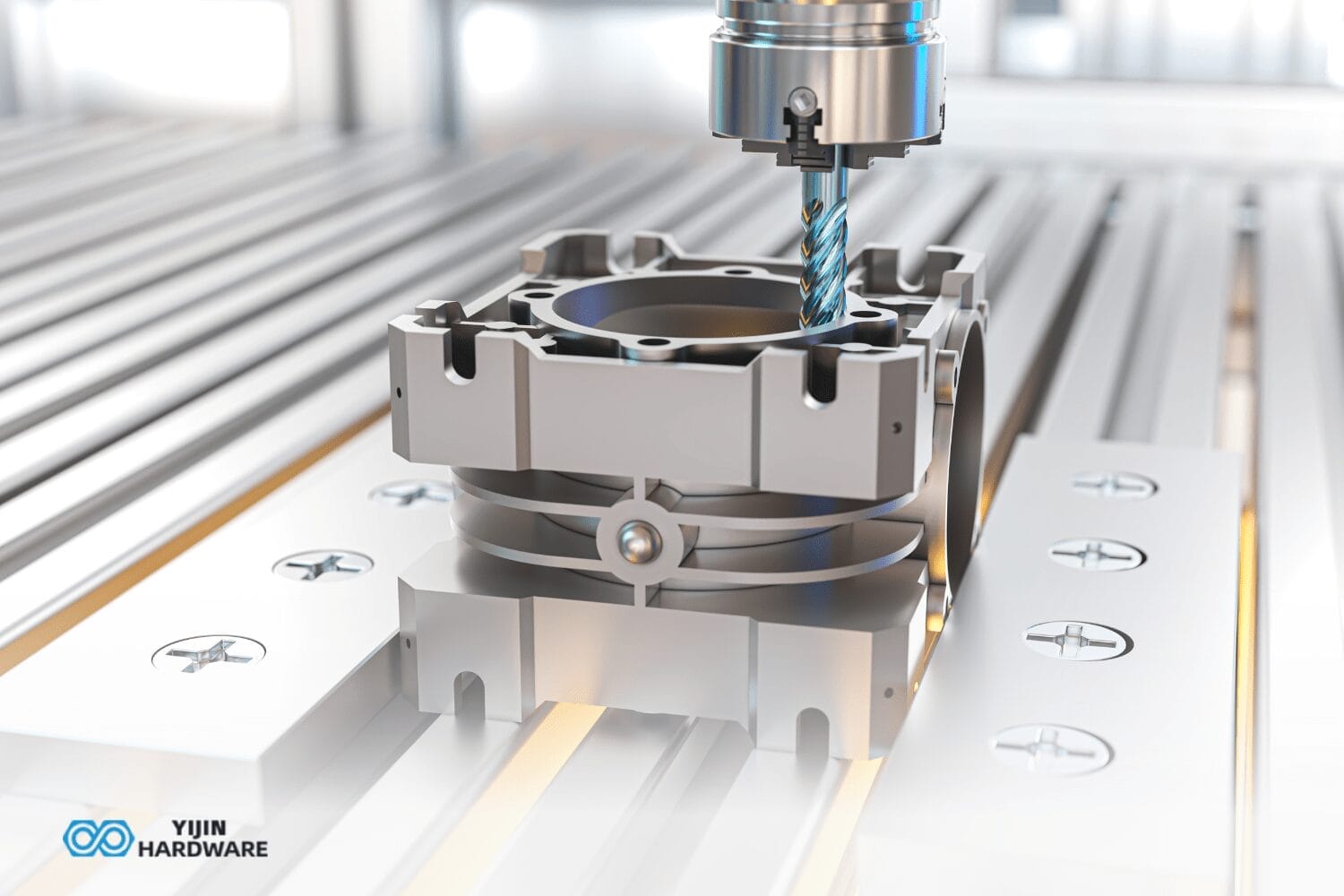
3-axis machining is going to new heights. Despite it is quite affordable and deliver excellent results for simple designs, more researches are emerging. For instance 3-axis machining adds value to additive manufacturing.
