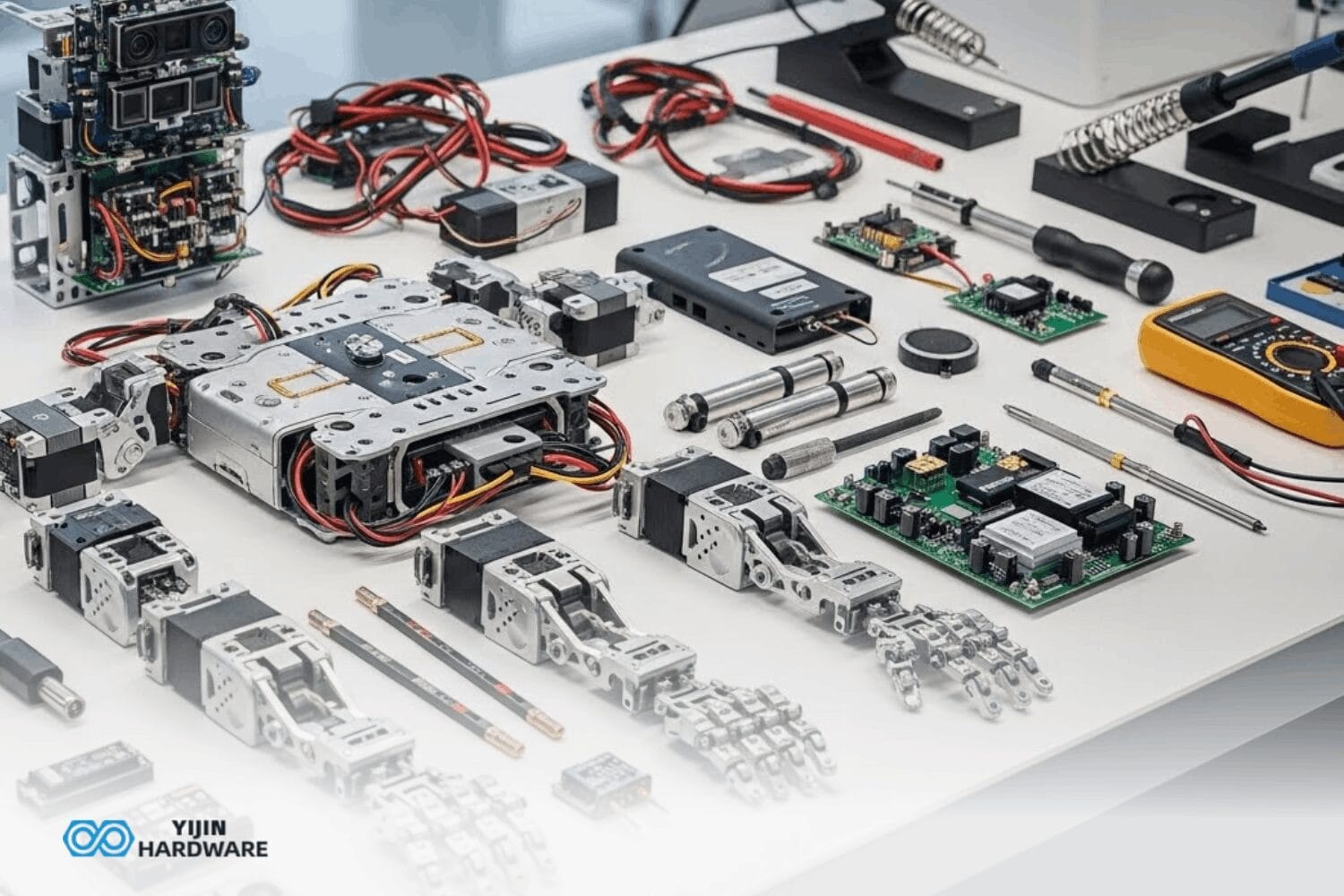
Humanoid robots aim to move and behave like humans. These machines use special body parts working together to handle cardinal, complicated jobs, whether that’s climbing stairs, picking up fragile items, or adjusting their movements based on what’s happening around them. With AI, machine learning, and increasingly sophisticated mechanical systems all moving forward together, humanoid robotics is growing faster than most people even realize.
