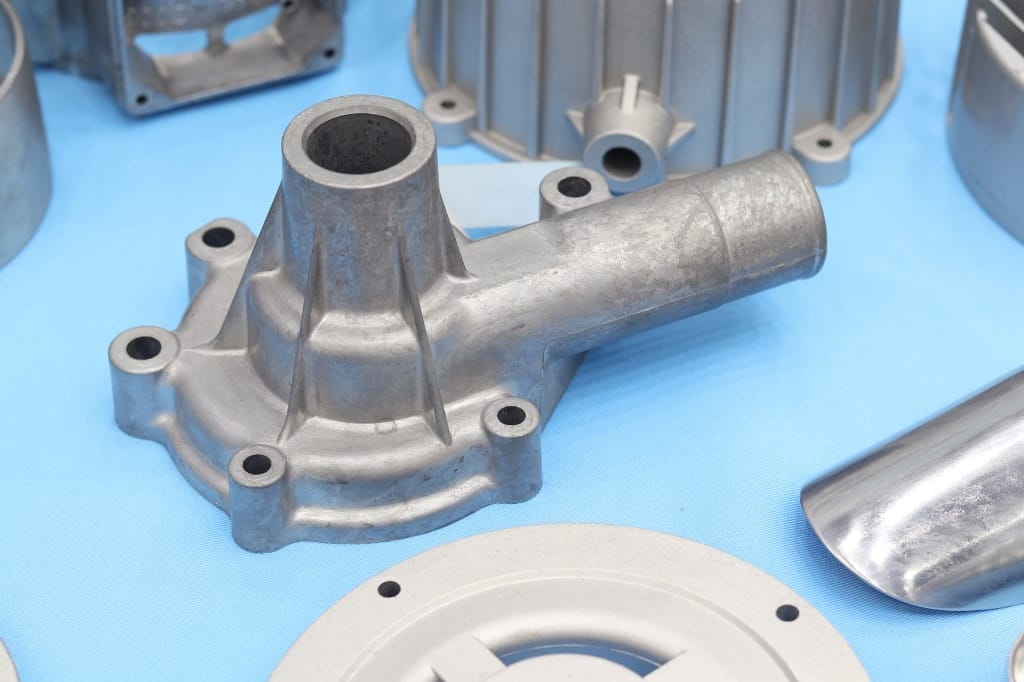
Understanding the difference between additive manufacturing and CNC machining is crucial for anyone involved in modern production methods. CNC machining is a subtractive process that removes material from a solid block to create parts, while additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer from nothing. These manufacturing processes serve different needs based on design complexity, material requirements, and production volumes.
At Yijin Hardware, we specialize in providing top-quality CNC machining services for custom parts while staying informed about all manufacturing technologies. The key difference between AM and CNC machining affects which approach will best suit your specific project requirements, whether you’re working with a simple 2D drawing or complex 3D model.
Key Takeaways
- CNC machining achieves tolerances as precise as ±0.005 mm, making it ideal for high-precision components
- Additive manufacturing enables complex geometries impossible with traditional machining operations
- Material waste in CNC can reach 90%, while additive manufacturing creates minimal waste limited to support structures
- The global additive manufacturing market is growing at 23.3% CAGR through 2030 according to Grand View Research
- Your product design requirements should determine whether to use CNC machining and additive manufacturing techniques
What are CNC Machining and Additive Manufacturing?
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that removes material from a solid block using computer-controlled cutting tools. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, builds parts layer by layer by adding material based on a digital model. These two methods represent opposite approaches to manufacturing—one removes material to create parts, while the other adds material.
A CNC machine emerged in the 1950s as computers became more advanced, while additive manufacturing appeared much later, with the first 3D printing technology patented in 1984. According to Statista, 3D manufacturing was once used only as a tool for prototyping.