Source: Hybrid additive and subtractive machine tools (Joseph M. Flynn)
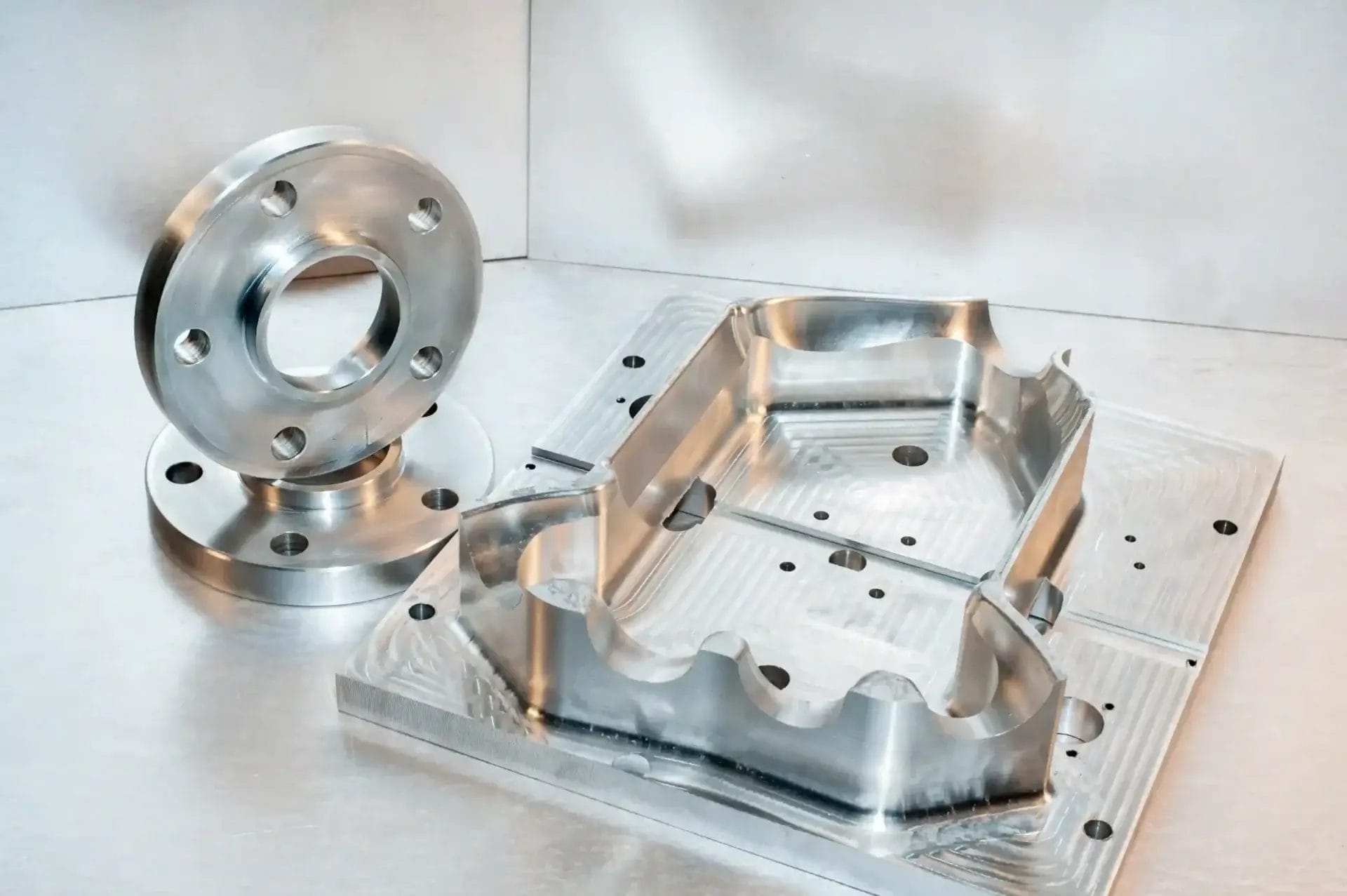
Consider a hunk of metal and want to make it an awesome gear or stylish phone case. This is where 3-axis machining plays a key role. Can you imagine any object around you, plastic or metal, with pinpoint accuracy? All metal objects with precise finishing incorporate CNC machines. They go through a complex process to end in a fine metal part.
