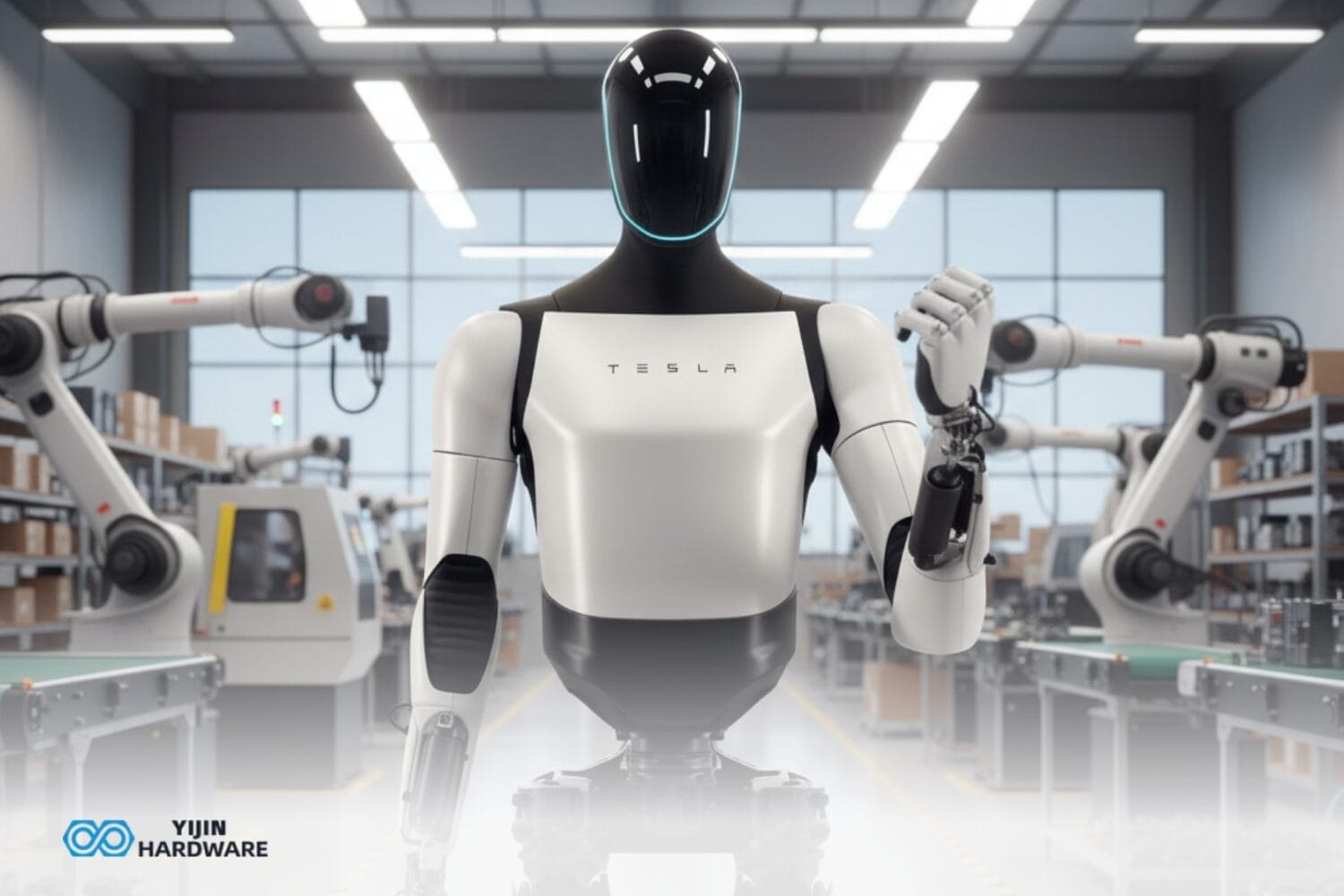
Humanoid robots aren’t just fancy machines that look human-shaped, they’re complex systems engineered to replicate human-like movement, perception, and decision-making in ways that interact naturally with environments designed for people. Making that happen requires sophisticated humanoid robot components working together seamlessly. Each component plays a specific role, and understanding how they function together is essential.