Both technologies have evolved significantly, with computer numerical control remaining the standard for precision parts and additive manufacturing growing beyond its initial prototyping applications. There are also multiple types of CNC machining, such as lathes and routers, making it a helpful option for mass production and diverse projects.
Historical Development Timeline
| Era | CNC | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-1950s | Manual machining with early automation | Non-existent |
| 1950s-1960s | First machine developed | Non-existent |
| 1970s-1980s | CNC becomes industry standard | First stereolithography patent (1984) |
| 1990s-2000s | Multi-axis CNC milling emerges | Early commercial 3D printers |
| 2010s-Present | Advanced CNC with simulation | Industrial AM adoption across sectors |
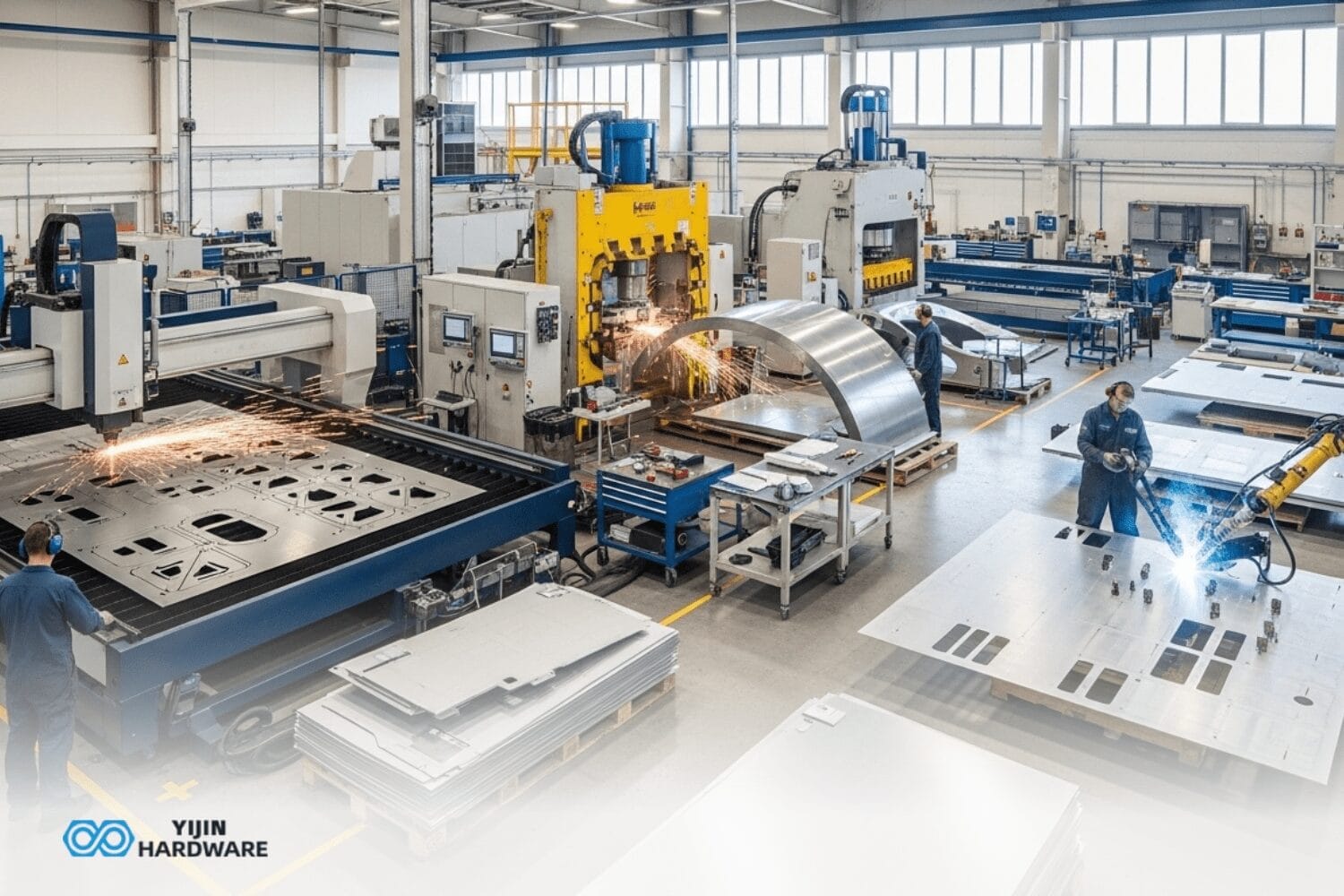
How does CNC Machining Work?