You can think of different engine parts and complicated metal objects of multiple machines. A 3-axis machine usually does the job perfectly at lower prices than a 5-axis machine. However, do you want to learn more about this milling machine? Let’s explore every detail!
What is 3-axis machining?
This type of machining works along three main directions: X, Y, and Z. Just think out of the box to grasp the concept. X moves you left and right, Y moves you forward and backward, and Z goes up and down.
3-axis milling machines deliver adequate movement control, so they are considered a good option for all types of materials.
Example of 3-axis machining:
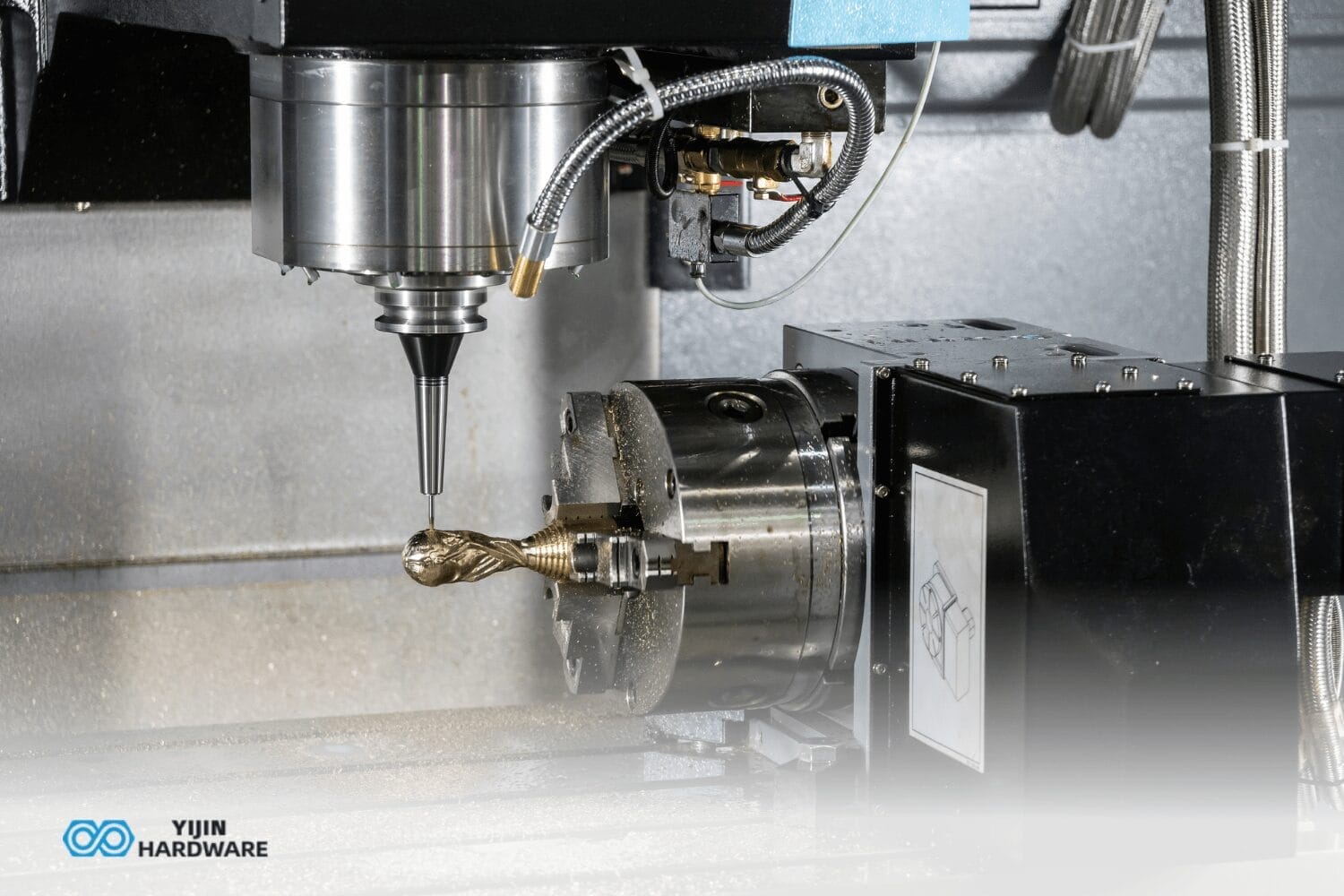
You have a piece of metal, and you want to engrave something amazing on its top side. To this end, a 3-axis machining tool is gonna perform all functions from cutting to the final part! It’s like an exceptionally fine carving machine. For example, it rotates the drill in three dimensions:
- From left to right (X)
- From front to back (Y)
- And up and down (Z).
