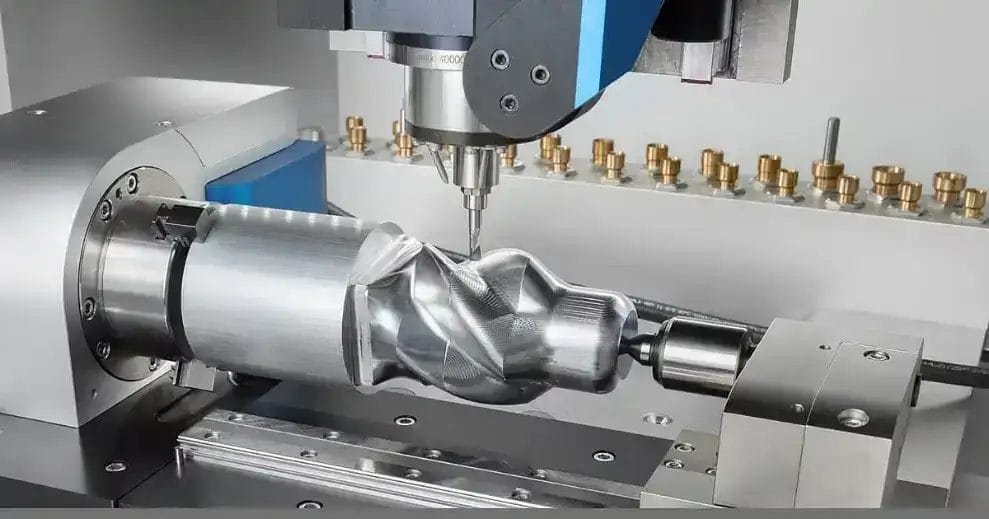
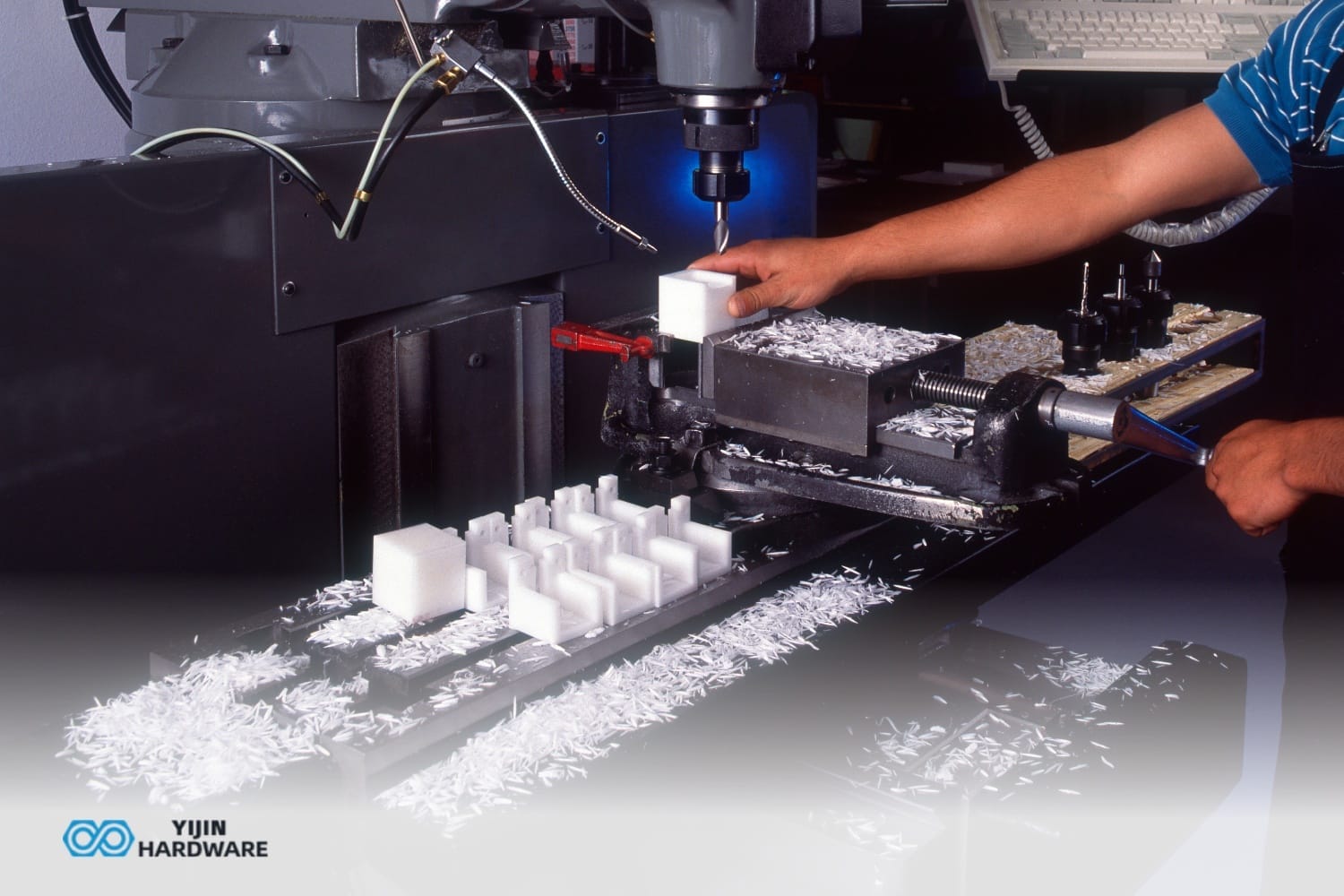
CNC machining keeps getting more advanced. The latest 4 axis CNC capabilities now allow contouring complex 3D shapes in one setup. 4-axis CNC enables more complex geometries and effective machining by allowing movements along four different axes.