CNC machining works by using computer-aided manufacturing to automate cutting tools that remove material until the desired shape remains. The process begins with computer-aided design (CAD) software like AutoCAD or Autodesk Fusion 360, which is used to create the initial design. This CAD file is then processed through CAM software to generate G-code, the programming language that guides the cutting tool along precise paths.
The CNC machining process involves several steps: design creation, programming, setup, machining, and finishing. Modern CNC machinery can operate with minimal human intervention once programmed, making them excellent for consistent, repeatable results. Various CNC techniques work with a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, wood, and composites.
CNC Machining Process Steps
- Design creation: Part designed using CAD software
- CAM programming: Tool paths are generated and converted to G-code output of the CAM
- Machine setup: Material fixturing and cutting tool selection
- Machining operations: Automated material removal by the mill
- Quality inspection: Verification of geometry and tolerances
- Finishing processes: Deburring, polishing, heat treatment as needed
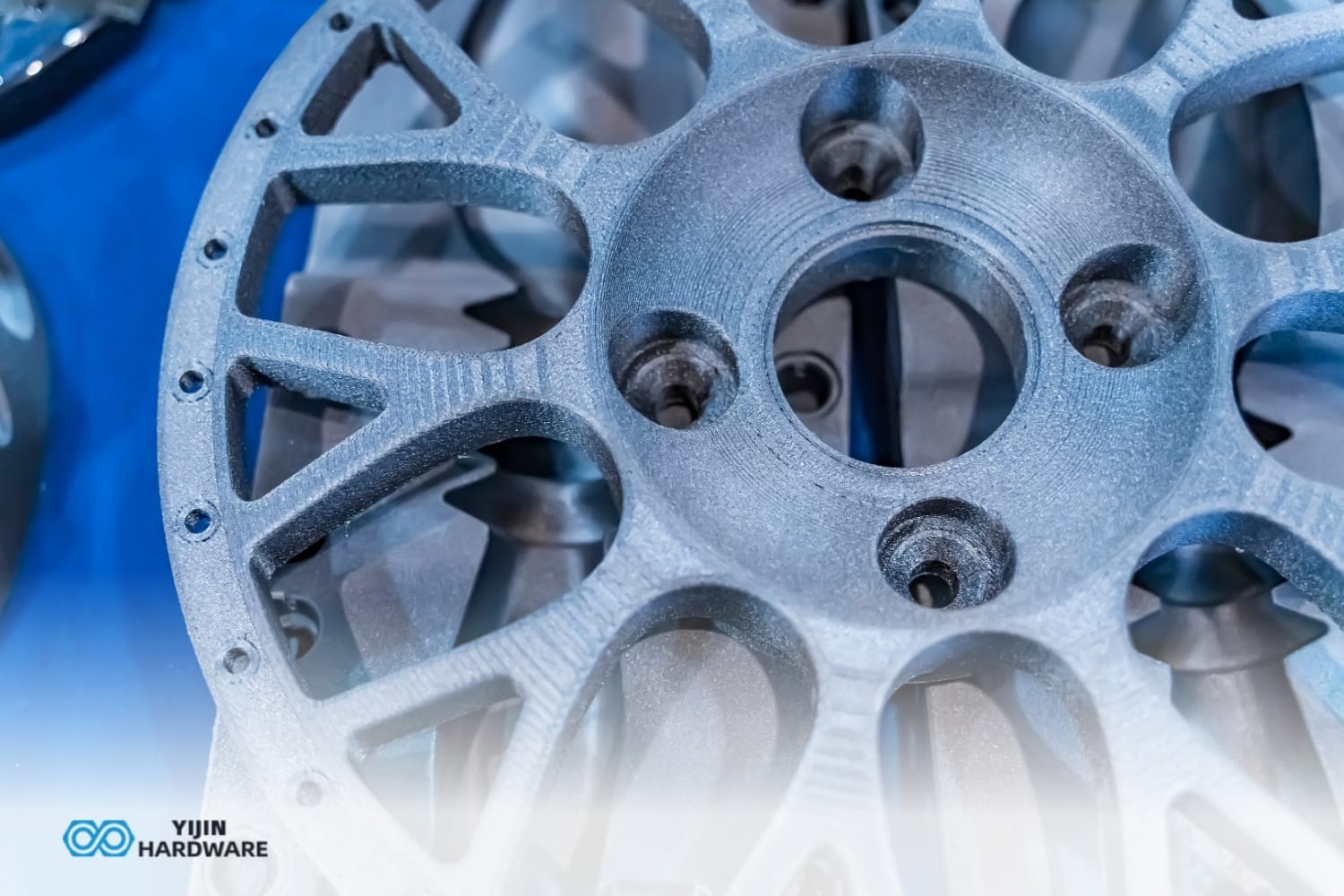
How does Additive Manufacturing Work?
Additive manufacturing works by building parts layer by layer using various technologies that solidify material according to a 3D CAD file. The process of creating starts with a 3D model that gets “sliced” into thin horizontal layers by specialized software programs. The 3D printer then creates the object by depositing or solidifying material one layer at a time.
Several additive technologies exist, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), which extrudes melted plastic filament; Stereolithography (SLA), which uses light to cure liquid resin; and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), which fuses powder materials with lasers. File formats used in CNC machining are step and IGES, which are also commonly used for additive manufacturing, making it easier to switch between processes.
