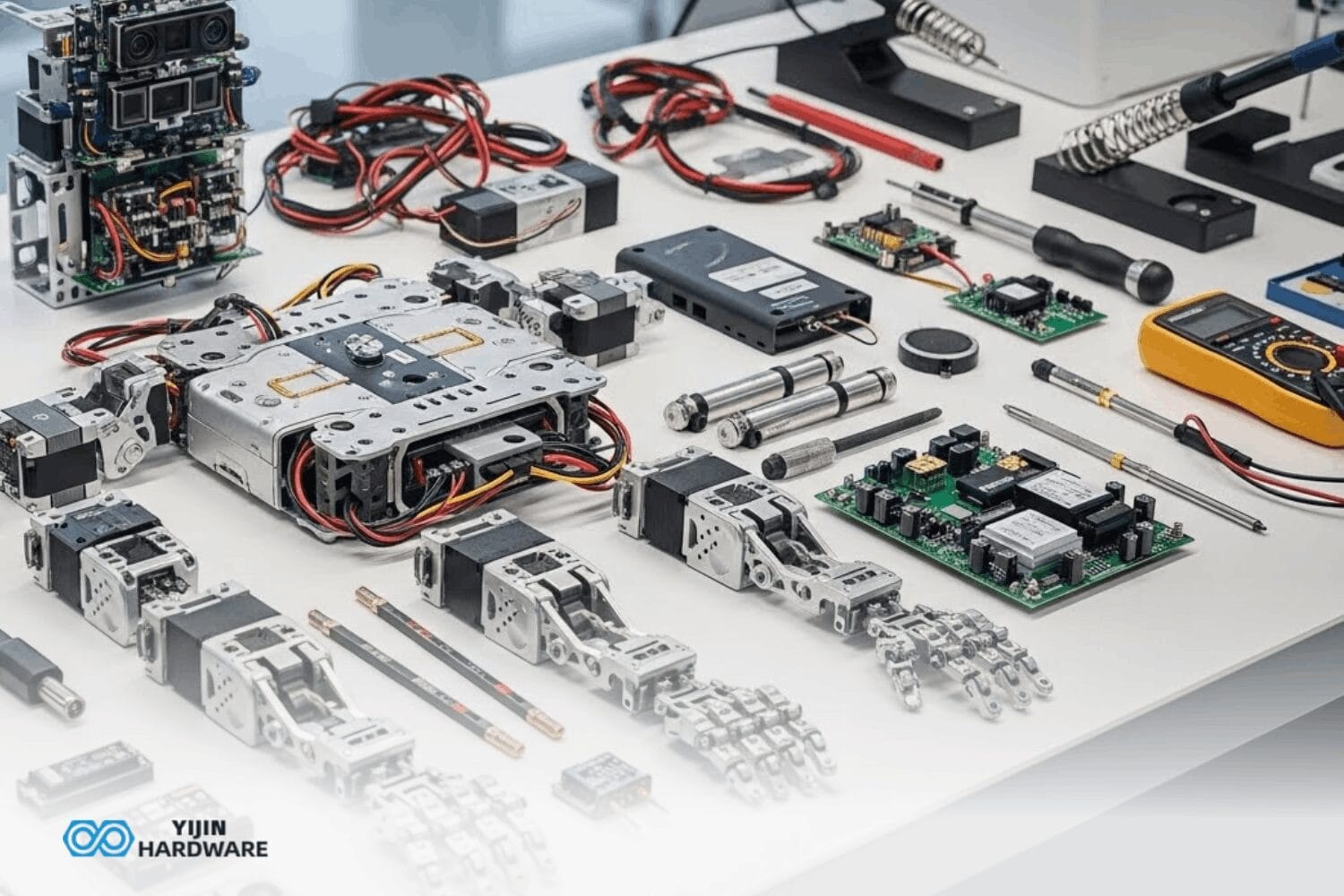
What is CNC prototyping? CNC prototyping is the process of using computer-controlled machining to create physical prototypes from digital designs. This advanced manufacturing method transforms CAD models into functional prototype parts with exceptional precision and speed, enabling design validation, functional testing, and market evaluation before mass production begins.
