CNC machining for beginners starts with understanding this revolutionary manufacturing technology that automates the control of machine tools using computers. This advanced process creates precise, complex parts by following digital instructions, offering unmatched accuracy and repeatability compared to manual methods. For those interested in a CNC machining tutorial or considering CNC machining careers, understanding computer numerical control fundamentals is essential to harness this powerful technology.
At Yijin Hardware, we’ve helped countless clients transition from CNC novices to confident users through our comprehensive training approach.
Key Takeaways
- CNC machines follow computer-generated instructions (G-code and M-code) to precisely cut and shape materials automatically.
- The complete CNC process includes three phases: design (CAD), programming (CAM), and physical machining.
- Beginners should start with simpler 3-axis machines before advancing to complex multi-axis systems.
- Proper safety protocols and machine setup are critical for successful CNC operation.
- Learning both software fundamentals and machine operation is essential for CNC machinist training and proficiency.
What is CNC Machining and How does it Work?
CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machines to automatically cut and shape materials with extreme precision. The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system interprets digital designs and translates them into mechanical movements of cutting tools. This technology evolved from Numerical Control (NC) when computers were integrated to enhance flexibility and capability. According to Business Wire, the global CNC machines market is growing rapidly, with projections indicating a market size of USD 132.93 billion by 2030.
