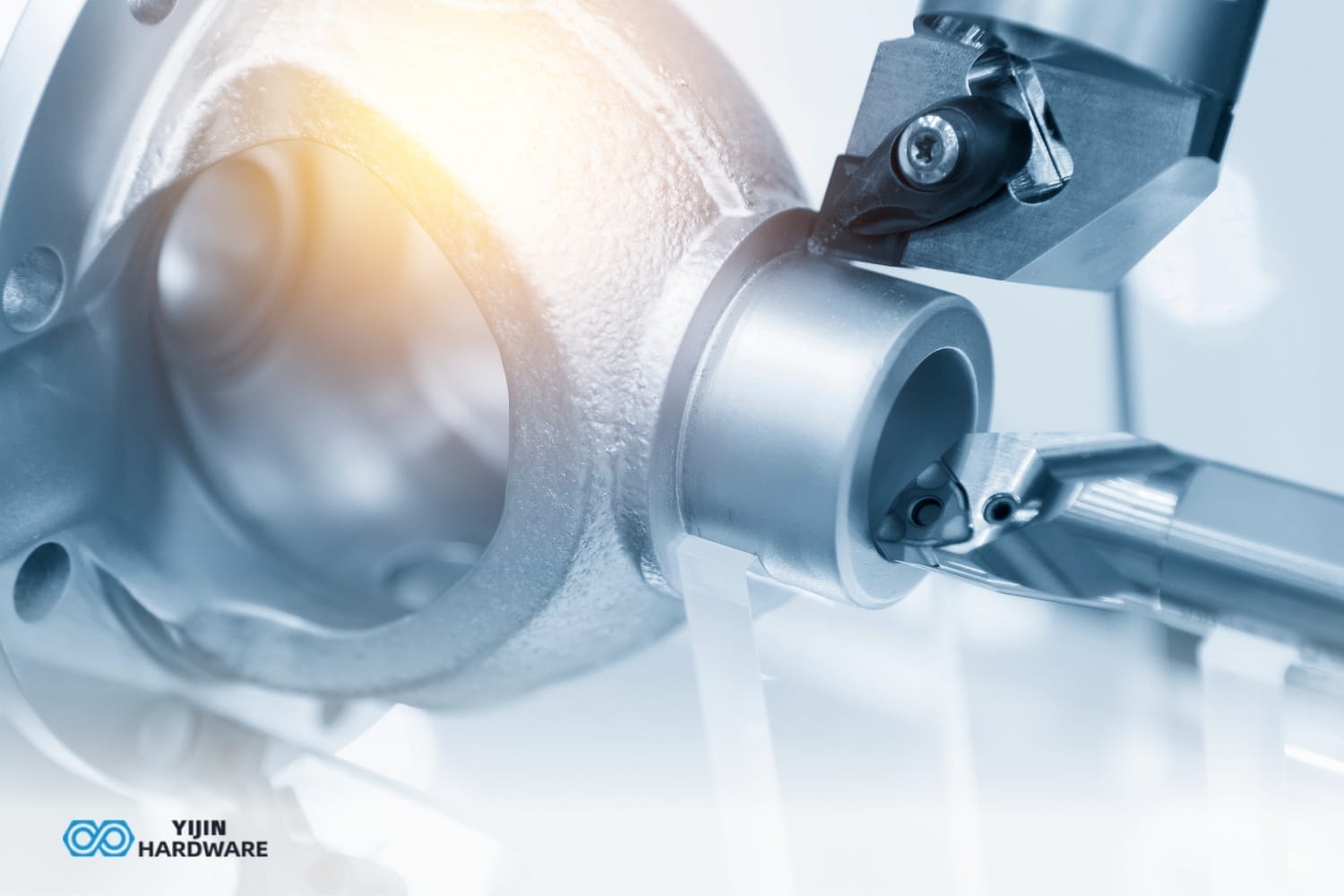
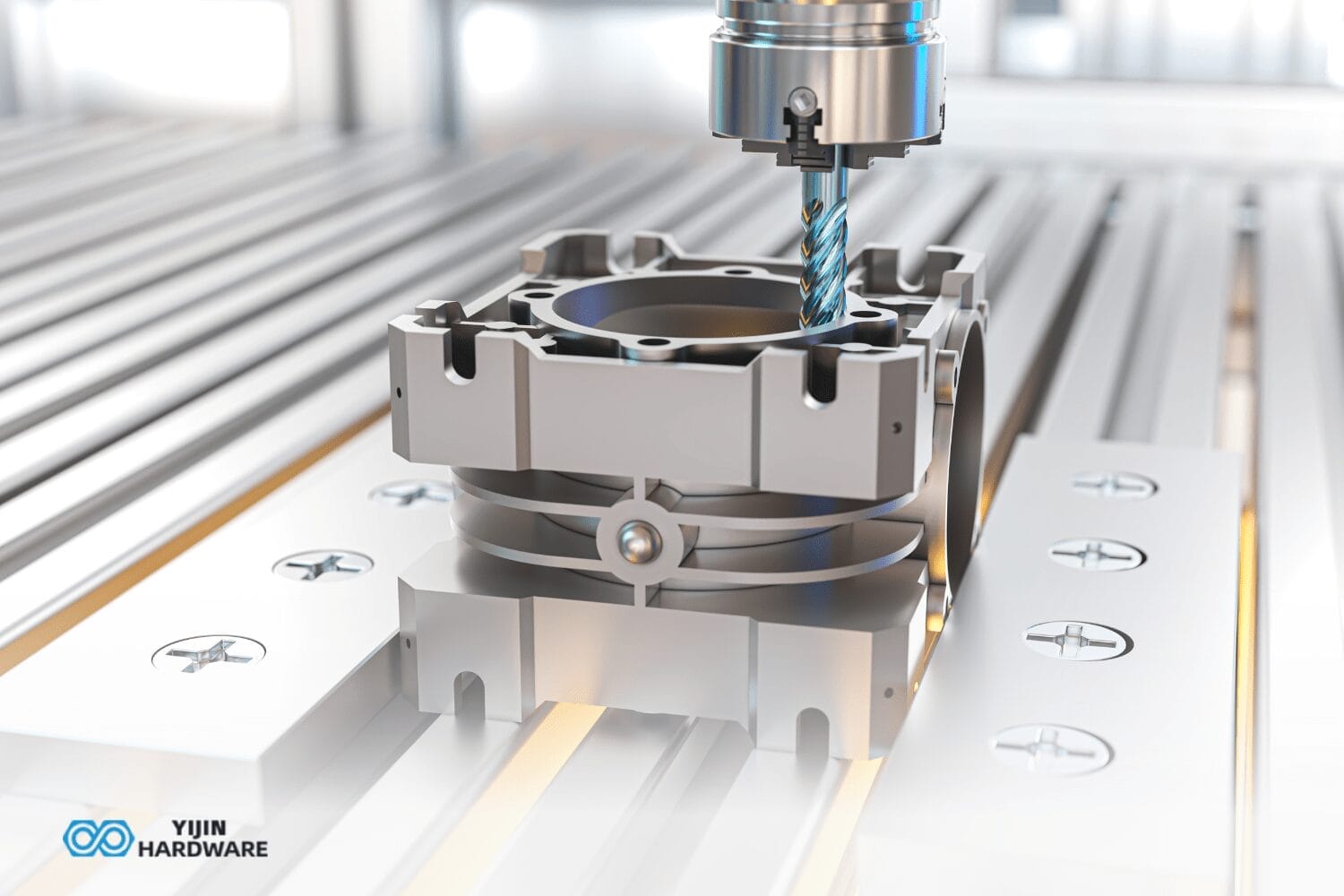
Complex CNC machining is the multifaceted process necessary to achieve extraordinary accuracy in manufacturing. It refers to the use of computer numerical control machines to create highly intricate and detailed parts that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional machining methods. These components typically feature intricate designs, tight tolerances, and specific material requirements that demand advanced techniques to produce successfully.