The accuracy of the 2-axis CNC milling machine depends on three things:
- Perfect Design
- Material
- Operator command over the machine
3-axis machining is good for parts that are not very curved. Examples include flat plates with holes or grooves and blocks with simple steps. It’s a 2D drawing given life in 3D. However, its simplicity lies in its accuracy. The computer-guided machine performs this task perfectly; thus, all your pieces will have the same size and shape.
Read More: 4 Axis CNC Machining
How does 3-axis machining work?

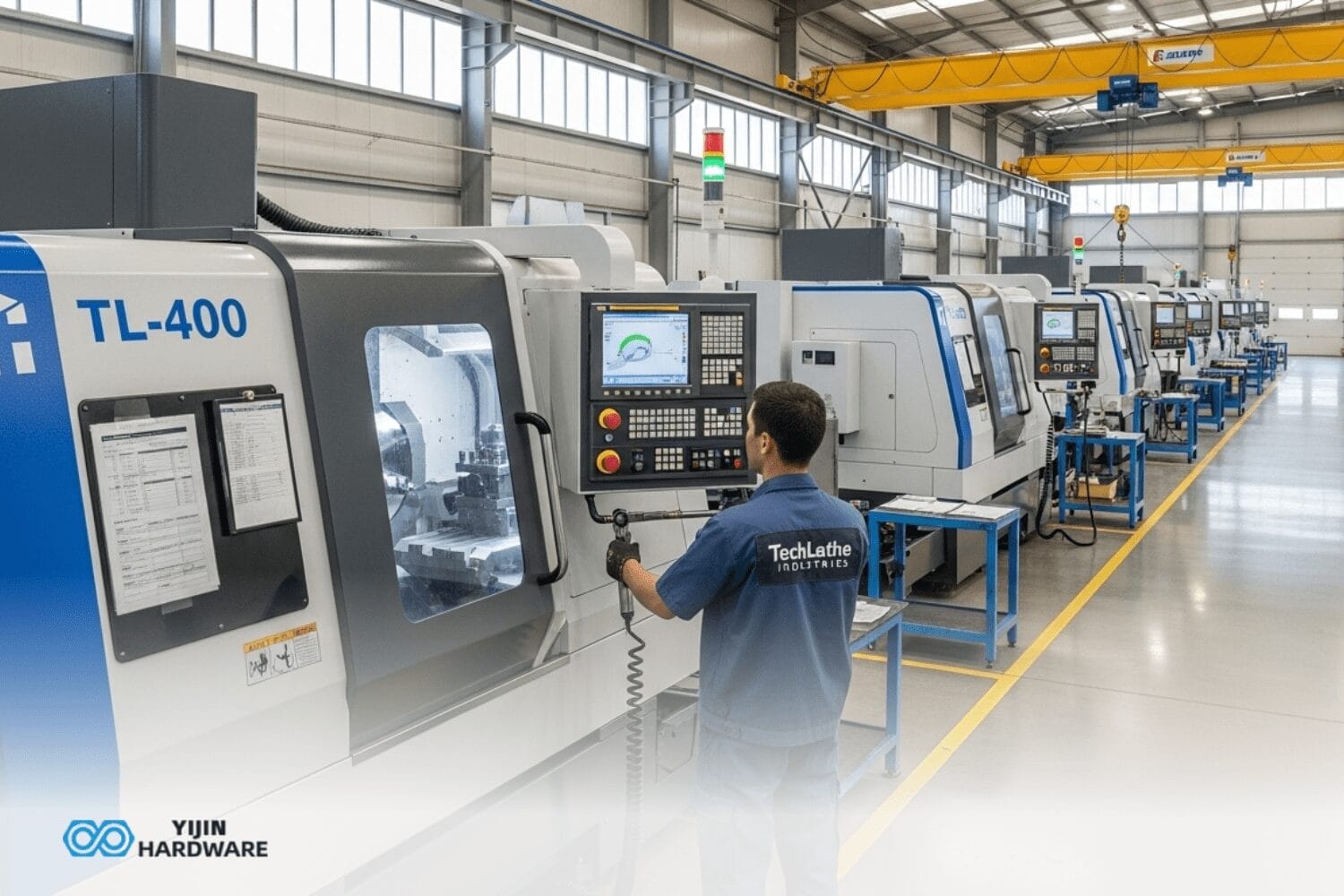
The working of 3-axis CNC machines goes through 6 steps. We are gonna describe each one by one.