At its core, CNC technology works by following a set of coded instructions called G-code and M-code. These instructions guide the machine’s movements in multiple directions (axes), controlling aspects like tool position, speed, and cutting depth. The CNC programmer prepares these instructions, which the machine follows to remove material from a workpiece until the desired shape is achieved.
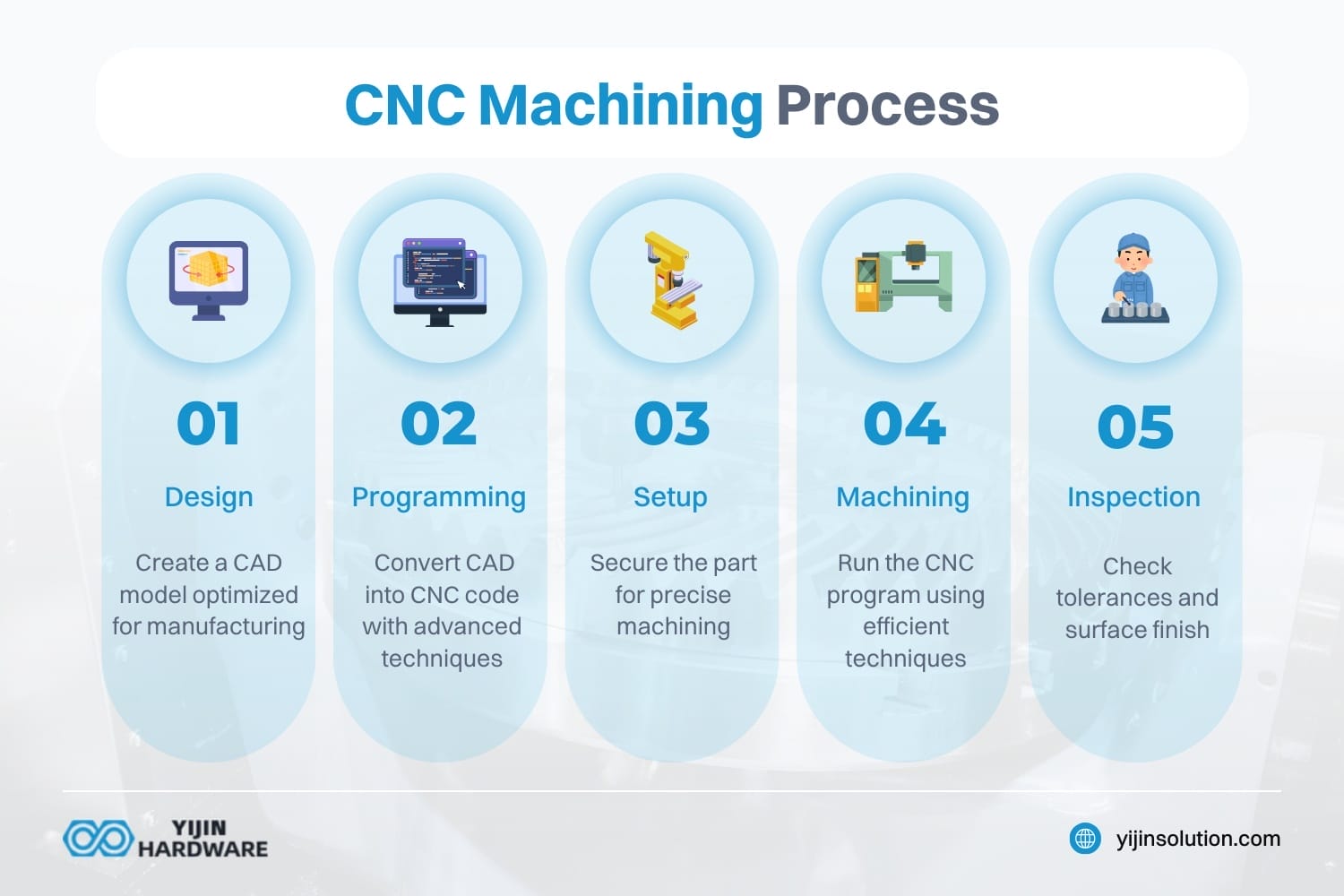
What Makes Up the Complete CNC Machining Process?
The complete CNC machining process consists of three main phases: design, programming, and physical machining. The design phase uses Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to create a digital model of the part. The programming phase employs Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software to convert the design into machine instructions (G-code). This manufacturing process requires expertise and skills to produce machined parts that meet production standards.
During the physical machining phase, the CNC machine executes these instructions to create the actual part. This involves setting up the machine, securing the workpiece, loading tools, establishing reference points, and running the program. The CNC machine operator must have an eye for detail when preparing the program and setting up tools to ensure quality production.
Key CNC Coordinate Systems
The CNC system operates using a Cartesian coordinate system (X, Y, Z axes):
- X-axis: Horizontal movement (left/right as you face the machine)
- Y-axis: Vertical movement (front/back as you face the machine)
- Z-axis: Depth movement (up/down)
- Advanced machines: Additional rotational axes (A, B, C) for complex geometries