We’re going to break down the core parts that make up a humanoid robot, what each component actually does, and how they all coordinate to produce movements that look genuinely human. Walking smoothly, gripping objects with just the right amount of force, responding to their surroundings—things that would’ve been a dream a decade back are now happening in labs and factories. Once you understand these parts, you’ll get a clearer picture of what humanoid robots can already accomplish and where this technology is headed next.
Key Takeaways
- The robot’s head contains cameras and microphones that help it understand what’s happening around it and interact properly
- Movement comes from motors (usually brushless DC types) working with actuators that control joints precisely—think of actuators as the muscles
- Walking on two legs requires sophisticated balance systems that constantly adjust to keep the robot upright, much like your inner ear does for you
- Artificial intelligence lets these robots mimic how humans behave, learn from what they experience, and handle situations they haven’t seen before
- Builders typically use titanium and aluminum for the frame—strong enough to support movement but light enough that the robot isn’t lugging around unnecessary weight
What Makes Up a Humanoid Robot?
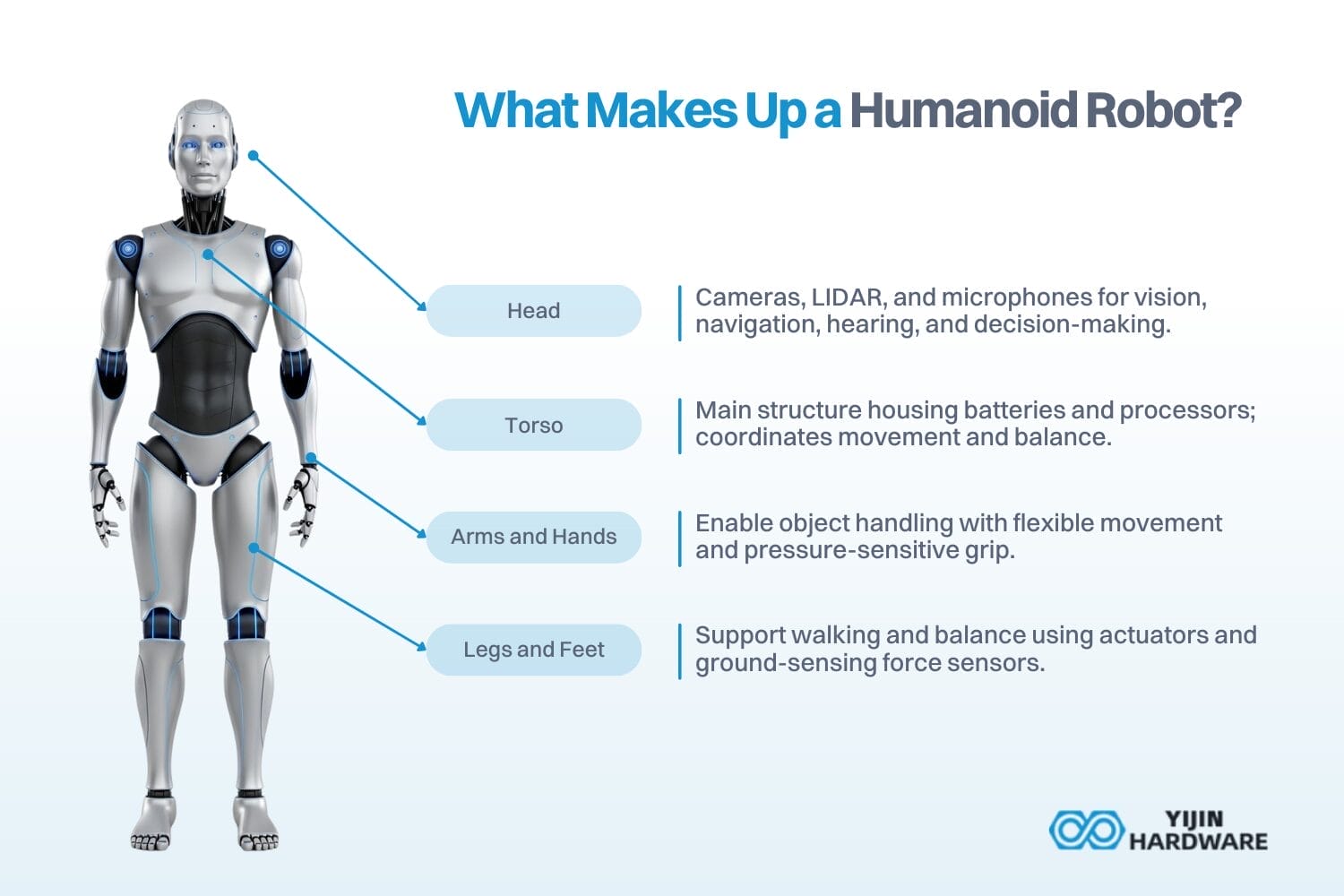
A humanoid robot is built from several key components that work together to create movement and interaction that resemble human capabilities. Yijin Hardware works diligently to make the production of these humanoid parts possible. Here’s what these machines are made of:
- Head: Contains cameras, LIDAR sensors, and microphones that let the robot see, map its surroundings, and hear what’s happening. These sensors help it recognize faces, navigate spaces, and interact naturally with people. The head also processes environmental input so the robot can make autonomous decisions about what to do next.