- Design Preparation: The first step is design, created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This program gives:
- Exact dimensions
- Shapes
- And features of the object.
- CAM Conversion: The CAD design is then converted into a set of instructions for the 3-axis machine
- Machine Setup: The workpiece (material to be machined) is securely fastened onto the machine’s work table. The operator selects the cutting tool and transfers the design code to the machine’s control system later.
- Machining Process: The machine follows the programmed instructions. The cutting tool moves along the X, Y, and Z axes according to the program. This activity repeats until you get to the final part. There is also a risk of material waste.
- Coolant Application:A coolant (often a water-based solution) is typically applied to the cutting tool. It gives several advantages, such as:
- Cool down the cutting zone
- Reducing friction and wear on the tool
- And improved surface finishing.
Example:
If you were building with Legos, 3-axis machining would be similar to having a tool that can accurately cut and shape a single Lego part. You can make all types of fancy objects, but they might lack the tough curves and angles that other advanced metal objects have.
Common 3-Axis Machines
Several types of machines are used in 3-axis machining:
What is different in 3-axis machining is the type of machine that performs it, though these milling tools follow same three directions (X, Y, and Z). Here’s a brief overview of some common examples:
CNC Milling Machines – These are like powerful tools capable of making flat parts with:
- Pockets
- Steps
- Pockets
Imagine a powerful drill that can move around in all directions to precisely remove material.
CNC Machining Centers – These are like having an entire toolbox in one machine as they can both drill holes, tap threads and mill surfaces at once. They are ideal for complicated parts requiring multiple operations.
CNC Lathes – The workpiece spins while a cutting tool shapes it. CNC lathes are great for producing cylindrical objects such as axles or pipes.
CNC Routers – Picture an ultra-powerful router for your workshop but bigger and much more accurate. Such machines work well when it comes to cutting up large sheets of wood, plastic or even softer metals.
CNC Engraving Machines – In terms of detail they come out on top using very small cutting tools to engrave patterns into various materials. Think about an extremely accurate pen which can etch whatever you want onto metal, plastic or even glass.
CNC Plasma Cutters – Plasma cutting machines are highly effective for cutting through thick metal sheets with precision, speed, and efficiency. This makes them a valuable tool for a wide range of industrial applications, especially when you require plasma cutting service to achieve clean, precise cuts for larger steel components. Their ability to handle intricate designs and deliver quality results ensures they are a preferred choice for many machining projects.
Applications of 3-Axis Machining

Three-axis machining may sound simple, but it is incredibly versatile! This is because this machining method can create exact shapes for many diverse industries. Here are some areas where 3-axis machining delivers impeccable custom-milled parts:
Automotive: Next time you’re driving your car, just come and have a look inside the bonnet. Most engine parts, such as pistons and transmissions, are likely to be shaped using 3-axis machining. This ensures all the components fit together perfectly for a smooth ride.
Aviation: Safety is key when dealing with airplanes or spaceships. 3-axis machining makes the high-precision and durable parts required in airplanes possible. Think about wing components or engine parts that must be strong yet light.