Understanding these coordinate systems is fundamental for a CNC machinist to ensure precise measurements during the CNC machine’s operation. This knowledge allows for making necessary adjustments to achieve high accuracy in the final product.
What are the Main Types of CNC Machines for Beginners?
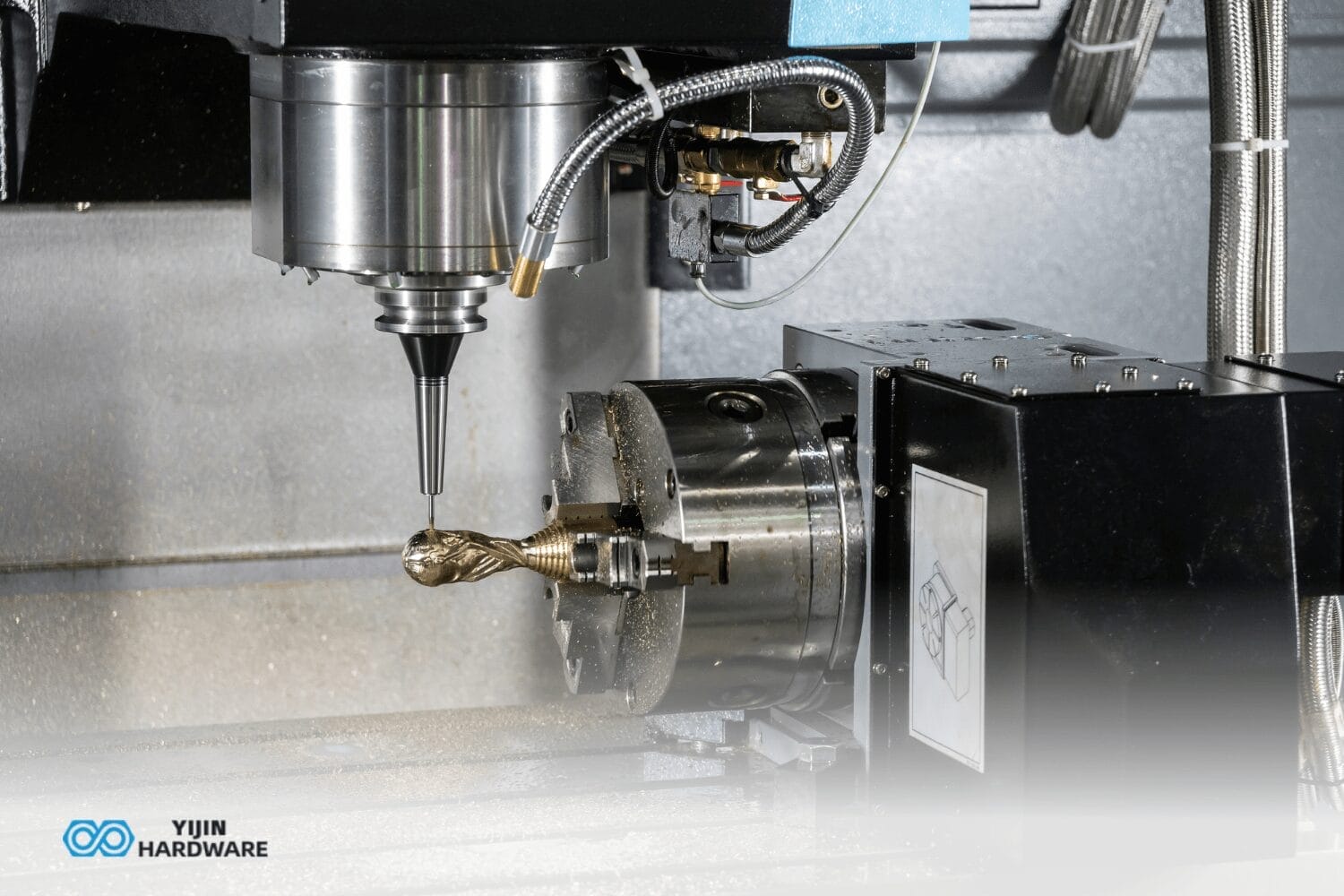
CNC mills are versatile machines that use rotating cutting tools to remove material from a stationary workpiece. These machines excel at creating complex three-dimensional shapes and are ideal for beginners due to their wide application range. Entry-level 3-axis mills move in the X, Y, and Z directions and can produce the most basic parts. The machine’s operation requires understanding milling machine tools and their capabilities.
CNC routers are similar to mills but are designed specifically for softer materials like wood, plastic, and foam. Routers typically have a larger working area but less rigidity than mills, making them perfect for sign-making, woodworking, and other light-duty applications. They’re often more affordable and accessible for hobbyists and small businesses interested in CNC equipment and CNC technology.
| Machine Type | Best For | Typical Materials | Complexity Level | Key Components |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Mill | Complex 3D shapes | Metals, plastics, wood | Moderate | Spindle, bed, column, toolholder |
| CNC Router | Large flat parts, signs | Wood, plastics, foam | Low | Gantry, spindle, bed, stepper motors |
| CNC Lathe | Cylindrical parts | Metals, plastics | Moderate-High | Headstock, tailstock, chuck, tool turret |
| Desktop CNC | Learning, small parts | Soft metals, plastics | Low | Integrated frame, controller, stepper motors |
For companies looking for reliable CNC milling China or CNC turning services, Yijin Hardware provides high-quality solutions tailored to diverse manufacturing needs.