Common Additive Manufacturing Technologies
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Thermoplastic filament extrusion
- SLA (Stereolithography): Liquid photopolymer curing with UV light
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Powder fusion using lasers
- DMLS/LPBF (Direct Metal Laser Sintering/Laser Powder Bed Fusion): Metal powder fusion
- Binder Jetting: Liquid binding agent deposited onto powder bed
What are the Key Differences Between Additive Manufacturing and CNC Machining?
The key differences between additive manufacturing and CNC machining involve precision, material use, design capabilities, and production economics. CNC machined parts achieve tolerances as precise as ±0.005 mm with excellent surface finish, while additive manufacturing typically produces rougher surfaces with layer thicknesses between 0.1-0.5 mm. These fundamental differences affect when each technology should be used.
| Parameter | CNC Machining | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Subtractive | Additive |
| Precision | High (±0.005 mm) | Moderate (0.1 to 0.5 mm layers) |
| Material Waste | High (up to 90%) | Minimal |
| Design Complexity | Limited by tool access | Virtually unlimited |
| Production Speed | Fast for simple parts | Fast for complex parts |
CNC machining preserves material properties better than additive methods, making it ideal for parts that need consistent mechanical performance. Additive manufacturing enables complex internal geometries, organic shapes, and lattice structures that would be impossible to create with a machining center or even 5-axis machines.
Industry-Specific Applications
Different industries leverage CNC machining and additive manufacturing based on their unique requirements. According to a study published in the Journal of Manufacturing Technology, aerospace companies increasingly use both technologies in complementary ways, with AM for complex internal structures and CNC for precision mating surfaces.
