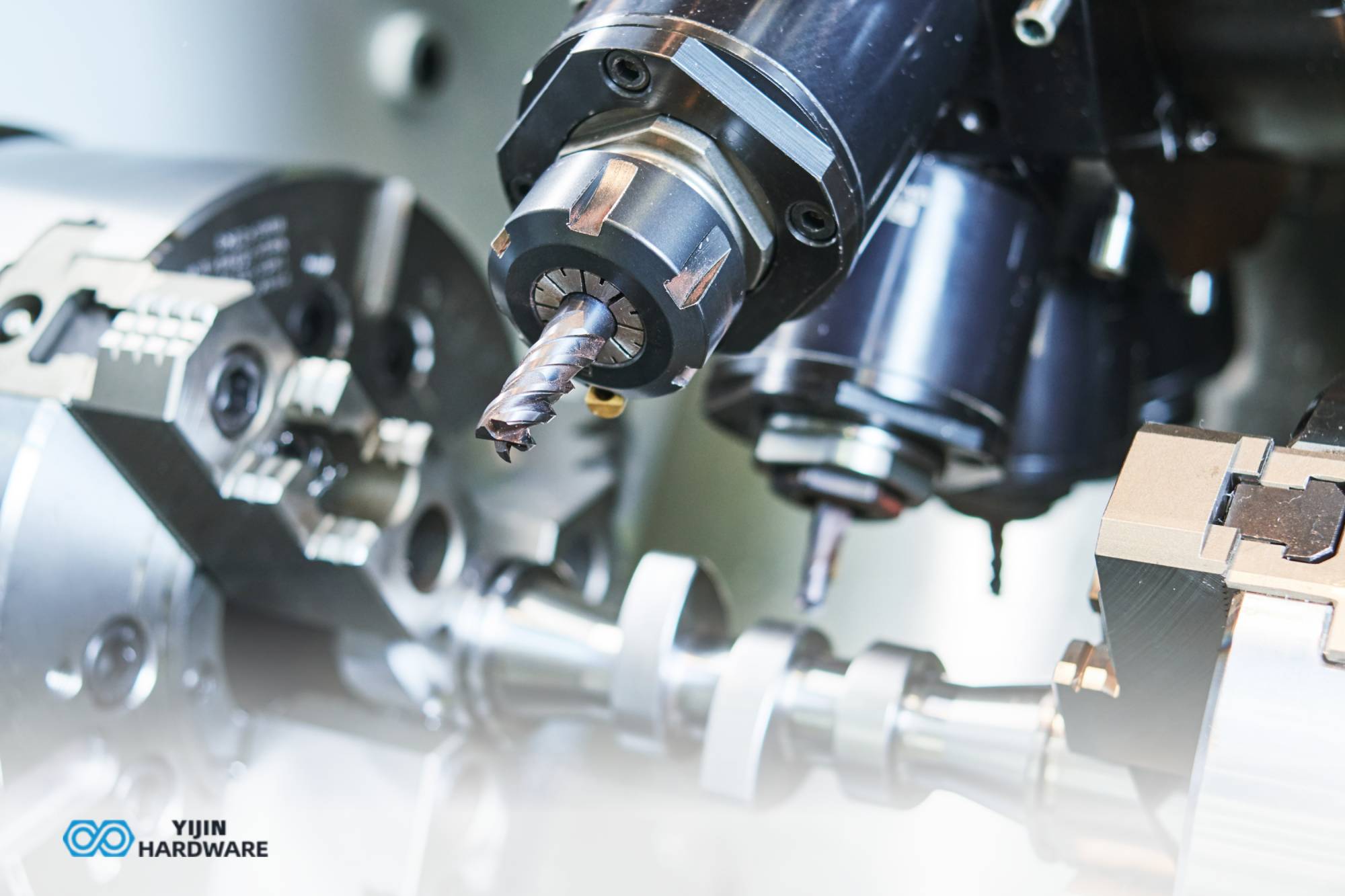
Micro CNC machining is a specialized manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control (CNC) technology to create incredibly small and precise components, often measuring in the micrometer range. This advanced technique is essential for producing intricate microcomponents for various industries, including aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
As the demand for smaller, more complex parts increases, CNC micro machining companies like Yijin Hardware are significant, providing high-quality micro machining services that meet stringent tolerances and surface finish requirements.