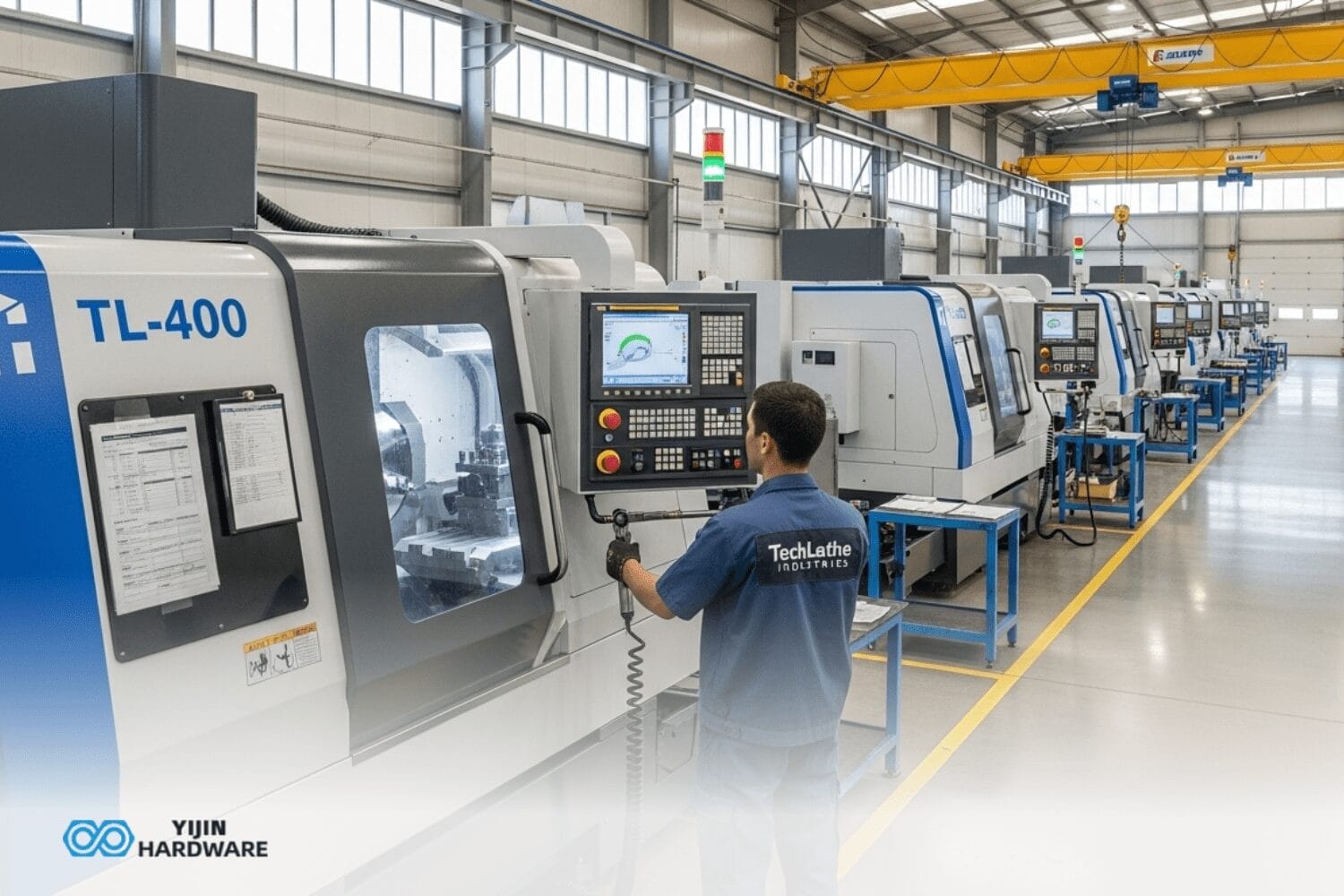
At Yijin Hardware, we specialize in leveraging this technology to produce high-quality, complex CNC machining parts. We work with CNC machines, including mills and lathes, that are designed to meet the demands of modern manufacturing by providing precision and flexibility. We’ve written this guide to help you understand what complex CNC machining is and the advantages it provides to various industries.