Aerospace Applications
The aerospace industry uses additive manufacturing for lightweight components with complex internal structures. According to research from NASA’s Advanced Manufacturing Initiative, topology-optimized brackets produced through metal AM can reduce weight by up to 30% compared to traditional designs while maintaining structural integrity. CNC machining remains essential for high-precision components like turbine blades where tolerances must be within microns.
Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical device manufacturers utilize additive manufacturing for patient-specific implants and surgical guides. According to data from the Medical Device Manufacturing Association, over 100,000 3D-printed titanium implants have been implanted worldwide, with a success rate comparable to traditional manufacturing methods. CNC machining is still preferred for surgical instruments requiring extreme precision and reliability.
Automotive Industry Applications
The automotive industry employs both technologies strategically. Formula 1 racing teams use additive manufacturing for rapid prototyping and production of complex components like conformal cooling channels in tooling. Traditional automakers primarily use CNC machining for high-volume production parts but are increasingly incorporating AM for specialized low-volume components where complex geometries offer performance advantages.
How can these Manufacturing Methods Work Together in Hybrid Approaches?
Hybrid manufacturing combines additive and subtractive processes to maximize benefits while minimizing limitations. According to research from the Additive Manufacturing Research Center, hybrid approaches reduce overall production costs by up to 25% compared to using either method exclusively.
Integrated Hybrid Systems
Modern integrated hybrid systems combine additive and subtractive capabilities in a single machine. These systems can deposit material and then machine critical surfaces in the same setup, maintaining precise alignment between processes. According to manufacturing technology provider DMG MORI, their LASERTEC 65 3D hybrid system reduces overall production time by up to 40% for complex components compared to separate AM and CNC operations.
Sequential Hybrid Processing
More common than integrated systems is sequential processing, where parts are first created using additive manufacturing and then finished with CNC machining. Aerospace manufacturer Pratt & Whitney uses this approach for turbine components, achieving both complex internal geometries and precision external surfaces. This method is particularly effective for components that would be impossible to machine conventionally but require high precision in specific areas.
Case Study: Injection Mold Tooling
A particularly effective hybrid application is in injection mold tooling. According to the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, conformal cooling channels created through additive manufacturing and then finished with CNC machining can reduce cooling time by up to 60% and improve part quality by eliminating hot spots. This approach combines AM’s ability to create complex internal geometries with CNC’s precision for mating surfaces.
Economic Factors and Cost Models
Understanding the economics of both manufacturing methods is crucial for making informed decisions. According to manufacturing economist Dr. Eric Cunningham, “The cost crossover point between these technologies is shifting as both continue to evolve.”
Detailed Cost Structure Comparison
| Cost Factor | CNC Machining | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment | $50,000-$500,000 | $5,000-$1,000,000 |
| Material | Low-moderate | High (3-10× raw material) |
| Setup/Programming | High initial cost | Low initial cost |
| Labor | Moderate-high | Low-moderate |
| Energy | Moderate | High for metal AM |
| Per-Part Scaling | Improves with volume | Remains relatively constant |
Volume-Based Cost Model
Research from the Journal of Manufacturing Systems provides a generalized cost model for decision-making:
For simple geometries:
- 1 to 10 units: AM often more economical
- 10 to 100 units: Crossover point (varies by complexity)
- 100+ units: CNC typically more economical
For complex geometries:
- 1 to 50 units: AM typically more economical
- 50 to 500 units: Evaluate case-by-case
- 500+ units: Consider investment casting or other methods
According to manufacturing economist Dr. Sarah Martinez, “The economic advantage of additive manufacturing expands as design complexity increases, while CNC maintains advantages for simpler geometries and higher volumes.”
When Should You Choose CNC Machining?
You should choose CNC machining when precision, material properties, and surface finish are critical requirements for your project. CNC machining is the superior choice for parts that need tight tolerances, excellent structural integrity, and consistent mechanical properties. This method delivers superior results when working with specific CNC applications like aerospace components or medical devices.