- Torso: Acts as the central structure, housing essential systems like batteries, control units, and processors. It supports the arms, legs, and head whilst maintaining balance and serving as the coordination center for all movement throughout the robot’s body.
- Arms and Hands: Give the robot the ability to grab objects and interact physically with its environment. The arms typically move with about 7 degrees of freedom (meaning they can rotate and position themselves in multiple directions), whilst the hands use force and tactile sensors to grip things with appropriate pressure—delicate enough for an egg, strong enough for a tool.
- Legs and Feet: Enable the robot to walk on two legs like humans do. These limbs use hydraulic or pneumatic actuators (pressurized systems that create movement) to walk, run, and even jump. Force sensors in the feet constantly monitor pressure and contact with the ground, helping maintain balance during movement.
Internal Breakdown of Tesla Optimus: Core Components
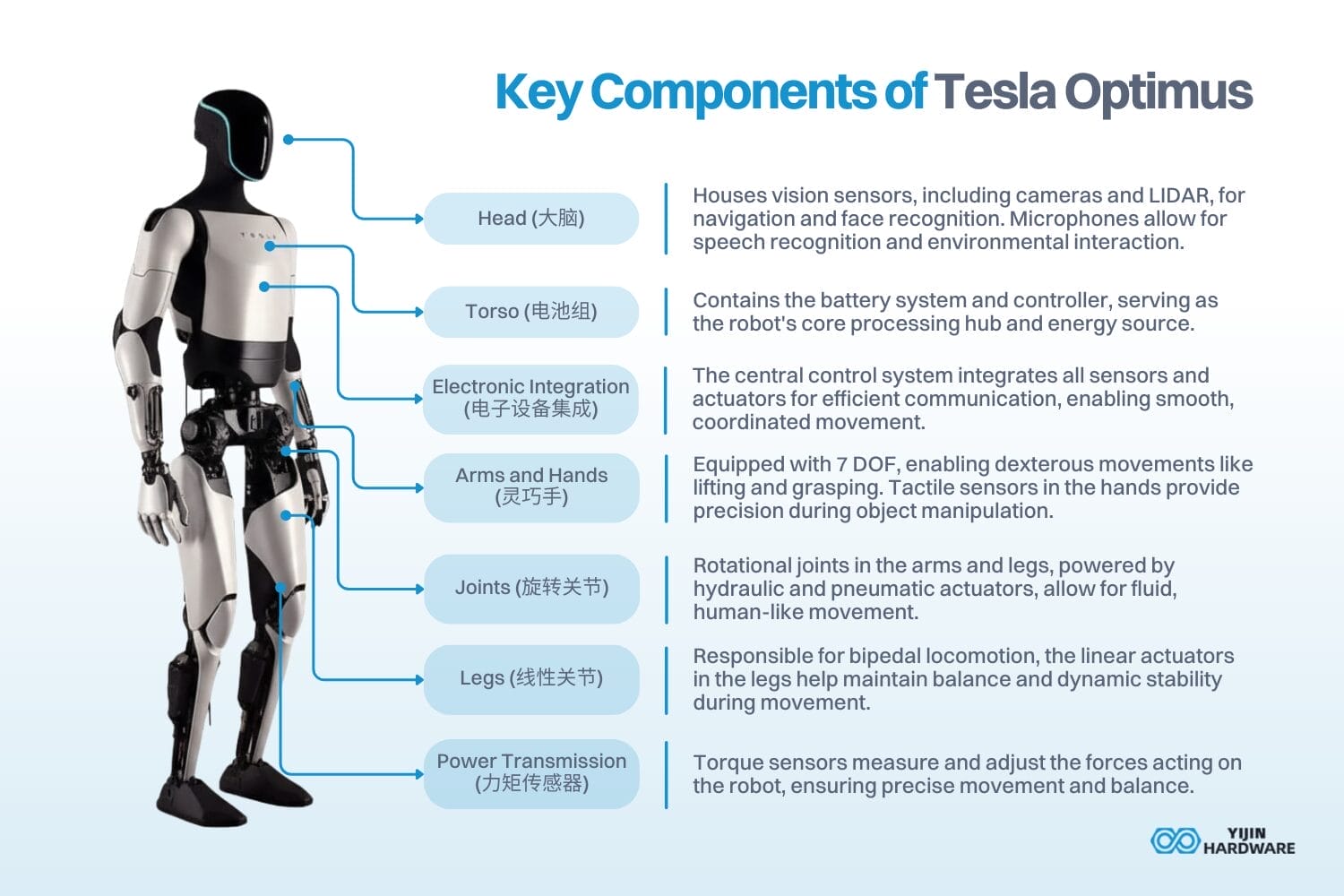
Tesla’s Optimus humanoid robot is made up of key components that enable it to perform human-like tasks. The diagram below highlights these essential parts:
Key Components of Tesla Optimus:
- Head (大脑): Houses vision sensors, including cameras and LIDAR, for navigation and face recognition. Microphones allow for speech recognition and environmental interaction.
- Torso (电池组): Contains the battery system and controller, serving as the robot’s core processing hub and energy source.
- Arms and Hands (灵巧手): Equipped with 7 DOF, enabling dexterous movements like lifting and grasping. Tactile sensors in the hands provide precision during object manipulation.
- Joints (旋转关节): Rotational joints in the arms and legs, powered by hydraulic and pneumatic actuators, allow for fluid, human-like movement.
- Legs (线性关节): Responsible for bipedal locomotion, the linear actuators in the legs help maintain balance and dynamic stability during movement.