Key Takeaways
- Complex CNC machining uses computer numerical control machines and sophisticated techniques like 5‑axis and high‑speed machining to produce parts with intricate designs, tight tolerances, and demanding material requirements.
- Evaluating part complexity involves measurable factors such as size, wall thickness, feature geometry, internal cavities, tolerance levels, and material properties that determine tooling and setup needs.
- Aerospace, medical, and automotive industries rely on complex CNC machining to deliver precision components with exacting specifications and intricate geometries beyond the capabilities of simpler methods.
What Makes a part “Complex” in CNC Machining?
Complexity in CNC machining isn’t a subjective assessment but is determined by specific measurable factors. Understanding these elements is crucial for engineers and manufacturers to properly plan, budget, and execute machining projects.
How do you Evaluate Part Complexity?
Part complexity is dependent on multiple interrelated factors, including its size, weight, wall thickness, and more. Take a look at the following factors that help you determine how potentially complicated a part is or isn’t.
Part size and weight
Larger parts (exceeding 1000 mm or the typical work envelope of standard CNC machines) require specialized equipment and present challenges in maintaining consistent quality across large surface areas.
Wall thickness
Thin walls below 0.8 mm for metals or 1.5 mm for plastics are prone to deflection during machining, requiring fixturing and reduced cutting speeds.
Feature depth-to-width ratio
Features with a depth-to-width ratio greater than 3:1 can cause tool deflection, heat buildup, and chip removal issues.
Internal cavities and undercuts
Limited-access features require unique tooling, multiple setups, or alternative methods like EDM, increasing cost and production time.
Surface geometry
Curved or intricate surfaces often necessitate 5-axis machining and multiple setups, adding machining time and expense.
Microscale features
Features smaller than 2.5 mm or very small radii demand customized tooling and techniques, increasing complexity and tool wear.
Tolerance requirements
Maintaining tight tolerances (±0.0004” or 0.01 mm) increases cost and machining time significantly.
Material properties
Hard materials like titanium or hardened steel increase tool wear and require slower cutting speeds, while ductile materials demand unique strategies for chip removal and heat management.
What’s the Difference Between Complex vs. Simple Parts?
This comparison table illustrates the key differences between simple and complex CNC machined parts, tackling particular characteristics that we use to measure complexity. We’ve outlined the most common ways to discern if a part is simple or complex, although real-world examples often come with more nuance.
| Characteristic | Simple Parts | Complex Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Axes required | 3-axis sufficient | 4-axis or 5-axis necessary |
| Setups needed | Single setup | Multiple setups |
| Feature accessibility | All features accessible from standard angles | Features require tailored access angles |
| Internal geometries | Minimal or none | Multiple internal features |
| Tolerance requirements | Standard (±0.005” or 0.127 mm) | Tight (±0.0004” or 0.01 mm) |
| Surface finish | Standard (125 microinch) | High (32 microinch or better) |
| Tooling requirements | Standard tooling | Specialized or custom tooling |
| Programming complexity | Basic G-code sufficient | CAM programming required |
What is the Complex CNC Machining Process?