Let’s discuss it in simpler words. A prototype is a basic product version that assists designers or technicians in improving their design. If they find any issue, they can fix it before going into large-batch manufacturing. So in this context, rapid prototyping CNC also plays its part in prototype machined parts. Professional rapid prototyping cnc machining services deliver the following advantages:
- Quicker Turnaround time
- Higher Fidelity
- High Precision
For a basic understanding for beginners, prototyping is the early stage of rough model production. It helps in testing the viability of a design or process. Prototype is a beginner step between your initial idea and the final product.
How can CNC machining help in prototyping?

As you can read a brief introduction on CNC machining in the link below, we shall provide a concise concept. CNC machining is a method to make high-precision parts. We use computer-controlled machines to remove material from a solid block in this type of machining method. Hence, these machines produce a precise prototype of your design.
The goal of CNC machined prototypes is to get your idea out of your head and into a physical form to:
Visualize the design:
How would it look like in the final production?
Test functionality:
Ensure different parts work together as planned in the design process.
Identify flaws:
Discover weaker areas before investing in mass production.
Read More:
CNC Machining Basics
What Is CNC Machining:From Basics To Advance
What is CNC Prototype Machining?
If you have seen a professional sculptor, what if he uses a CNC machine instead of traditional tools?
Here are three main stages of CNC machines that execute any prototype:
1: Part Design
2: CNC Machine Tools Setting
3: CNC part Manufacturing
So, let’s explain each briefly.
Part Design
Prototype CNC machining starts with the ideas for a part. Engineers and designers use CAD software to make a comprehensive digital model. They make sure about the minute details such as dimensions and tolerances. They also incorporate materials and turnaround time. This digital model plays a crucial role in determining the final manufacturing.
CNC Machine Tool Settings
As soon as we finalize the design, we will send it for CNC machining. This step involves using CAM software that effectively translates the CAD model into a CNC program. This software helps in generating toolpaths and cutting the following:
- The part’s geometry
- Tooling parameters
- Machining requirements.
At this stage, a professional CNC machining center will focus on choosing the right cutting tools, materials, and fixture methods. Subsequently, they also control machining parameters, for instance, cutting speeds and feed.
CNC Part Manufacturing
The next step is to load the CNC program into the machine’s control unit. Later, the operator sets up the workpiece on the CNC machine. The machine can be 3, 4, or 5-axis. Following the programmed toolpaths automatically, the CNC machine uses cutting tools to shape the workpiece according to the design. The machine adjusts cutting parameters automatically for greater precision during the entire process.
Read More:
Top 10 China CNC Machining Companies
Top 5-Axis CNC Machining Companies
Why Choose CNC Machining for Prototyping?

CNC machining is one of the prominent choices for making prototypes due to numerous critical advantages:
Greater Precision
CNC machining is quite popular due to its tight tolerance ability. Since it works on software, the cutting-edge technology of a CNC machine can effectively control the dimensions of prototype machined parts. This high level of accuracy makes the CNC machining method a prominent choice. Because making parts with complex geometry is highly convenient.
Rapid Prototyping
Time is everything in product development. Therefore, CNC machining is the best choice to accelerate part manufacturing. CNC machining is relatively faster than traditional machining methods. Thanks to its automated computer-controlled process, CNC is much quicker than manual machining. Rapid prototyping CNC is crucial when multiple prototype iterations are required for further design improvements.
Read More:
CNC Machining vs Manual Machining
Better Choice of Materials
CNC machining has the potential to machine several important materials. This includes metals like:
- Aluminum and steel: Aluminum is a popular choice for lightweight prototypes due to its excellent machinability and versatility. Collaborating with experts in CNC machining aluminum ensures precision and efficiency in creating high-quality components.
- Plastics: Plastics are frequently used for prototypes and low-weight applications. Leveraging specialized CNC machining for plastics ensures that even delicate materials are processed accurately without compromising their integrity.