As humanoid robots advance, robot design keeps pushing into new territory. This evolution is driving automation across industries from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and customer service. Whether you’re working with industrial robots performing repetitive tasks or developing next-generation mobile robots navigating complex environments, knowing the key components and how they integrate helps ensure robots perform their tasks efficiently, safely, and reliably. Let’s break down what actually powers these machines and makes them function.
Key Takeaways
- Humanoid robot components like motors, sensors, and actuators enable precise and dynamic movements.
- Advanced AI and algorithm-driven control systems help humanoid robots make decisions in real-time.
- Robotic arms, grippers, and sensors ensure that humanoid robots can perform dexterous tasks with high-precision.
- Humanoid robots rely on advanced motion control techniques to maintain stability and adapt to different environments.
- Materials like aluminum, carbon fiber, and silicone are used in modern humanoid robots to balance strength and flexibility.
What are the Key Components of a Humanoid Robot?

The components of humanoid robots include several core systems working together to allow the robot to function like a human. Motors provide torque and enable movement, while actuators convert electrical signals into physical actions, powering robot joints like the shoulder or knee. Sensors such as LiDAR and IMUs allow the robot to perceive its surroundings and maintain balance.
The AI controller processes data from these sensors and issues commands to actuators and motors, ensuring that the humanoid can move, interact, and adapt. Humanoid robot applications span from personal assistants to industrial robots used in manufacturing and other fields.
- Motors: Provide torque and enable movement.
- Actuators: Convert electrical signals into physical actions, powering joints like the shoulder or knee.
- Sensors: Include LiDAR and IMUs, allowing the robot to perceive its surroundings and maintain balance.
- AI Controller: Processes data from sensors and issues commands to actuators and motors, enabling the robot to move, interact, and adapt.
- Applications: Range from personal assistants to industrial robots used in manufacturing and other fields.
How do Motors Function in Humanoid Robots?
Motors are at the heart of a humanoid robot’s movement system, driving both linear actuators and rotary actuators. Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are commonly used for their high efficiency and longevity, delivering the torque needed for continuous motion without excessive wear. These motors are crucial for the precise motion and stability required in applications like walking or lifting.
Along with servo motors, which allow for precise control of smaller, more intricate motions like hand gestures, BLDC motors provide the foundational power for tasks requiring higher torque. The combined use of these motors ensures that humanoid robots can carry out complex tasks like navigating complex environments or operating in dynamic settings.
What Types of Sensors are Used in Humanoid Robots?