Key Takeaways
- Micro CNC machining creates extremely small components with high precision.
- It uses advanced CNC machines designed for intricate geometries and tight tolerances.
- Various methods, such as micro milling and micro EDM, are employed in the machining process.
- Industries like aerospace and medical devices heavily rely on micro machining for their products.
- Yijin Hardware is highly experienced in precision micro machining, ensuring quality and accuracy.
What is Micro CNC Machining?
Micro CNC machining is the process of using CNC machines to manufacture tiny parts with unparalleled precision. This technology removes material from a workpiece to create complex shapes and features often required in high-tech applications. The level of precision is crucial, as tolerances are typically measured in micrometers. This capability makes CNC micromachining indispensable in sectors where accuracy is paramount.
Micro Machining System Components
The system components of micro CNC machining include several important elements, like CNC machines, complex software, and cutting tools, that all work together to produce high-quality micro parts:
- CNC Machines: These machines have advanced software and hardware designed specifically for micromachining. They can control the movement of tools with extreme accuracy.
- Cutting Tools: Micro tools perform various operations such as milling and drilling. These tools are designed to handle intricate geometries and ensure a smooth surface finish.
- Spindle: The spindle is an important component that rotates the cutting tool at high RPMs, allowing for efficient material removal. The speed and stability of the spindle directly affect the quality of the finished part.
- Tool Path Software: This software controls the movement of the cutting tool along a predetermined path, ensuring that each operation is executed with micro precision and consistency.
How does Micro CNC Machining Work?
Micro CNC precision machining operates by following a series of programmed instructions that control how a cutting tool interacts with the workpiece:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Design | Create a 3D model of the desired part using CAD software |
| 2. Conversion | Convert the CAD design into a CNC-compatible format |
| 3. Setup | Mount the workpiece securely on the machine bed |
| 4. Tool Selection | Choose appropriate micro tools suited for the part’s complexity |
| 5. Machining | Cutting tool moves along specified tool paths at controlled speeds (RPM) with precision manufacturing to remove material from the workpiece and shape the part |
| 6. Quality Control | After machining, inspect finished parts to confirm they meet required tolerances and surface quality |
This process allows for high-speed machining of intricate parts while maintaining tight tolerances, precision, and quality.
The Methods of Micro Machining

Micro machining uses various techniques tailored to specific applications:
- Micro Milling is a process that uses small cutters to remove material from a workpiece to create complex geometries.
- Grinding is used to achieve smooth surface finishes on tiny parts; it involves abrasive wheels that grind away material.
- Turning involves rotating cylindrical parts against a cutting tool to achieve precise dimensions.
- Ultrasonic Machining uses high-frequency vibrations to assist in cutting hard materials; it’s highly effective for intricate designs.
- Drilling uses micro drills to create small holes in components; this is essential for electronic devices and medical applications.
- Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) uses electrical discharges to remove material; ideal for creating complex shapes in hard materials.
- Thermal Machining includes techniques like laser beam machining that use heat to cut or engrave materials.
- Electron Beam Machining is a highly precise method using focused beams of electrons to remove material at an atomic level; it’s suitable for ultra-fine details.
Each method has its unique advantages and is selected based on factors like material type, desired finish, and complexity of the part.
What are Chemical and Electrochemical Micro Machining?
Chemical and electrochemical micro machining use chemical reactions to remove material from a workpiece at a microscopic level.
- Chemical Machining: This method uses chemicals to etch away material without mechanical force, allowing for intricate designs without physical stress on delicate components.
- Electrochemical Machining (ECM): In ECM, an electric current facilitates material removal from conductive materials through anodic dissolution. This technique is particularly effective for creating complex shapes while maintaining excellent surface quality.
Both methods are valuable in applications requiring precision without compromising the integrity of sensitive materials.