This blog-post covers what 4 axis CNC machining is, its key benefits, differences between 3, 4 and 5 axis CNC machining, and ideal uses for 4 axis machining.
What is 4 Axis CNC Machining?
- axis CNC machining utilizes Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology to make intricate parts. Unlike 3-axis CNC machines (which move along X, Y and Z axes), 4-axis machines add an extra rotational A-axis. This provides greater flexibility in machining operations.
The A-axis enables workpiece rotation around X-axis. This rotational capability allows production of more complex geometries than their 3-axis counterparts. Comparing 4 axis and 5 axis CNC machining, 5-axis incorporates two additional rotational axes (B and C) for even more complexity.
A typical 4-axis CNC machine has a spindle, table, control unit and rotary A-axis. The spindle holds cutting tool and moves along X, Y and Z axes. The table supports workpiece . The control unit, which is equipped with computer software, coordinates the machine’s precise movements. Adding A-axis to traditional three axis facilitates various machining operations. These operations include milling, drilling and turning.
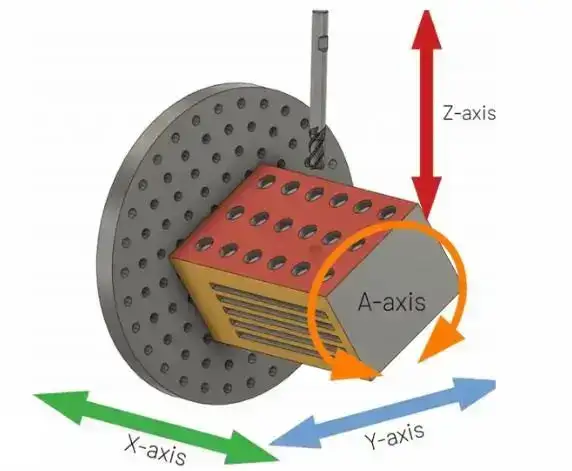
When looking at 3 vs 4 vs 5 axis cnc machining, it’s vital to understand operational mechanics of each setup. In 4-axis machining, A-axis works with X, Y and Z axes to create more intricate designs and features. Software critically controls machine movements to ensure accuracy and precision throughout machining process.
You May Also Like:
CNC Machining 101 For Beginners
Advantages and Disadvantages of 4-Axis Machining
4-axis CNC machining has some several advantages over 3-axis machining, but a couple downsides to consider too. Let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of this cutting-edge manufacturing technique.
Advantages of 4-Axis CNC Machining
- Makes parts more precise and accurate.
- Allows complex shapes with intricate details that were not possible with 3-axis.
- Reduces production time by needing fewer setups.
- Can work on multiple sides of a part without repositioning.
- More efficient and cost-effective for high volume productions.
- Better surface finishes due to closer proximity of cutting tools to the workpiece.
- Less need for manual intervention.
Disadvantages of 4-Axis CNC Machining
- Machines and maintenance cost more than 3-axis, including ongoing costs.
- Programming and operation gets more complicated with fourth (A) axis.
- Limited in some geometries compared to 5-axis machines.
- Needs operators with advanced training.
- Machines take up more space.
4-Axis CNC Machining Process
Making something with 4-axis CNC machining involves several key steps, from early design to finished product:
CAD Modeling
Engineers first make a 3D model in CAD software. This virtual model matches desired shape and size of real part. It also shows all necessary features and dimensions. When done, CAD file gets converted to a format, like G-code, that CNC machine understands.