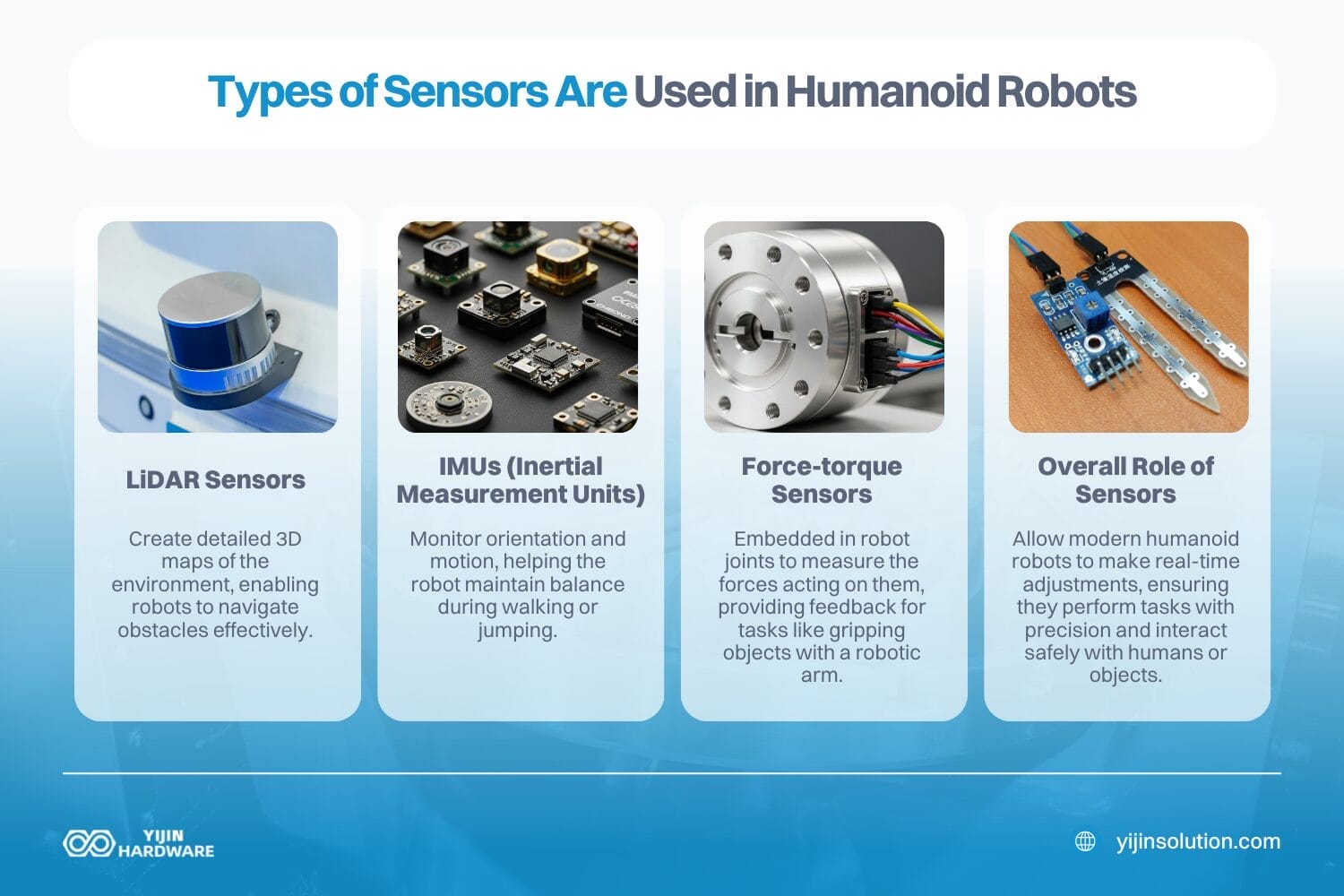
- LiDAR sensors: Create detailed 3D maps of the environment, enabling robots to navigate obstacles effectively.
- IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units): Monitor orientation and motion, helping the robot maintain balance during walking or jumping.
- Force-torque sensors: Embedded in robot joints to measure the forces acting on them, providing feedback for tasks like gripping objects with a robotic arm.
- Overall Role of Sensors: Allow modern humanoid robots to make real-time adjustments, ensuring they perform tasks with precision and interact safely with humans or objects.
How do Actuators Enable Movement in Humanoid Robots?
Actuators are the devices that convert energy into motion, enabling humanoid robots to replicate human-like movements. Electric actuators drive joint movement, while Series Elastic Actuators (SEAs) provide compliance, allowing for smoother motion and shock absorption. SEAs are particularly useful in applications where robotic arms or legs need to adjust quickly or deal with unpredictable forces.
Actuators work in tandem with motors and gearboxes to deliver the necessary torque and control to each joint, enabling a humanoid robot to complete tasks like lifting, walking, or manipulating objects with a gripper. These devices are essential for dexterous tasks, ensuring that robot joints are capable of performing actions that require high-precision control.
What Role does AI Play in Humanoid Robots?