Materials Compatible with Micro CNC Machining
Micro CNC machining can work with various materials, including metals, ceramics, and plastics, making it versatile across multiple industries:
- Metals: Aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and other alloys are commonly micro machined due to their strength and durability.
- Plastics: High-performance plastics like PEEK and PTFE are used in medical devices due to their biocompatibility.
- Ceramics: Advanced ceramics can be machined for applications requiring high wear resistance or thermal stability.
Choosing the right material depends on the specific requirements of the application, including mechanical properties and environmental resistance.
Micromachining Applications and Industries
Micro CNC machining offers applications across the aerospace, medical device, and electronics industries:
- Aerospace Industry: Precision parts such as brackets and connectors require tight tolerances due to safety standards.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Intricate components like surgical instruments and implants benefit from micro precision to ensure functionality and safety.
- Electronics Industries: Tiny components such as connectors, housings, and circuit boards rely on micro machining for effective performance.
The Difference Between Micro Machining vs. Conventional Machining
The main difference between micro machining and conventional machining lies in scale and precision:
- Size: Micro machining focuses on extremely small parts, often less than 1 mm in size, whereas conventional machining typically deals with larger components.
- Precision Levels: Micro machining gets smaller and more precise tolerances measured in micrometers (µm), as precision is absolutely essential for micro CNC machining. In contrast, conventional methods may have tolerances measured in millimeters (mm).
This difference means that while conventional machining is suitable for general manufacturing needs, micro machining is essential for specialized applications demanding high levels of detail and accuracy.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High precision for intricate, tight-tolerance components | High initial setup costs for specialized equipment |
| Versatile with metals, plastics, and ceramics | Requires skilled operators and programming expertise |
| Enables complex geometries unachievable with traditional methods |
The Advantages of Micromachining
Micromachining offers several major benefits, including accuracy, material versatility, and the ability to execute highly sophisticated designs:
- High Precision: Capable of producing intricate components with tight tolerances essential for critical applications.
- Material Versatility: Can machine various materials including metals, plastics, and ceramics without compromising quality.
- Complex Geometries: Allows manufacturers to create parts with intricate designs that would be impossible or impractical with traditional methods.
The Limitations of Micro CNC Machining
Micro CNC machining also has limitations, which primarily revolve around cost and technical expertise:
- Cost: Initial setup costs can be high due to the specialized equipment required for micromachining operations.
- Technical Expertise Required: Operating advanced CNC machines requires skilled personnel familiar with both programming and handling delicate tools.
These challenges can make it difficult for some companies to adopt this technology fully but investing in training and equipment can mitigate these issues over time.
Yijin Hardware: Highly Skilled CNC Micro Machining Company
Yijin Hardware distinguishes itself as a highly skilled provider of micro CNC machining and micro-milling services. With expertise in precision manufacturing technology, we offer top-of-the-line quality in producing intricate micro components tailored to meet specific industry needs. If you’re looking to leverage advanced micromachining capabilities in your projects or products, contact us today!
FAQs on What is Micro CNC Machining?
What is an example of micromachining?
Microfluidicslike organs-on-chips (OOCs) are produced using micro machining. Micro machining uses laser-based processes to create precise, small-scale components for applications of micro electronics. This technique is also common in the automotive industry for detailed part manufacturing.
What are the classifications of micro manufacturing processes?
Micro manufacturing processes are classified as subtractive (like micro CNC machining), additive, or forming methods. Using micro processes, industries achieve high precision essential for advanced electronics and medical devices.
What is the tool life of a micro CNC machine?
The actual tool life for a micro CNC machine can vary, often ranging between 1 and 100 hours. The tool life in micro CNC machining is crucial and typically depends on factors like RPM spindle speed and material hardness. Proper maintenance and controlled parameters can extend tool life significantly, ensuring machining is critical for manufacturing quality.
Back to Top: What is Micro CNC Machining?

 info@yijinsolution.com
info@yijinsolution.com (+86) 188-2253-7569
(+86) 188-2253-7569