Advanced CNC Machine Types
- Electrical Discharge Machines (EDM): Uses electrical discharges to remove material, ideal for hard metals and complex shapes
- Plasma Cutters: Employs high-velocity ionized gas to cut through conductive materials
- Waterjet Cutters: Utilize high-pressure water (often with abrasives) at around 60,000 PSI to cut various materials
What Software do you Need to Start CNC Machining?
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is essential for creating the digital models that will be machined. Beginners should consider user-friendly options like Fusion 360, which offers a free hobbyist license, or FreeCAD, which is open-source. These programs allow you to design parts with precise dimensions and specifications before sending them to a CNC machine.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software converts your CAD designs into machining instructions. This software generates toolpaths that determine how the cutting tool will move to create your part. Popular CAM options for beginners include Fusion 360 (which combines CAD and CAM), MeshCAM, and CamBam, each offering different levels of complexity and price points.
Understanding G-Code & M-Code
G-code controls geometric movements:
- G00: Rapid positioning
- G01: Linear interpolation
- G02/G03: Circular interpolation (clockwise/counterclockwise)
- G20/G21: Imperial/metric units
M-code controls machine functions:
- M03/M04: Spindle start (clockwise/counterclockwise)
- M05: Spindle stop
- M06: Tool change
- M08/M09: Coolant on/off
How do you Set Up and Operate a CNC Machine Safely?
Machine inspection is the critical first step before any CNC operation. Always check for loose components, proper lubrication, and clear debris from previous CNC machinist jobs. This preventive step ensures the machine will operate correctly and safely before you begin cutting. Machinists must stay vigilant when performing routine maintenance and making necessary adjustments.
Workpiece setup involves securely mounting your material to prevent movement during machining. Use appropriate clamps, vises, or vacuum tables depending on your material and machine type. Improper fixturing can lead to inaccurate cuts, damaged parts, or dangerous projectiles if the workpiece shifts during operation. This requires high accuracy and a focus on time management to ensure efficient production.
Critical Setup Procedure
- Machine Homing: Establish machine zero points
- Work Coordinate System (WCS): Set workpiece zero points for X, Y, and Z axes
- Tool Offsets: Measure and set tool length offsets
- Program Verification: Conduct an air cut (dry run) before actual cutting
What Common Mistakes do CNC Beginners Make?
Incorrect feed and speed settings are the most frequent mistake beginners make. Using speeds that are too fast or feeds that are too aggressive can break tools, damage your machine, or ruin your workpiece. Always research the appropriate settings for your specific material and tool combination, starting conservatively before optimizing.
Improper tool selection leads to poor results and tool breakage. Beginners often choose inappropriate cutting tools for their material or application. For example, using a wood-cutting bit on aluminum will quickly dull the tool and produce inferior results. Always match your tool to your material and the type of cut you’re making.
Preventing Machine Crashes
- Verify tool paths in simulation before running
- Check for potential collisions between tooling and fixtures
- Set software limits that prevent over-travel
- Use feed rate override control during the first runs
- Implement proper machine homing procedures
How long does it Take to Learn CNC Machining?
Basic machine operation can be learned in 2 to 4 weeks of dedicated practice through a training program. During this period, beginners can master basic setup, programming, and simple part production as a CNC operator. This foundational knowledge allows you to start creating basic parts while continuing to build new skills for your career path.
Intermediate proficiency typically requires 3 to 6 months of regular practice and project work. At this stage, you’ll understand CAD/CAM software more thoroughly, be comfortable performing routine maintenance, and produce more complex parts with multiple operations. You’ll also develop a better eye for detail and proper cutting parameters.
Recommended Skill Progression Path
- Foundation: CAD basics, simple 2D designs, machine familiarization
- Intermediate: 2.5D machining, tool selection, feeds, and speeds calculation
- Advanced: 3D contours, multi-setup operations, fixture design
- Expert: Multi-axis programming, advanced toolpath strategies, process optimization
This progression represents an ideal career path for someone interested in CNC machining careers. With proper time management and dedication to developing your career, you can experience significant career growth in the CNC machinist field. Many begin as a CNC setup operator. They do this before advancing to more specialized roles, with a higher starting average salary for a CNC machinist.