AI systems are essential for humanoid robots to make decisions and interact in real time. By processing data from sensors like LiDAR, IMUs, and force-torque sensors, AI enables the robot to navigate environments, recognize objects, and perform tasks autonomously. For example, natural language processing algorithms allow humanoid robots to engage in conversations or respond to voice commands.
AI in modern humanoid robots also enables complex decision-making, allowing robots to understand and respond to human gestures or facial expressions. As AI continues to advance, robots will become even smarter, learning from real-world interactions and refining their behavior through algorithms designed for path planning and human-robot interaction.
What is the Best Material for Humanoid Robot Construction?
The materials used in humanoid robot construction must be strong yet lightweight to support movement without compromising efficiency. Aluminum is a popular choice for the robot’s frame due to its balance of strength and light weight. Carbon fiber is also used in high-stress areas where additional strength is needed but with minimal added weight.
For outer coverings and skin, silicone is commonly used. It provides the flexibility required for sensors, ensuring humanoid robots can integrate tactile sensors for interaction. These materials allow humanoid robots to balance durability with adaptability, enabling them to perform complex tasks while maintaining a human-like appearance.
What Power Sources are Used in Humanoid Robots?
The power source is a crucial element for humanoid robots to operate effectively. Lithium-polymer batteries are commonly used because they offer high energy density and can support power-hungry systems. These batteries allow robots to run for hours, depending on their power needs.
Along with batteries, DC-DC converters are used to regulate voltages for different components, ensuring stability and efficiency. With these power systems, humanoid robots can perform continuous operations in industries like automation or in research projects like Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robot, which showcases impressive endurance and mobility.
How do Humanoid Robots Achieve Balance and Movement?
Achieving balance is one of the biggest challenges in humanoid robot design. IMUs and advanced balance algorithms are used to track the robot’s orientation and adjust its movements accordingly. The Zero Moment Point (ZMP) algorithm is commonly used to maintain stability during walking, ensuring the robot’s support polygon remains within its center of gravity.
As robot joints like the ankles and knees work together to maintain balance, advanced humanoid robots can move smoothly across uneven terrain or complex environments. These systems allow robots to handle a variety of tasks that require both stability and adaptability.
How does Robot Joint Design Affect Humanoid Movement?
The design of humanoid robot joints is critical for achieving natural, human-like motion. Each joint is designed with a specific range of motion and degrees of freedom (DOF) to ensure that it can move in multiple directions. For example, the shoulder joints often have 3 DOF, while the knee joints have 1-2 DOF.
The combination of these joints powered by motors and actuators allows the robot to perform complex tasks like walking, running, or even lifting objects. The joint design is essential for creating the precise motion control required for activities like operating a robotic arm or using a gripper to handle delicate objects.
Explore the Future of Humanoid Robotics
As humanoid robots evolve, their applications are expanding across various industries, from healthcare to robotics research. Understanding the core components that make these robots work is essential for optimizing their design and performance. These robots are expected to perform more sophisticated tasks and interact with humans in increasingly intuitive ways.
If you’re interested in learning more about humanoid robots and how they can enhance productivity in your field, contact us today for a consultation. Yijin Hardware specializes in helping organizations integrate cutting-edge robotics into their operations.
Humanoid Robot Components FAQs
What are humanoid robots made of?
Humanoid robots are primarily made from aluminum for the frame, carbon fiber for strength, and silicone for skin-like flexibility. These materials provide a balance of strength, weight, and adaptability.
What is the best material for humanoid robots?
The best materials for humanoid robots are aluminum and carbon fiber, as they offer a strong, lightweight structure. Silicone is used for external covers that allow tactile sensing and flexibility.
What metal is best for robots?
Aluminum is commonly used for robots due to its lightweight and strong properties. In certain applications requiring higher strength, titanium is also used, though it adds weight.
Back to Top: Humanoid Robot Components | What Actually Makes these Machines Work









