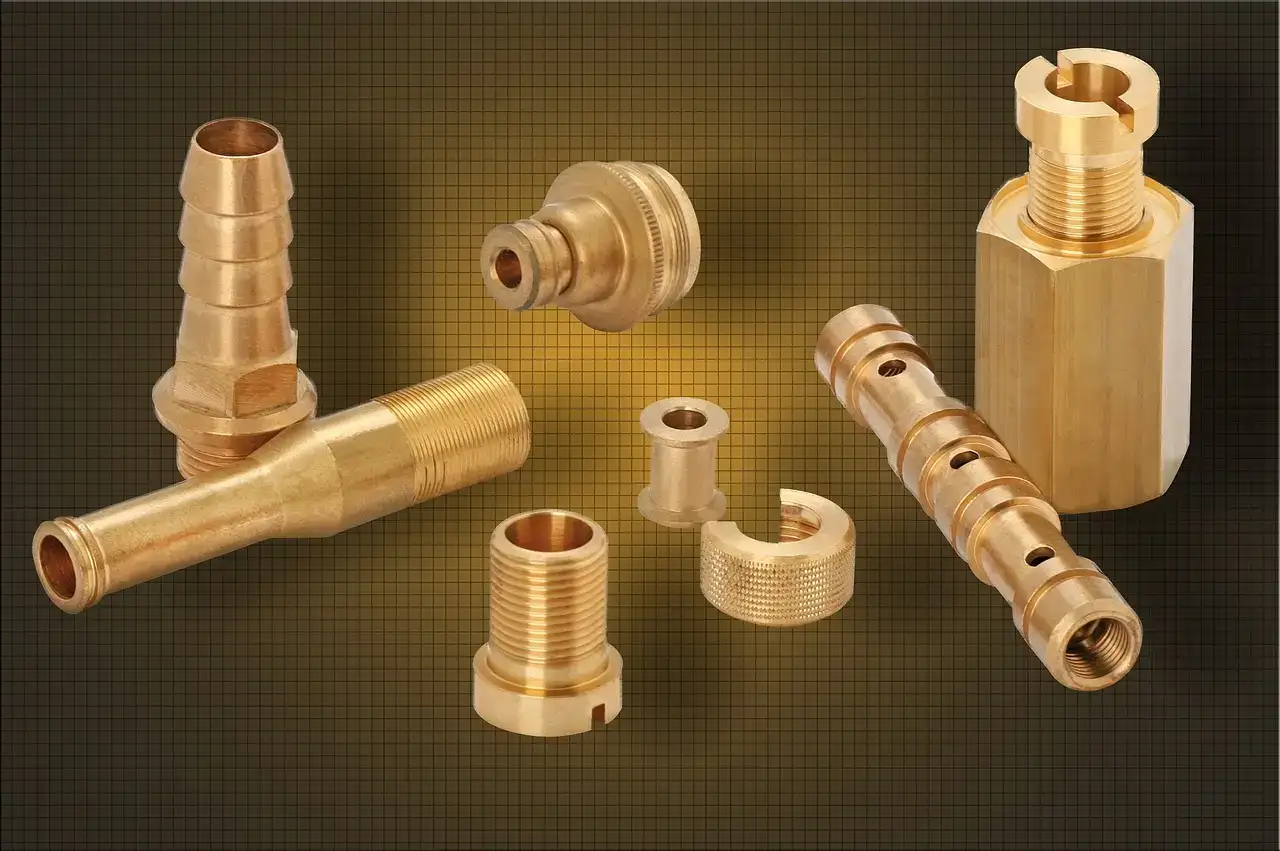

High Machinability
Brass is a popular metal for its easy-to-work characteristics with CNC machining. Adding lead to different brass alloys assists in reducing harm to cutting tools and offers smooth and quicker machining without damage to the hardware. So this makes brass an incredible choice for making complex parts with precise machining.
Resistance to Wear and Tear
As we know, brass has plenty of copper, so it doesn’t rust or erode easily. Moreover, it is great for tough environments when exposed to water, moisture or dampness, or harmful phosphorus synthetics. It makes brass an ideal metal for the ocean, plumbing, and construction fields.
Electrical and Heat Conductivity
Although it’s not as great as pure copper, brass is still great at directing heat and electricity. Accordingly, it makes it an astounding choice for creating electrical apparatuses, connectors, and different parts for electronic gadgets. Therefore, its capacity to conduct heat well makes it ideal for use in warmers and radiator parts.
Strength and Ductility
Due to its flexible and strong characteristics, brass is easy to shape and does not break. So, its strength makes it good to withstand hits and stretch, and its flexibility makes it a perfect choice for complex and complicated shapes. Thus, brass is precious for beautifying things like handles, fasteners, and latches.
Low Friction
Brass doesn’t create much resistance when it’s rubbed, so it’s good for things like locks, gears, hinges, and valves that need to move easily. Additionally, this function ensures the machine runs well and lasts a long time without any problems.
Aesthetic Appeal
Brass is a shiny metal that people use to make things look pretty. It can be polished to look shiny and clean or given an old-fashioned or brushed finish. These finishes look good in interior designs, jewelry, and musical instruments.
Antimicrobial Properties
Brass surfaces hinder the development and transmission of germs and bacteria. That’s why brass is a common choice for places that need cleaning, like hospitals and food processing gadgets. These qualities make brass very helpful in many industries because it can be used in many ways.
Also Read:
Use of Different Types Of Brass Grades For CNC Machining
Different types of brass alloys are employed in CNC machining, each possessing its individual properties. In this section, we will explain the various kinds of brass grades and their pros and cons.
Free Cutting Brass (C36000)
Free Cutting Brass (C36000) is a trendy type of brass that works well with CNC machines. C36000, also known as free-machining brass, contains lead, which makes it easier to cut and shape. This is really good for making complicated parts that must be exact and smooth. It is commonly used to make parts like fittings, clasps, and gears.
Advantages
- Excellent machinability
- Clean, precise cuts
- Good corrosion resistance
Disadvantages
- Lead may not be allowed in some uses.
Naval Brass (C46400)
Maritime brass (C46400) is great for use in the sea because it doesn’t wear away easily, especially in saltwater. It’s a good option for things used in the ocean. Usually, it has about 40% zinc and a small amount of tin, which makes it more resistant to damage and rust. So this makes it affordable for propeller shafts, marine hardware, and decorative items.
Advantages
- Great ability to resist being damaged by saltwater
- Strong and stiff
- Resistance to dezincification
Disadvantages
- More expensive
- Heavier than other mixtures of brass
Red Brass (C23000)
Ruddy Brass (C23000) is also called 85% brass. And this 85% copper gives it a beautiful reddish color and makes it resistant to rust. and gives it a reddish color. So, rust-resistant makes it ideal to use in oceany area, in plumbing, and in construction equipment.
Advantages
- Beautiful natural red color
- Rust-resistant
- Good for shaping and bending.
Disadvantages
- Less strong than other alloys.
- It’s more expensive because it has copper in it.
Cartridge Brass (C26000)
Cartridge Brass (C26000) is very bendable and can be shaped when cold. It contains around 30% of zinc. It is mainly used for making bullets because it is easy to shape when cold. It can also be used to make radiator cores and musical instruments.
Advantages
- Very easy to shape and form.
- Strong protection against rust.
- Versatile applications
Disadvantages
- It’s not as powerful as other types of brass.
- Moderate ability to be machined easily.
