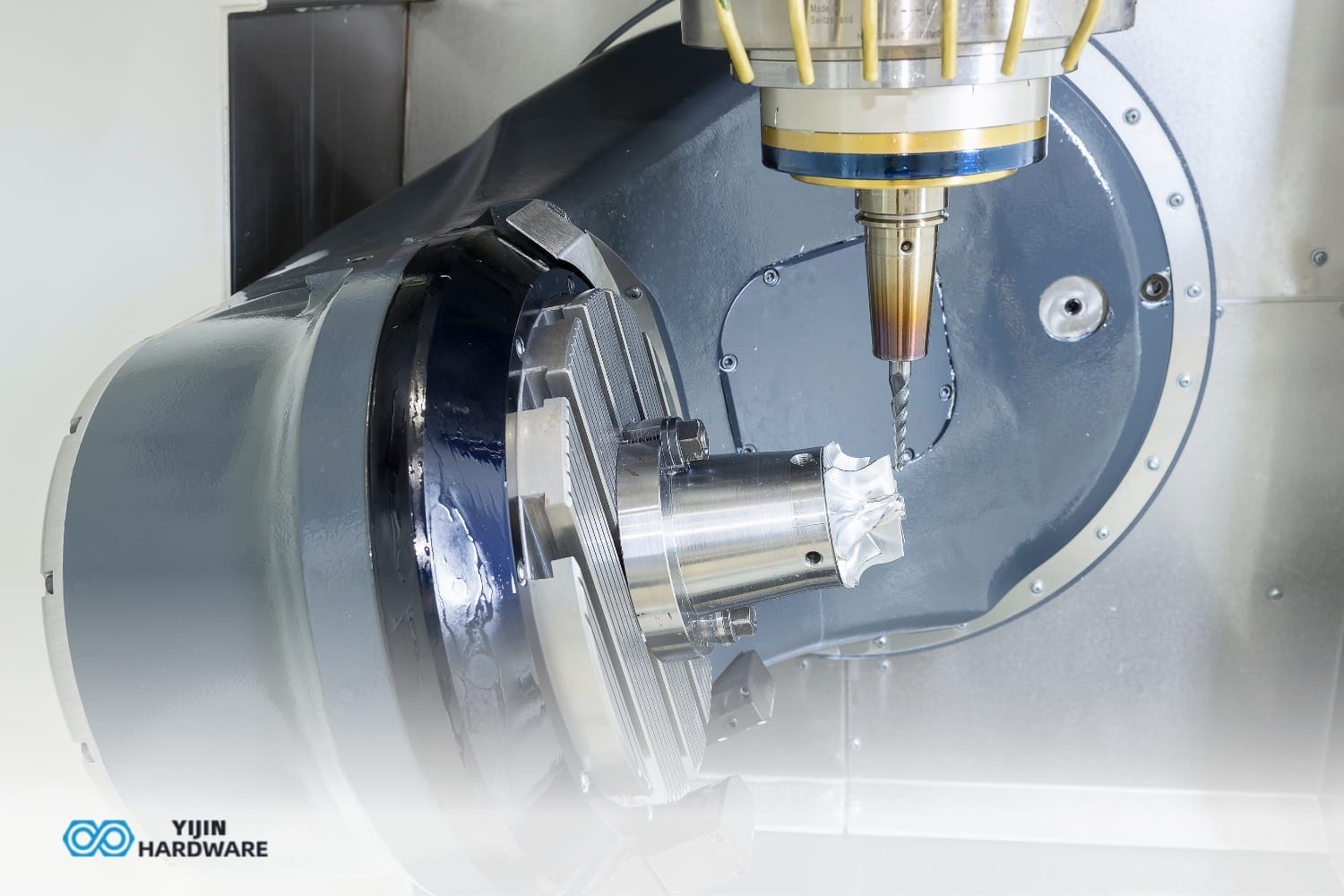
CNC machining uses computer-controlled tools to cut materials into precise shapes. It automates the manufacturing process, increasing accuracy and efficiency. CNC machines follow programmed instructions to move cutting tools and create complex parts. Yijin Hardware offers affordable CNC machining services for various industries and applications.
Key Takeaways
- CNC machining uses computer-controlled tools to cut materials.
- G-code programming directs CNC machine movements and operations.
- Common CNC machines include mills, lathes, routers, and laser cutters.
- CNC machining works with metals, plastics, wood, and other materials.
- CNC technology improves precision, consistency, and production speed.