What Materials Can Beginners Work With on CNC Machines?
Soft woods like pine and poplar are ideal starter materials for CNC beginners. These materials are forgiving, inexpensive, and easy to cut with minimal tool wear. They allow new users to practice machine operation and programming concepts without significant risk or cost. Machine operators typically start with these materials when entering the field of CNC machining.
Plastics such as acrylic, HDPE, and PVC offer an excellent progression from wood. These materials machine predictably to produce clean edges when cut properly and require only slightly more advanced techniques than wood. Each plastic type has unique properties, so research specific cutting parameters for your chosen material. The manufacturing industry uses these materials extensively for prototype development.
Material-Specific Cutting Parameters
| Material | Cutting Speed (SFM) | Feed Rate Range | Tool Recommendation | Coolant Needs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pine | 500 to 800 | High | Upcut/downcut wood bits | Optional |
| Acrylic | 300 to 500 | Medium | Single flute plastic bits | Air blast |
| Aluminum 6061 | 250 to 350 | Low to Medium | 2 to 3 flute carbide endmills | Required |
What Safety Precautions are Essential for CNC Beginners?
Proper eye and ear protection are non-negotiable safety requirements when operating CNC machines. Safety glasses protect against flying chips and debris, while ear protection prevents hearing damage from the high noise levels produced during machining. These basic protective items should be worn at all times when the machine is running.
Emergency stop procedures must be thoroughly understood before operating any CNC equipment. Familiarize yourself with the location and operation of emergency stop buttons, and practice reaching them quickly. Develop the habit of having one hand near the E-stop when starting new programs or testing unfamiliar operations.
Essential Safety Checklist
- Wear proper PPE (safety glasses, hearing protection, dust mask when appropriate)
- Remove jewelry, secure loose clothing, and tie back long hair
- Understand machine limits and emergency shutdown procedures
- Maintain a clear working area around the machine
- Never bypass safety guards or door interlocks
- Keep a fire extinguisher rated for electrical fires nearby
How Can You Troubleshoot Common CNC Problems?
Poor surface finish issues are typically caused by incorrect cutting speeds, dull tools, or excessive vibration. To resolve these problems, first check that your cutting speed and feed rate match the recommended values for your material. Next, inspect your cutting tool for wear and replace it if necessary. Finally, verify that your workpiece is securely clamped to eliminate vibration.
Dimensional inaccuracies often result from improper machine calibration or tool deflection. Correct these issues by first verifying your machine’s calibration using precision measuring tools. For tool deflection problems, try taking lighter cuts, using shorter, more rigid tools, or upgrading to higher-quality cutting tools with better rigidity.
Tool breakage is usually caused by excessive cutting forces or improper tool selection. Prevent this costly problem by reducing your depth of cut and feed rate, especially in harder materials. Ensure you’re using the correct tool for your material, and verify that your tool is properly seated in the holder. Implement proper coolant or lubrication methods to extend tool life.
What’s the Best Way to Maintain Your CNC Machine?
Regular cleaning of your CNC machine prevents buildup of chips and debris that can damage moving parts. After each use, thoroughly clean all surfaces, rails, and screws using compressed air and appropriate cleaning solutions. Pay special attention to areas where chips can accumulate around ball screws and linear guides.
Proper lubrication according to the manufacturer’s schedule prevents premature wear of critical components. Most CNC machines require periodic application of specific lubricants to ball screws, linear rails, and other moving parts. Create and follow a lubrication schedule based on your machine’s manual and usage frequency.
Calibration checks help maintain machining accuracy over time. Periodically verify your machine’s positioning accuracy using dial indicators or precision blocks. Small adjustments to your controller settings can compensate for wear and maintain tight tolerances. Document all calibration activities for future reference.