Admiralty Brass (C44300)
Admiralty brass has a small amount of tin and is mainly used in applications involving heat. The tin material resists erosion in water, so it’s good for tubes in machines that use salt water.
Advantages
- Contains tin to help prevent rusting in water.
- Good at transferring heat efficiently.
Disadvantages
- More expensive because of tin.
- Few uses outside of marine and heat exchangers.

What are the Finishing Options For CNC Machined Brass?
When you finish making brass parts with a CNC machine, there are different ways to make the surface look how you want. Here are some popular ways to finish something:
-
Polishing
Many people use cleaning to make brass parts shiny and smooth. This could be done by using rough materials, polishing tools, or chemical cleaning processes to remove imperfections and create a shiny finish.
-
Brushing
Brushing means rubbing the surface of the brass to make it look shiny and smooth. And this wrap makes the part look even better with soft lines, adding to its stylish look.
-
Anodizing
Anodizing is a process that uses electricity to create a protective layer on the surface of brass. Plus, it could be painted in different colors to look nice and last longer.
-
Plating
Brass items can have other metals like nickel, chrome, or gold added to make them look better or have unique qualities like being more durable or conducting electricity better.
-
Patination
Patination is when chemicals are put on brass to change its color and make it look more aged or exciting. And this may result in distinct hues and patterns, adding individuality to the piece.
-
Lacquering
Adding a clear protective coating to brass to stop it from turning color or rusting is called lacquering. That cover keeps the brass looking normal and ensures it lasts a long time.
-
Painting or Powder Coating
Brass parts can also be painted or coated with powder to make them the color or finish you want. Usually, people do it to improve things or keep themselves safe, especially outside or in busy places.
-
Media Blasting
Media impacting is when materials are moved at high speeds to remove surface defects and create a smooth or finished surface on the custom brass part. Every finishing option has its advantages and can be chosen based on how it looks, how useful it is, and how well it fits with the CNC-machined brass parts.
Applications Of Brass CNC Parts
Manufacturers use brass for many industries due to its high strength, flexibility, and easy to machine properties. Here are some usual uses of brass CNC parts:
Automotive Industry
- We use brass in the automotive sector to make hydraulic systems, fuel systems, mounts, and engine parts.
- Also used in the fuel injection components, exterior & interior trim or decorations.
Electronics Industry
- Further, brass is used to make electronic cases, switches, terminals, connectors, heat sinks, plugs and electrical housing due to its excellent heat-conductive and rust-resistant nature.
Plumbing and Sanitary Fittings
- You can use brass in plumbing gadgets, like doorknobs, pipes, fluid control systems, faucets, cabinet hardware, valves, couplings, pump components, and fittings because they don’t rust and handle extreme pressure.
- Manufacturers also use brass in cleaning and bathroom accessories.
Aerospace Industry
- We use brass in airplanes, engine mounts, aviational components, brackets, aircraft components, and hydraulic systems to produce high quality parts owing to resistance to wear and tear.
Medical Devices
- Manufacturers use brass to make medical parts and equipment like housings, surgical tools, implants, fittings, connectors, and diagnostic instruments.
Marine Uses
- Brass CNC parts are used in boats for fittings, equipment, and parts that resist saltwater damage.
- They are used in boat fittings, navigation equipment, ship & boat components, nautical components, and marine plumbing systems.
Architectural Hardware
- Brass CNC parts are used in building equipment like door handles, knobs, hinges, and decorative parts.
- They are known for their stylish design, strength, and ability to be applied to various surfaces in different colors.
Musical Instruments
- Brass is also used to produce musical instruments like trumpets, trombones, and saxophones.
Industrial Machinery
- Brass CNC parts are used in machines for parts that need to be very strong, stay the right size, and conduct electricity.
- They are used in gears, positioning, bushings, and tool parts.