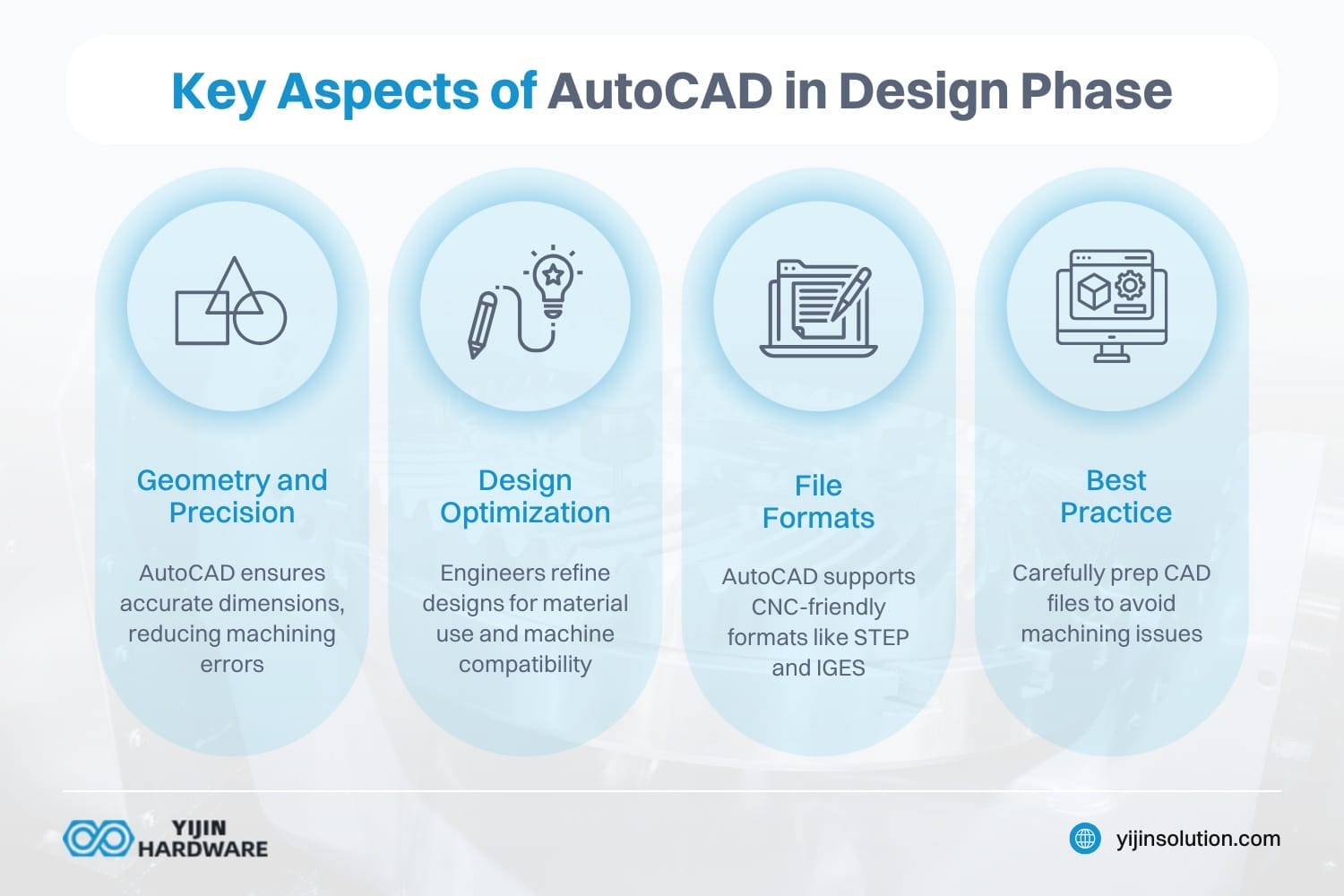
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control. It automates the movement of machine tools through programmed commands. CNC machines can perform various operations like milling, turning, and drilling. They create precise parts from a wide range of materials.
How does CNC Machining Work?
CNC machining works by following a programmed set of instructions. The process starts with a CAD model of the desired part. CAM software converts the model into a series of tool paths. These tool paths become G-code instructions for the CNC machine. The machine then executes these commands to cut the workpiece.
Components of a CNC Machine
A typical CNC machine consists of several key components, including a controller and the machine tool:
- Controller: The computer that reads G-code and directs machine movements
- Machine tool: The actual cutting device (mill, lathe, router, etc.)
- Axes: Linear and rotational directions of tool movement
- Spindle: Holds and rotates the cutting tool
- Workholding device: Secures the material being machined
- Coolant system: Reduces heat and removes chips during cutting
Types of CNC Machines

CNC technology powers various machine types, from mills to lathes. Each type specializes in different machining operations. Common CNC machines include:
CNC Mills
CNC mills use rotating cutting tools to remove material. They can create complex 3D shapes and features. Mills work well for flat surfaces, slots, and holes. 3-axis and 5-axis CNC mills offer different levels of complexity.