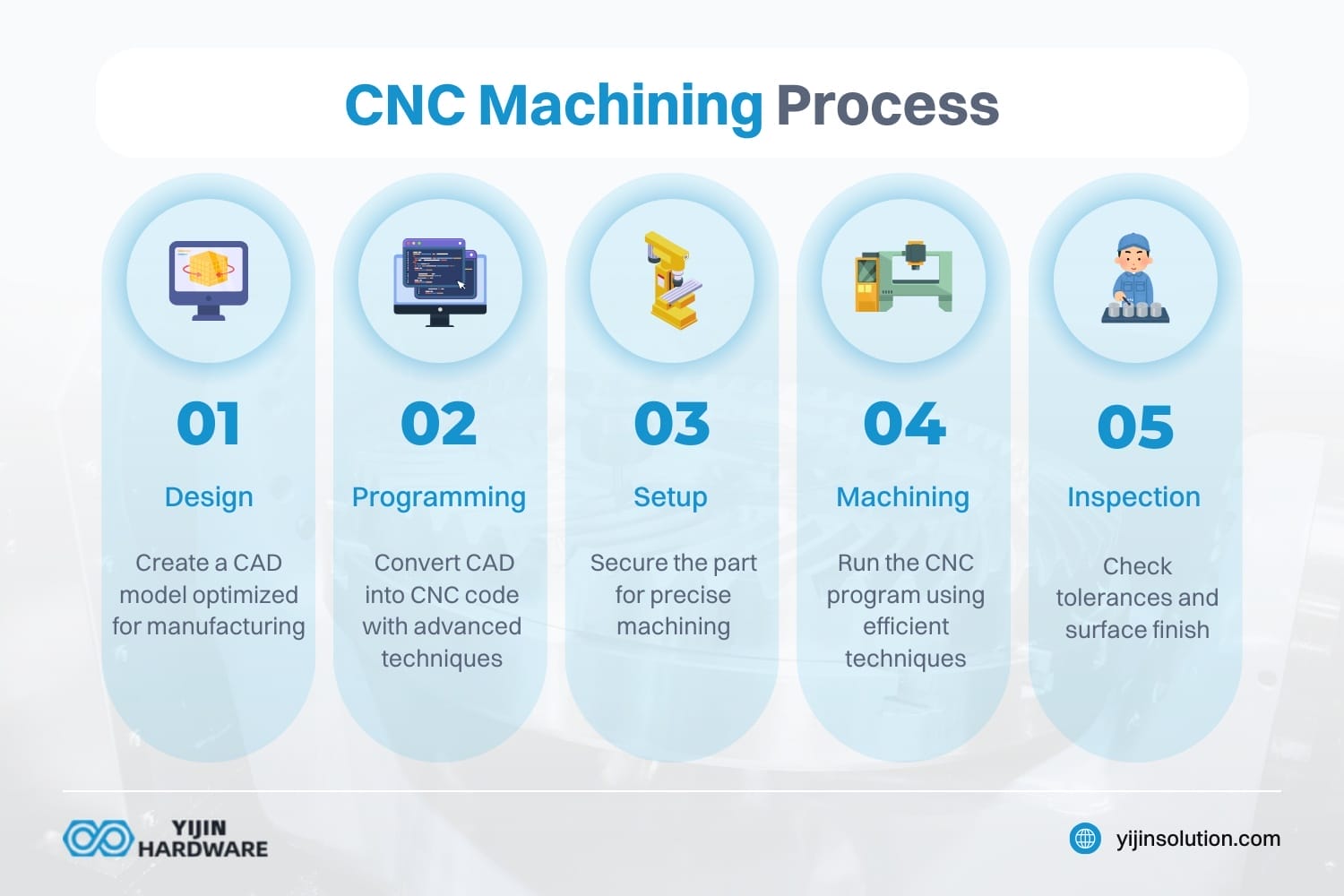
The CNC machining process begins with designing the part using CAD software. This design is then translated into G-code or M-code instructions that guide the CNC machine’s movements.
The machine tool, such as a mill or lathe, executes these instructions to remove material from the workpiece, creating the desired part. This process is highly efficient and accurate, making it suitable for producing complex CNC machining parts.
Steps in the CNC Machining Process
- Design: Create a CAD model of the part, ensuring it meets design for manufacturing criteria.
- Programming: Convert the CAD design into CNC code using cutting-edge CNC programming techniques.
- Setup: Prepare the machine and fixture to hold the part securely, ensuring precise machining.
- Machining: Execute the CNC program to machine the part, using techniques like high-speed machining for efficiency.
- Inspection: Verify the part meets specifications, including tolerance and surface finish requirements.
Machining Capabilities and Techniques
Complex CNC machining capabilities include state-of-the-art techniques like 5-axis machining and high-speed machining. These techniques allow for the precision and efficiency of the production of complex parts. Additionally, CNC technology supports various machining processes, including milling, turning, and grinding, which are essential for producing parts with complex geometries.
Advanced Machining Techniques

- 5-Axis Machining: Enables the creation of complex geometries in a single setup, reducing production time and enhancing precision.