- Power Transmission (力矩传感器): Torque sensors measure and adjust the forces acting on the robot, ensuring precise movement and balance.
- Electronic Integration (电子设备集成): The central control system integrates all sensors and actuators for efficient communication, enabling smooth, coordinated movement.
The Tesla Optimus robot’s ability to simulate human behavior and perform tasks comes from the integration of these advanced components, powered by AI and robotic control systems.
What Role do Motors Play in Humanoid Robots?
Motors are essential in humanoid robots for powering their movements. Different types of motors are used depending on the task requirements:
- BLDC Motors: These brushless DC motors provide high efficiency and precision. They are used in various robot joints and actuation systems, ensuring smooth and quiet motion with minimal maintenance.
- Servo Motors: Used for precise control, servo motors allow the robot to make small, accurate adjustments to its movements. These motors are vital for tasks requiring high precision, such as robotic arm manipulation.
- Frameless Torque Motors: These motors are compact and efficient, providing high torque with low inertia. They are often used in robotic joints, where space is limited but high precision and strength are needed.
Motor Comparison for Humanoid Robots
| Motor Type | Key Features | Application |
|---|---|---|
| BLDC Motors | Long lifespan, low maintenance, high precision | General movement and actuators |
| Servo Motors | Closed-loop control, precise positioning | Joint movement and fine manipulation |
| Frameless Torque Motors | High torque density, compact design | Robot joints requiring high precision and strength |
These motors, in conjunction with actuators, ensure that humanoid robots can perform a wide range of movements, from simple tasks to complex actions.
How do Sensors Enable Humanoid Robots to Interact with the Environment?
