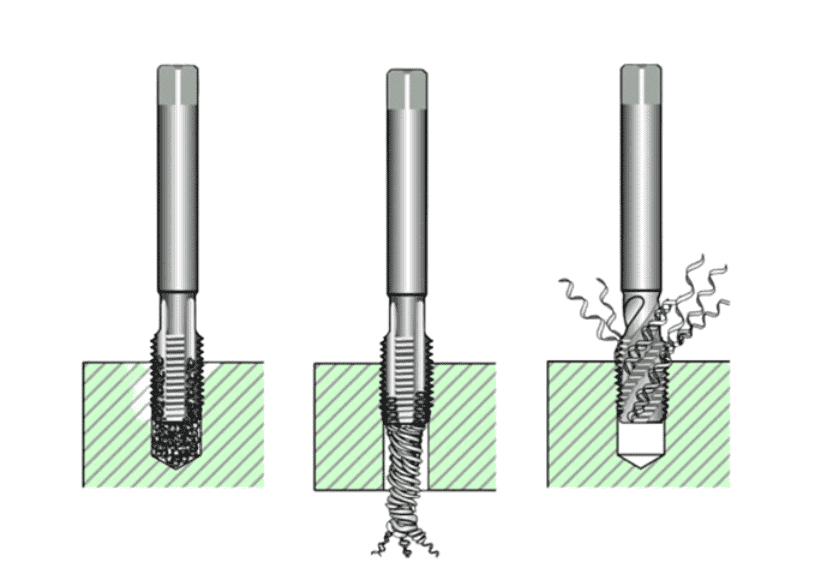
What is CNC Roughing in CNC Machining?
CNC Roughing is the initial stage of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, focused on quickly removing excess material from a workpiece to create a rough shape close to the final design. Using robust tools like end mills or roughing mills, the process prioritizes speed and efficiency over precision. Guided by a CNC program, the cutting tool operates at high speeds and feeds to maximize material removal while maintaining tool durability. 
Key Points:
- The goal is to remove material as quickly as possible while leaving enough stock for subsequent operations.
- Depending on the complexity of the part and the material being machined, the process may require multiple passes.
- Each pass removes a set amount of material, progressively reducing the stock to the desired level.
- The CNC program determines the tool path and cutting parameters to optimize efficiency and accuracy.
- Roughing helps relieve internal stresses in the workpiece, minimizing the risk of deformation during later machining.
- Ensures sufficient material remains for achieving the final product’s dimensions and surface finish.
The Key Objectives of Roughing Are:
- Material removal: Roughing removes the majority of the excess material, transforming the raw workpiece into a shape that closely resembles the final part.
- Time efficiency: Roughing aims to be fast, removing material at high speeds to reduce overall machining time.
- Tool longevity: Roughing involves using more robust tools that can withstand the high cutting forces generated during material removal.
Roughing typically utilizes larger cutting tools with fewer flutes (cutting edges) to accommodate higher chip loads and facilitate efficient material removal. Cutting parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut are usually adjusted to higher levels during roughing to optimize material removal rates. 
CNC Roughing Process
There are several significant factors to consider for the CNC roughing process. Roughing is the technique of swiftly and efficiently removing large amounts of material to produce the required shape and size of the item before proceeding to the finishing procedures. When roughing in machining, there are several important things to consider.
- Material Removal Rate: The fundamental goal of roughing is to remove the material as rapidly as possible. As a result, optimizing the material removal rate while preserving process stability is critical. If we need to achieve efficient chip evacuation and reduce cutting time then we need to select the correct cutting parameters, such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut.
- Tool Selection: Choosing the right cutting tool is crucial for roughing operations. Typically, roughing involves the use of solid carbide or high-speed steel (HSS) end mills, roughing end mills, or indexable milling cutters. The tool should be capable of withstanding the high cutting forces and provide adequate rigidity and heat resistance.
- Cutting Parameters: Selecting appropriate cutting parameters is essential for successful roughing. The cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut should be balanced to ensure efficient material removal while avoiding excessive tool wear or breakage. Depending on the material being machined, machine capability, and equipment, optimal parameters may differ.
- Chip Control: Effective chip control is necessary to prevent chip clogging, tool damage, and poor surface finish. Proper chip evacuation can be achieved by selecting appropriate cutting parameters, using chip breakers on the cutting tool, employing coolant or lubrication, and employing chip evacuation methods such as through-tool coolant or chip conveyors.
- Tool Life and Cost: Roughing operations can be demanding on cutting tools due to the high material removal rates involved. Balancing tool life and cost is essential. It may be more cost-effective to use cheaper or less durable tooling for roughing operations, reserving high-performance tools for finishing operations where surface finish and dimensional accuracy are critical.
By considering these factors, manufacturers can optimize the roughing process, reduce machining time, minimize tool wear, and achieve the desired part shape efficiently, setting the stage for subsequent finishing operations. 
Differences between Roughing and Finishing
| Parameter | Roughing | Finishing |
| Goal | The rough pass’s goal is to remove the majority of excess material from the workpiece in each pass. | The goal of the finish pass is to increase surface quality, dimensional accuracy, and tolerance. |
| Feed Rate | Higher feed rate | Very low feed rate |
| Material Removal Rate | The material removal rate (MRR) is high. | The material removal rate (MRR) is low. |
| Surface Finish | Surface roughness increases following a harsh pass, resulting in a poor surface finish. | Surface roughness is low after the finish pass, indicating that the surface finish is good. |
| Dimensional Accuracy | It is not capable of providing great dimensional accuracy and close tolerance. | It has the ability to deliver great dimensional precision and close tolerance. |

 info@yijinsolution.com
info@yijinsolution.com (+86) 188-2253-7569
(+86) 188-2253-7569