Preventative Maintenance Schedule
- Daily: Clean machine surfaces, check coolant levels, and inspect the tools
- Weekly: Lubricate guide rails, check belt tensions, clean filters
- Monthly: Verify calibration, check electrical connections, and inspect the spindle
- Quarterly: Deep clean all systems, check backlash, update software
How much does it Cost to Get Started with CNC Machining?
Entry-level desktop CNC machines range from $1,000 to $5,000, making them accessible for hobbyists and small businesses. These machines typically have smaller work areas and lower power, but can produce high-quality parts in wood, plastic, and soft metals. Brands like Carbide 3D, Bantam Tools, and Millright offer reliable options in this category.
Mid-range CNC equipment costs between $5,000 and $15,000 and provides increased capabilities and durability. These machines feature larger cutting areas, more robust construction, and higher spindle power. They’re suitable for small production runs and can handle a wider range of materials, including aluminum and other metals.
Complete Startup Cost Breakdown
- Machine: $1,000-15,000 depending on size and capabilities
- Software: $0-5,000 depending on features needed
- Cutting Tools: $200-500 for a starter set
- Workholding: $100-300 for basic clamps and vises
- Materials: $100-300 for practice stock
- Safety Equipment: $50-100 for PPE
What Projects Should Beginners Start With?
Simple nameplates and signs are perfect first projects for CNC beginners. These flat designs focus on basic 2D cutting operations, helping new users master machine setup, tool changes, and basic programming without complex 3D considerations. Create personalized signs using different fonts and simple designs to build confidence.
Small household items like coasters, phone stands, or desktop organizers provide practical experience with slightly more complex designs. These projects introduce concepts like pockets, profiles, and simple 3D contours while producing useful items. They typically require only basic tools and can be completed in a single setup.
Beginner Project Progression
- 2D Profiles: Simple cutouts requiring only perimeter cuts
- Pocket Operations: Projects with internal material removal
- 2.5D Projects: Items with varying depths but vertical walls
- Simple 3D Projects: Basic contoured surfaces and shapes
- Multi-setup Jobs: Parts requiring machining from multiple sides
At Yijin Hardware, we provide top CNC machining services for custom parts and support clients at every experience level. Whether you’re just starting your new career in CNC or looking to outsource complex machining projects, our expertise ensures precision results that meet exact specifications.
With strong demand for CNC machinists in the United States and attractive permanent job prospects, CNC machining could be both a reliable 9-to-5 job and a fulfilling career.
Contact us if you’re interested in taking advantage of our CNC machining services for your next project.
Frequently Asked Questions About Working as a CNC Machinist
Is CNC machining difficult to learn for absolute beginners?
CNC machining has a moderate learning curve, but is accessible to motivated beginners with a high school diploma or equivalent education. The process involves multiple skills, including design software, programming, and machine operation, that must be learned sequentially. Most beginners can create simple parts within a few weeks of dedicated practice, though mastering advanced techniques takes months or years of experience. Machinists must stay committed to learning as CNC technology continues to evolve.
What computer specifications do I need for CNC software?
CNC software requires at minimum a modern multi-core processor (i5/Ryzen 5 or better), 8GB RAM (16GB recommended), a dedicated graphics card with 2GB VRAM, and 256GB SSD storage. CAD/CAM software is particularly demanding when working with complex 3D models. A separate computer dedicated to machine control is recommended for production environments to prevent system crashes during operation. This setup helps when you prepare the program, set up tools, and test the program before actual production.
How do I know which CNC machine is right for my needs?
The right CNC machine depends on your typical workpiece size, materials, precision requirements, and budget. Consider the working area needed for your largest parts, the power required for your hardest materials, and the precision necessary for your applications. Research machines within your budget that meet these minimum requirements, and prioritize reliability and support over maximum specifications. Understanding machine tools and their capabilities will help you make informed decisions when entering the field of CNC machining.
Back to Top: CNC Machining for Beginners | Manufacturing & Design Guide