Sensors are critical to a humanoid robot’s ability to perceive and interact with the world. These sensors are classified into two types:
- Proprioceptive Sensors: These internal sensors track the robot’s own movements. Accelerometers and gyroscopes help the robot understand its orientation and adjust its position accordingly. Force sensors measure the forces exerted on the robot’s joints, aiding in precise movement and dynamic balance.
- Exteroceptive Sensors: These sensors allow the robot to perceive its surroundings. Vision sensors (like cameras and LIDAR) help detect obstacles, recognize faces, and navigate the environment. Microphones enable speech recognition, allowing the robot to understand and respond to human commands.
Together, these sensors form the backbone of the robot’s ability to interact with humans and adapt to its surroundings.
How do Actuators Contribute to Movement and Precision?
Actuators are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, enabling a humanoid robot to perform tasks such as walking, grasping, and manipulating objects. There are several types of actuators used in humanoid robots:
- Electric Actuators: Found in BLDC motors and servo motors, these actuators provide high precision and control, making them ideal for delicate tasks like manipulating small objects.
- Hydraulic Actuators: These actuators provide high torque, making them suitable for tasks requiring strength, such as lifting heavy objects or performing complex tasks.
- Pneumatic Actuators: These actuators are often used for tasks that require flexibility, such as simulating muscles and joints in a soft robot.
By choosing the right actuator type, humanoid robots can achieve the necessary balance between strength and precision for various applications.
How do Humanoid Robots Achieve Bipedal Walking and Balance?
Bipedal locomotion is one of the most complex movements humanoid robots can perform. To achieve this, robots rely on a combination of advanced control systems, sensors, and actuators. The key components involved in walking and balance are:
- Leg Joints: Humanoid robots use 3 DOF at the hip, 1-2 DOF at the knee, and 2 DOF at the ankle to simulate human-like leg movement. These joints allow the robot to adjust its posture and walk smoothly.
- Balance Control: Zero Moment Point (ZMP) control is used to ensure stability during movement. This system keeps the robot’s center of gravity within a stable region, preventing it from falling over.
- Foot Sensors: Force sensors in the feet help track the robot’s interaction with the ground, adjusting its movement and ensuring stable walking.
These technologies enable humanoid robots to perform bipedal walking while maintaining dynamic balance in diverse environments.
What Materials are Used in Humanoid Robots?
The materials used in humanoid robots are crucial to ensuring they are lightweight, strong, and durable. Common materials include:
- Aluminum: Lightweight and strong, ideal for the robot’s frame and moving parts.
- Titanium: Often used in joints and parts that require extra strength and durability.
- Carbon Fiber: Provides strength without the added weight, making it perfect for robotic limbs and moving parts.
These materials ensure that the humanoid robot is capable of withstanding the mechanical stress of movement while maintaining energy efficiency.
The Future of Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are complex machines that combine advanced robotics, AI, and cutting-edge engineering. Their body parts, including motors, actuators, and sensors, work together to enable tasks that closely mimic human movement. As technologies like machine learning, AI, and hydraulic actuators continue to improve, the capabilities of humanoid robots will expand.
In industries like automation, robotics launches, and human-robot interaction, humanoid robots are set to revolutionize workflows, assist human workers, and tackle complex tasks. With advancements in AI and sensors, these robots will continue to evolve, performing even more human-like tasks with increasing dexterity and precision. Yijin Hardware provides premium humanoid robot body parts; contact us to learn more.
Humanoid Robot Body Parts FAQs
What is the body structure of a robot?
The body structure of a robot includes its head, torso, arms, legs, and feet. The torso houses the robot’s internal systems, like controllers and batteries, while the arms and legs allow movement. Sensors help with perception, and actuators enable fine motor skills.
What are the 4 D’s of robotics?
The four D’s of robotics are Dull, Dirty, Dangerous, and Dear. These represent the tasks robots are best suited to handle: repetitive (Dull), hazardous (Dirty and Dangerous), and high-cost (Dear), improving safety and efficiency in these areas.
What is the 5th law of robotics?
The 5th law of robotics is often referred to as the “Law of Ethics”: A robot should act in the best interest of humans, considering the greater good. This law emphasizes ethical decision-making in robots as they become integrated into human environments.
Back to Top: Humanoid Robot Body Parts