CNC machining becomes increasingly cost-effective as production volume increases, since initial setup and machine time costs are distributed across more parts. For high-volume production runs, CNC machining typically offers better unit economics than additive manufacturing. The process is also generally faster for larger parts with simpler geometries.
Projects that require already optimized design for CNC machining often benefit from this approach, as it works with a wide range of engineering-grade materials with well-documented properties. Many CNC processes are ideal for industries including aerospace, automotive, and medical, where performance and reliability cannot be compromised.
When Should You Choose Additive Manufacturing?
You should choose additive manufacturing when your design doesn’t conform to traditional manufacturing limitations. Additive manufacturing excels at producing intricate parts that would require multiple CNC operations or be entirely unfeasible with traditional machining methods. The freedom to create complex designs without additional cost is a significant advantage of using CAD models directly from the 3D CAD environment.
Additive manufacturing is particularly valuable for low-volume production or rapid prototyping where tooling costs would be prohibitive. When you need just a few parts or want to test multiple design iterations quickly, 3D printing offers faster turnaround without the setup time required for CNC machining systems. This technology allows for rapid design changes without significant cost penalties.
Projects requiring weight optimization through internal lattice structures or consolidated assemblies benefit greatly from additive manufacturing capabilities. Even if your design seems simple, the best practice is to export it to proper file formats and evaluate whether additive methods might provide advantages for your specific CNC order.
Yijin Hardware | Efficient CNC Machining Solutions
The choice between CNC machining and additive manufacturing depends on your specific project requirements including design complexity, material needs, production volume, and mechanical specifications. CNC machining delivers superior precision and surface finish for high-volume production, while additive manufacturing enables complex designs, and is often more economical for low-volume or highly customized parts.
At Yijin Hardware, we specialize in providing top-quality CNC machining services for custom parts to meet your exact specifications. Our expertise helps clients navigate manufacturing decisions to achieve optimal results in terms of quality, cost, and production time. Whether you need technical drawings for CNC manufacturing or assistance with CAD to production in less time, contact us to help you make the best choice for your project.
CNC Machining vs. Additive Manufacturing FAQs
How do lead times compare between CNC machining and additive manufacturing?
Lead times for CNC machining typically increase with part complexity due to additional setups and programming requirements. Simple parts can be machined quickly, but complex geometries may require extensive preparation and multiple operations. The lead time is primarily affected by design complexity, material availability, and machine settings.
Additive manufacturing lead times primarily depend on build volume and height rather than geometric complexity. A complex part takes approximately the same time to print as a simple part of similar size. This fundamental difference makes additive manufacturing advantageous for rapid prototyping of complex designs.
What is the future outlook for these manufacturing technologies?
The global additive manufacturing market is experiencing rapid growth, expected to expand at a CAGR of 23.3% from 2023 to 2030 according to Grand View Research. This growth reflects increasing adoption across industries and continual technological advancements. The market size was valued at USD 20.37 billion in 2023 and is predicted to surpass USD 125.94 billion by 2034 according to Precedence Research.
CNC machining continues to evolve with advancements in multi-axis capabilities, automation, and integration with digital workflows. Modern CNC technology, including base software improvements and CNC cam innovations, remains the backbone of precision manufacturing and will continue to be essential for high-volume production and precision components across industries.
How are environmental impacts compared between these manufacturing methods?
According to a life-cycle assessment study published in the Journal of Cleaner Production, additive manufacturing typically produces 25-30% less carbon emissions compared to CNC machining for complex parts. This advantage comes primarily from reduced material waste, with CNC machining sometimes wasting up to 90% of the original material block for complex geometries.
Energy consumption varies significantly between processes. Metal additive manufacturing using laser powder bed fusion consumes approximately 50 to 100 kWh per kg of material processed, while CNC machining averages 7 to 10 kWh per kg of final part weight, according to the International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology. However, when considering the entire life cycle including material production, the gap narrows significantly.
Back to Top: CNC Machining vs Additive Manufacturing