- High-Speed Machining: Increases productivity while maintaining precision, making it ideal for high-volume production of metal parts.
- CNC Grinding: Provides a high surface finish for critical components, ensuring they meet stringent quality standards.
What Industries Benefit Most from Complex CNC Machining?
The aerospace, medical, and automotive industries benefit most from complex CNC machining. Complex CNC machining serves these industries by providing critical precision components with intricate geometries and tight tolerances, without which many products and services would be unavailable.
How does Aerospace Utilize Complex CNC Machining?
The aerospace industry represents one of the most demanding applications for complex CNC machining. Engine components like turbine blades feature intricate cooling channels, thin walls, and complex curves that can only be created using 5-axis machining. Aerospace structures often require monolithic parts machined from solid blocks to eliminate joints and fasteners, while satellite components demand the highest precision to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations from -150 °C to +150 °C.
These applications typically require machining tolerances of ±0.0005” (0.0127 mm) or better, with surface finishes as fine as 16-32 microinches Ra, often manufactured from challenging materials like titanium alloys, Inconel, and other heat-resistant super alloys.
What Medical Applications Depend on Complex CNC Machining?
The medical industry relies on complex CNC machining for devices that interact directly with the human body. Implantable devices such as orthopedic implants and cranial plates must meet stringent requirements for precision and biocompatibility. Surgical instruments with articulated ends and patient-specific cutting guides require complex geometries for specific procedures. Medical imaging and diagnostic devices rely on high-precision components with non-magnetic properties and sub-millimeter accuracy.
Which Automotive Components Require Complex CNC Machining?
The automotive industry leverages complex CNC machining for performance-critical components. Engine parts such as cylinder heads with complex port geometries directly influence power, efficiency, and emissions. Transmission components like valve bodies with intricate hydraulic circuits and differential cases require precise gear mounting surfaces. Suspension components including steering knuckles and lightweight control arms with optimized stress distribution affect vehicle handling and safety.
Automotive applications typically require tolerances of ±0.001″ (0.025mm) for critical features, with surface finishes ranging from 32-63 microinches Ra, balancing precision with the efficiency demands of high-volume production.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, complex CNC machining faces challenges like high initial investment costs and material waste. Additionally, machining delicate materials can be challenging due to the mechanical forces involved. However, advancements in CNC technology and design for manufacturing strategies help mitigate these challenges.
Overcoming Challenges
- Material Selection: Choosing materials that minimize waste and are suitable for CNC machining, such as metal and plastic.
- Design for Manufacturing: Ensuring designs are optimized for CNC production to reduce complexity and enhance precision.
At Yijin Hardware, we specialize in providing the best complex CNC machining services. Our advanced CNC systems and skilled technicians ensure high-quality parts with precision and efficiency. We use multi-axis machines to produce complex parts and components, meeting the tight tolerances required by industries like aerospace. Contact us today to see how we can meet your complex machining needs and explore the capabilities of our modern CNC machining centers.
FAQs on What are CNC Complex Machining Parts?
What is the most accurate CNC machine?
The most accurate CNC machine is widely believed to be the Kern Microtechnik, as well as wire EDM machines, which achieve ultra-precise tolerances in machining. It uses electrical discharges instead of a cutting tool, minimizing mechanical stress. High-precision machining with wire EDM is ideal for CNC machining complex parts requiring extreme accuracy. Industries like aerospace and medical rely on their precision for critical components.
What is the future of CNC machining?
The machining industry is advancing with automation, AI, and improved manufacturing processes for efficiency. Today’s CNC machines integrate laser cutting, robotics, and data analytics for precision. Smart factories will use CNC technology for fully automated production with minimal human intervention. These innovations will enhance accuracy, speed, and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing.
Is CNC machining difficult?
Learning how machining works can be challenging, but manageable with proper training and practice. A machine shop requires knowledge of CNC milling, programming, and materials. Operating a spindle and managing toolpaths demands precision and experience. Mastering CNC techniques makes complex machining tasks easier over time.
Back to Top: What is Complex CNC Machining?