- Titanium: Titanium stands out for its strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for advanced prototyping. Working with specialists in CNC machining titanium ensures that this challenging material is handled with the precision it demands.
Choosing the right material is important for guaranteed results at the prototyping stage.
Common CNC Prototyping Options
CNC machining comes with a range of different manufacturing processes which is suitable for making CNC-machined prototypes. For components requiring formed metal features alongside machined details, sheet metal prototyping seamlessly complements traditional machining workflows. Generally, there are three procedures we follow in CNC machining. Let’s discuss each:
Turning

CNC machining centers use a lathe to shape prototypes like metal and plastic in this method. Turning tools keep rotating the workpiece by removing the extra material following CNC prototypes. It is commonly used in manufacturing shafts, pins, and bushings. For businesses needing reliable solutions, partnering with a trusted turned parts manufacturer can ensure precise results for all turning requirements.
Milling

In this method, the machinist places the workpiece on the table, where the tools do the rest of the job. These tools can move in multiple directions, following the computer’s commands. This process helps them in making the desired shape. The flexibility of the tools makes milling a prominent choice for making CNC machined prototypes. If you’re looking for a dependable CNC milling service China, Yijin Solution offers advanced milling solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Multi-Axis Machining

In multi-axis machining, the machinists use more than three axes. Multi axes allow machining centers to make prototypes with higher complex designs. This method also reduces the material waste. In more simple words this technique is like a sculptor with multiple hands working on different directions of the part.
CNC Plastic Prototyping
CNC plastic prototyping is one of the most cost-effective and versatile methods for creating functional prototypes. Plastic prototypes allow engineers and designers to test form, fit, and function before committing to expensive tooling or mass production. Unlike metal prototypes, plastic CNC machining offers faster turnaround times and lower material costs while still delivering high precision.
Common Plastics Used in CNC Prototyping
Different plastic materials serve different prototyping needs. Here are the most popular options:
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Known for its excellent impact resistance and ease of machining, ABS is ideal for consumer products, housings, and functional testing. It’s the same material used in LEGO bricks, offering good strength and durability.
POM (Delrin/Acetal): This engineering plastic provides exceptional dimensional stability and low friction properties. POM is perfect for gears, bearings, and moving parts in prototype assemblies.
PEEK (Polyetheretherketone): A high-performance plastic with excellent chemical and heat resistance. PEEK prototypes are common in aerospace and medical device applications where extreme conditions are expected.
Nylon (PA): Offering high strength and flexibility, nylon prototypes work well for mechanical parts, snap-fit assemblies, and wear-resistant components.
Polycarbonate (PC): Known for its optical clarity and impact resistance, polycarbonate is ideal for transparent prototypes, lenses, and protective covers.
Advantages of Plastic CNC Prototyping
Choosing plastic for your CNC prototypes offers several key benefits:
Cost-Effective: Plastic materials are significantly cheaper than metals, reducing overall prototyping costs by 40-60% compared to aluminum or steel.
Rapid Turnaround: Plastics machine faster than metals, allowing for quicker prototype delivery—often within 3-5 business days for standard projects.
Design Iteration: The lower cost makes it practical to create multiple prototype versions, enabling rapid design improvements and testing cycles.
Lightweight: Plastic prototypes are ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as drones, handheld devices, or automotive interior components.
Surface Finish Options: CNC machined plastic prototypes can achieve smooth finishes with minimal post-processing, or can be painted, textured, or polished as needed.
When to Choose Plastic Over Metal
Plastic prototypes are the best choice when:
Testing product ergonomics and user interface design
Creating visual models for client presentations or focus groups
Developing consumer electronics housings and enclosures
Prototyping parts that don’t require metal’s structural strength
Budget constraints make metal prototyping cost-prohibitive
Quick turnaround times are essential for meeting project deadlines
For projects requiring metal strength, thermal conductivity, or extreme durability, consider our CNC aluminum prototyping or metal prototyping services instead.
CNC Aluminum Prototyping
Aluminum is the most popular metal choice for CNC prototyping, offering an ideal balance of strength, weight, machinability, and cost. CNC aluminum prototyping allows engineers to create functional metal prototypes that accurately represent final production parts in both form and performance. From aerospace components to consumer electronics, aluminum prototypes deliver the durability and precision required for rigorous testing.