Medical: Medical devices and implants often require intricate details for functionality. These specific medical tools, from delicate surgical instruments to complex joint replacements, are made through 3-axis machining.
Electronics: We depend on many gadgets, from phones to laptops, which often have parts manufactured using 3-axis machined products. 3-axis milling significantly improve enclosures and internal components performance.
Everyday Toys: How do those cool plastic toys is manufactured? Most molds used for injection molding are done through 3-axis machining, which ensures precise shapes for items intended for mass production.
Construction: Even construction can benefit from three-axis machining. Some structural elements, especially those requiring precise cuts or forms, can be machined to fit precisely.
Jewelry: Take a closer look at this finely crafted piece of jewelry. 3-axis machining is capable of creating beautiful and precise details on precious metals.
Advantages of 3-Axis Machining
3-axis CNC machining delivers countless advantages. Below, we have mentioned some prominent benefits:
Best for Simple Designs: It requires movement in just three directions – right-left, back-forth and up-down – these make it easier to program and use as compared to the complex ones. This implies that your project’s delivery time will be much faster.
Precise Parts: It focuses on making flat or slightly curved surfaces, which suits a wide range of daily parts like brackets, gears or control panels. When a simpler machine can do that job then there is no need for an expensive one!
Inexpensive: Generally, 3-axis tools are less expensive than more complicated machines both in terms of initial cost and maintenance costs. Thus most of the time people prefer 3-axis milling because it is more affordable compared to 5-axis.
Accuracy: Three axis milling can generate highly accurate parts. Its process is quite simple due to computer controlled movements and sharp cutting tools.
Disadvantages of 3-Axis Machining
3-axis machines have some disadvantages too which make them a less prominent choice compared to 5axis.
Poor Performance in Making Complex Shapes: As far as 3-axis machines are concerned, curving super shapes and making angled cuts on their peripheries is impossible. They face difficulty every time they mill complex designs. It is due to limited angle reach. The material waste is also more.
Time Consuming: With complex parts having many sides, you may have to hold down the metal in different positions and re-machine each side. This requires more time and effort than if the machine moves in more directions.
Limited Reach: However accurate 3 axis machining can be; it cannot make very complex surfaces or tiny features at all. For your design that needs small holes or gentle curves you might require a more sophisticated machine tool.
3-Axis Machining vs. 5-Axis Machining
Earlier, we focused more on 3-axis machining. But there is also an advanced milling machine: 5-axis machines. With more angles, 5-axis machines deliver good results against complicated designs. Similarly, material waste is also less.
The Key Difference:
Suppose a painter has only three brushes (up, down, and sideways). That’s sort of like 3-axis machining. It can do many things, but it is hard to make complex shapes.
Now imagine the same painter with two extra paintbrushes that can rotate their wrists. That is called 5-axis machining! The additional axes enable more delicate moves and angles, which makes it ideal for producing super-complex shapes.
3-Axis vs. 5-Axis CNC Machining: Comparison Table
| Feature | 3-Axis CNC Machining | 5-Axis CNC Machining |
| Movement Capabilities | X (Left-Right), Y (Front-Back), Z (Up-Down) | X, Y, Z, A (Tilt), B (Rotation) |
| Surface Finishing | Good for flat and simple curved surfaces | Excellent for complex, 3D shapes with intricate details |
| Turnaround Time | Generally faster due to simpler programming and fewer setups | Can be slower for complex parts due to multiple setups |
| Programming Complexity | Lower | Higher – requires more advanced programming skills |
| Machine Cost | Lower – generally more affordable | Higher |
| Maintenance | Lower – simpler mechanics | Higher – additional rotational axes require more maintenance |
| Applications | – Prototyping – Simple parts (brackets, gears, control panels) | – Complex, 3D parts (medical implants, aerospace components) – Multi-sided parts |
Conclusion
Whether it is 3-axis CNC Machining Services or 5-axis machining, you need a professional machining company. If you are a newbie in this field, you cannot get the idea of the part by reading only. Why is it important? Because a seasoned machining center like Yijin Hardware has modern milling machines and highly professional operators. They provide the facility to process every material, metal or plastic.