Consumer Goods
- You can use brass in various products like jewelry, watches, pens, bezels, and decorations.
- They are respected for their excellent taste, strength, and ability to be wrapped up to a high standard.
Factors of Concern When Choosing Brass For CNC Machining
While choosing brass metal for CNC machining, it is vital to consider a few elements to guarantee its ideal performance and cost viability.
Material Properties
Pick the best blend for your necessities, and consider how much power it can deal with, what it looks like, and how it conducts power. Consider how hard it is to make the custom brass parts and choose a combination that will make it easier to create them well.
Cost
Brass mixtures change is affected by their composition and properties. Consider how much money you have and ensure the fabric you choose is affordable and meets your needs. Sometimes, a more expensive option may be worth it because it works better and lasts longer.
Erosion Resistance
Check the environment where the custom brass parts will be used. Choose a strong amalgam that can resist erosion well to ensure it will last a long time and be dependable. This is especially important for things used outside or in the ocean where they will be exposed to moisture and saltwater often.
Strength and Hardness
Pick a brass combination with the right quality and hardness for your application based on the mechanical requirements. Think about how much weight the machine parts can hold, how well they can handle impacts, and how well they resist wearing out. This will help make sure the parts last a long time and are reliable.
Surface Finish Requirements
Choose the type of finish for the machined parts and pick a brass mixture to achieve it. Brass can be finished in many ways, like cleaning, brushing, anodizing, plating, or patination, because it can flex easily. Different mixtures of metals might react differently to these finishing processes, so choose a metal that can achieve the desired appearance or function while meeting your project’s requirements.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure to follow essential instructions and standards when choosing brass materials for CNC machining. Think about how close lead is in some mixtures and any rules that say how it can be used. Choose mixtures that meet rules and laws, particularly for food contact, drinking water, or sensitive environments. Working with reliable suppliers who provide approved materials can help ensure that we follow the rules and regulations set by the government.

Supplier Reliability
Choose a reliable supplier with a reputation for providing suitable quality brass materials and delivering them on time. The fabric needs to be reliable and of good quality, delivered on time, and for the customer to receive good support throughout the CNC machining process. When choosing a supplier for your products, consider where the fabric comes from, if it’s certified, and what your customers want. Working together with a good provider can help reduce risks and ensure the success of your CNC machining project.
How To Know If Brass Is The Right Choice For Your CNC Project?
If you are uncertain or need assistance picking the best brass grade for your CNC project, it is prescribed to talk with a CNC machining master like Yijin Hardware. We can assist you with looking at the benefits and hindrances of various materials based on what you want. At Yijin Hardware,, we have a group of specialists who are prepared to assist you with any inquiries you have about CNC machining, particularly with regard to working with brass.

Our specialists know how to design custom brass parts with CNC machines, so we guarantee the parts are precise and of superior quality. We offer an extensive variety of CNC machining services and ensure our products meet ISO 9001 guidelines. Whether you want a quick prototype or mass volume we can be your trustworthy and reliable partner. So, send us your inquiry, and our team will rapidly survey your application and furnish a nitty gritty quote alongside DFM within 2-3 business days.
Conclusion
In conclusion, using CNC machining to make brass parts is a high-tech process that uses brass’s unique properties to make exact and high-quality parts. Brass CNC machining is a popular method for creating custom brass parts because it can be used for different purposes like making things better, electrical properties, or mechanical parts. As companies keep growing and need more advanced and precise parts, it will be crucial to understand and use the abilities of brass CNC machining. This guide helps producers and creators understand how to use brass in CNC machining projects to improve their products and sales.
 Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569
Call Us Today! (+86) 188-2253-7569