Popular Aluminum Grades for Prototyping
Different aluminum alloys offer varying properties suited to specific applications:
6061 Aluminum: The most versatile and commonly used grade for prototyping. 6061 offers excellent machinability, good strength, and superior corrosion resistance. It’s ideal for general-purpose prototypes, structural components, and parts requiring anodizing.
7075 Aluminum: Known as “aircraft aluminum,” 7075 provides the highest strength of common aluminum alloys. This grade is perfect for aerospace prototypes, high-stress components, and applications requiring maximum strength-to-weight ratio.
5052 Aluminum: Excellent for marine applications and parts exposed to harsh environments. 5052 offers superior corrosion resistance and is commonly used for sheet metal prototypes and enclosures.
2024 Aluminum: Another aerospace-grade material with high strength and excellent fatigue resistance. 2024 is ideal for prototypes that will undergo stress testing or simulate high-performance applications.
Key Benefits of Aluminum Prototyping
Lightweight Performance: Aluminum’s low density (one-third that of steel) makes it perfect for prototypes where weight reduction is critical—automotive, aerospace, and portable electronics.
Excellent Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Despite being lightweight, aluminum prototypes provide substantial structural strength, closely matching final production part performance.
Superior Machinability: Aluminum machines 3-4 times faster than steel, reducing production time and costs. This soft metal creates less tool wear and allows for intricate details and tight tolerances.
Corrosion Resistance: Natural oxide layer provides excellent protection against environmental degradation, making aluminum prototypes suitable for outdoor testing and marine applications.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum efficiently dissipates heat and conducts electricity, essential for electronic enclosures, heat sinks, and thermal management prototypes.
Anodizing and Finishing Options
CNC aluminum prototypes can be enhanced with various surface treatments:
Type II Anodizing: Creates a decorative, corrosion-resistant coating available in multiple colors (black, red, blue, gold, clear).
Type III Hard Anodizing: Provides extreme hardness and wear resistance for functional testing of high-wear components.
Bead Blasting: Creates a uniform matte finish, ideal for aesthetic prototypes and pre-anodizing preparation.
Polishing: Achieves mirror-like finishes for visual prototypes and consumer product mockups.
Powder Coating: Offers durable, colorful finishes with excellent UV and chemical resistance.
Industries Using Aluminum Prototypes
Aerospace: Aircraft components, UAV frames, satellite parts, and structural brackets
Automotive: Engine components, transmission housings, suspension parts, and trim pieces
Electronics: Heat sinks, device enclosures, mounting brackets, and EMI shielding
Medical Devices: Surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment housings, and prosthetic components
Robotics: Robot frames, actuator housings, and precision mechanical assemblies
Cost Comparison
While aluminum costs more than plastic, it’s significantly more affordable than other metals:
Aluminum vs. Plastic: 2-3x higher material cost, but provides metal performance
Aluminum vs. Steel: Similar cost, but faster machining reduces overall expenses
Aluminum vs. Titanium: 75-85% cost savings with comparable performance for many applications
For projects requiring the ultimate strength and biocompatibility, explore our CNC machining titanium services.
Applications of CNC Prototype Machining
The unique capabilities of CNC machines make machining methods appealing. Therefore, in CNC rapid prototyping, hobbyists prefer to work with these methods because they can execute complex shapes flawlessly. Here are a few cnc application examples:
More Functional Prototypes
Incorporating CNC machines is about more than just prototyping. The sole purpose is to demonstrate the effectiveness of the prototype machined parts. For example, a prototype product can give us functional and design aspects. Hence, we can detect the flaws quickly which ultimately helps us to improve our design.
Aerospace

With the new developments in the aerospace industry, everyone is looking for more reliable and lightweight parts. With CNC machines, we can effectively use titanium and aluminum alloys to make prototypes.