CNC Lathes
CNC lathes spin the workpiece while a stationary tool cuts it. They excel at creating cylindrical parts. Lathes can perform turning, facing, and threading operations. CNC turning centers combine lathe and milling capabilities.
CNC Routers
CNC routers use a spinning bit to cut softer materials. They work well for wood, plastics, and composites. Routers often have large work areas for sheet materials. They can create signs, furniture parts, and decorative items.
CNC Laser Cutters
Laser cutters use a focused beam of light to cut materials. They offer high precision for thin materials. Lasers work well for metals, plastics, and wood. They can cut intricate patterns and engrave surfaces.
CNC Programming and G-code
G-code is the standard programming language for CNC machines that tells the machine how to move and operate. G-code consists of alphanumeric commands that control:
- Tool movements and speeds
- Coolant on/off
- Tool changes
- Coordinate systems
CAM software generates G-code from CAD models. Machinists can also write and edit G-code manually. The CNC controller interprets G-code and executes machine operations.
Materials Used in CNC Machining

CNC machining works with a wide range of materials, including metals and plastics. Common choices include:
- Metals: Aluminum, steel, brass, titanium
- Plastics: ABS, nylon, acrylic, PEEK
- Wood: Hardwoods, softwoods, engineered wood
- Composites: Carbon fiber, fiberglass
Material properties affect machining parameters. Harder materials may require slower cutting speeds. Softer materials might need special workholding methods. CNC experts choose optimal tools and settings for each material.
Advantages of CNC Machining
CNC machining offers several benefits over manual methods, such as improved accuracy and consistent part quality:
- Improved accuracy and repeatability
- Faster production speeds
- Ability to create complex geometries
- Reduced human error
- Consistent part quality
- Easy replication of designs
- Flexibility to switch between parts
These advantages make CNC machining ideal for both prototypes and production runs.
Limitations of CNC Machining
While powerful, CNC machining has some limitations, including the fact that it’s not ideal for very small production runs, and it has limited abilities to create some internal features:
- High initial equipment costs
- Requires skilled programmers and operators
- Not ideal for very small production runs
- Limited ability to create certain internal features
- Can produce more material waste than additive methods
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining finds use across many industries, from aerospace to medical devices. Some common applications include:
| Industry | Example Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Engine components, structural parts |
| Automotive | Engine blocks, transmission housings |
| Medical | Implants, surgical instruments |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, chassis, molds |
| Consumer goods | Product housings, molds, prototypes |
Future Trends in CNC Technology
CNC machining continues to evolve, especially in terms of automation. According to Makera, AI can simplify CNC machining by automating complex programming, allowing users to focus on design and creativity, especially helpful for non-experts. Some emerging trends include:
- Integration with additive manufacturing
- Improved automation and lights-out production
- Use of artificial intelligence for optimization
- Development of hybrid CNC machines
- Increased focus on sustainability and efficiency
These advancements will further expand CNC capabilities and applications.
Yijin Hardware: Affordable CNC Machining Services
Yijin Hardware provides high-quality CNC machining services at competitive prices. We offer milling, turning, and multi-axis machining for various materials. Our experienced team ensures precise parts and fast turnaround times. Contact us today for a quote on your CNC machining project.
How does CNC Machining Work FAQs
How does a CNC cutting machine work?
A CNC machine’s operation begins with computer-aided design (CAD) to create a digital model. This design is converted into called G-code, which the machine can understand and execute precisely. CNC machining operations include laser cutting, plasma cutting, and CNC routing, depending on the material and required accuracy. The controlled machine follows programmed instructions to shape and cut materials with minimal error.
How does CNC milling work?
CNC milling machines remove material from a solid workpiece using rotating cutting tools. The CNC machining process utilizes computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software to convert CAD models into machine instructions. Unlike a manual machine, a milling machine operates autonomously with extreme precision. Various types of CNC cutting techniques ensure detailed and complex geometries in machine parts production.
How fast does a CNC machine work?
The speed of different CNC machines depends on the CNC controls, material, and operation type. Turning machines, CNC drilling, and milling have varied speeds based on tool cutting technology and feed rates. A CNC machine can understand and execute commands faster than any type of machine requiring manual input. The machine might use a laser beam for ultra-fast precision cutting in specific applications.
Back to Top: CNC Machining Technology Notes | A Complete Overview of How It Works

 info@yijinsolution.com
info@yijinsolution.com (+86) 188-2253-7569
(+86) 188-2253-7569