Automotive

CNC machining is playing a decisive role in manufacturing automotive industry prototype parts. Since car engines demand higher accuracy; CNC machining can meet the tight tolerances effectively.
Medical Devices
Precision is everything in the medical industry. Therefore, CNC machining is here to make accurate prototypes for medical devices. Here again, materials like titanium and stainless steel enhance the productivity of the machining process.
Benefits of Prototyping with CNC Machining
Design Verification and Iteration
CNC-machined prototypes offer a solid space for hobbyists to make a perfect part before mass production. Prototyping a machined part allows you to check the design and make further improvements. Hence, you can make quick modifications.
Lower Investment
Since CNC machining is expensive, we cannot test the product in mass manufacturing. It will lead to greater upfront costs which can be discouraging for the buyer too. CNC prototyping provides both cost-effective and quick solutions to overcome these challenges.
Vast Material Compatibility
Making prototypes in CNC machining is easy due to an extensive range of material selection. This characteristic gives machining a significant advantage over other prototyping methods.
For example, unlike 3D printing, CNC can make prototypes with any plastic material. This quality allows designers to assess the prototype performance accurately. Moreover, it reduces the initial investment, too. The other factor is the evaluation of material behavior. Machinists can easily check:
- Tolerance
- Material machining capacity
- Possible surface finishing.
Limitations of CNC Prototyping
While CNC machining offers an impressive array of benefits for prototyping, it’s essential to acknowledge its limitations:
Material Waste
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process. It means due to the limitations of the axis, there are higher chances of material waste. But modern CNC 5axis machines have solved this issue. Since it can work in multiple directions, the material waste is pretty low.
Cost per Unit
Although CNC machining produces accurate prototypes, its cost for precision is relatively high. For instance, single batches of prototypes can be much more expensive as compared to well-designed part mass production. The reason is the initial setting up cost of machines.
Key Considerations for CNC Prototyping
No doubt, CNC machining provides excellent capabilities but there are some considerations also. A machinist should undertake them before executing any prototype project.
Design Complexity
CNC machines are popular due to their efficiency in making perfect prototype parts for complex designs. However, if there are prototypes with complex designs, it can be challenging for CNC machines. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a professional CNC machining company.
Material Selection
Selecting the appropriate material is crucial to making a CNC machined prototype. CNC machining can handle a wide range of materials. For a beginner, some aspects need to be considered such as:
- Strength
- Weight
- Heat resistance
The same prototype cannot be used for all fields. We need to select materials according to industry requirements.
CNC Machining vs. 3D Printing
As we have discussed earlier CNC machining is a manufacturing process that can work swiftly on various materials with greater precision. However, it can be more expensive, especially for making prototypes. On the other side, 3D printing makes parts by adding layers gradually. You can say similar to a high-tech glue gun. Simultaneously, 3D printing is not only faster but also cheaper. It can effectively work on simple designs. However, CNC machining is a better choice for prototypes requiring metal strength.
| Factor | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High | Moderate |
| Lead Time | Faster for simple designs, slower for complex geometries | Can be faster for simple designs |
| Material Options | Wide range of metals, plastics, and even wood | Primarily plastics, limited metal options |
CNC Machined Prototypes vs. Injection Molding Prototypes
Choosing the proper prototyping method is crucial for any end-product performance. Comparing both methods will allow you to assess their functions, strengths, and weaknesses. For instance, skilled technicians can evaluate the material limitations of both methods during testing. Ultimately, it will help for further product refinement.
| Feature | CNC Machined Prototypes | Injection Molding Prototypes |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Low | High |
| Prototype Speed | Rapid | Faster (after mold creation) |
| Materials | Wider Selection (Metal, Plastics, Wood, and composites) | Primarily Plastics |
| Cost per Unit | High | Low (for mass production) |
To learn more about their differences, feel free to read our detailed guide: CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding
Yijin Solution: Your Premium Partners for CNC Rapid Prototyping
Yijin Solution offers full-range CNC prototyping solutions. Our seasoned team helps you convert your complex prototype designs into functional parts. From design to selecting the suitable material, we help you at every stage by incorporating state-of-the-art CNC machines.