CAM Programming
Next, CAM software takes CAD model and creates toolpath – instructions that show cutting tool movements relative to workpiece. Toolpath optimizes machining efficiency based on things like cutting speeds, feed rates and tool selection.
Machine Setup
Now 4-axis CNC machine gets prepared for the actual machining work. This means installing fixtures, tools, and loading up workpiece.
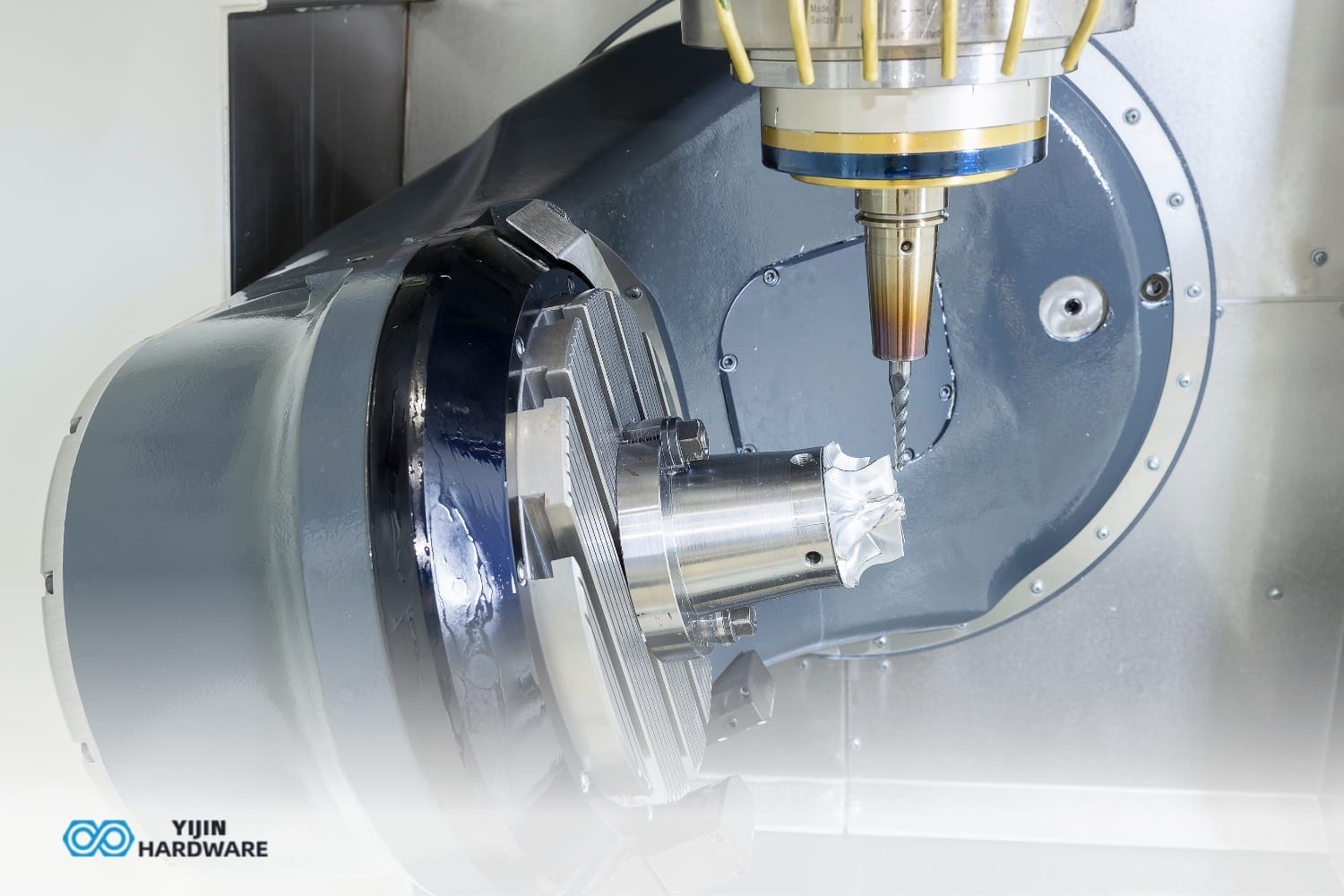
Machining
The A-axis rotation capability is what sets 4-axis CNC apart. It rotates workpiece around X-axis so cutting tool can access multiple sides without repositioning. Machine follows programmed toolpath, removing material from workpiece. Process gets monitored and adjusted as needed.
Finishing
After machining, part is cleaned, deburred and finished to achieve desired surface finish.
3 Types of 4-Axis CNC Machines
Many types of 4-axis CNC machines exist, each having unique abilities for different uses.
Milling Machines
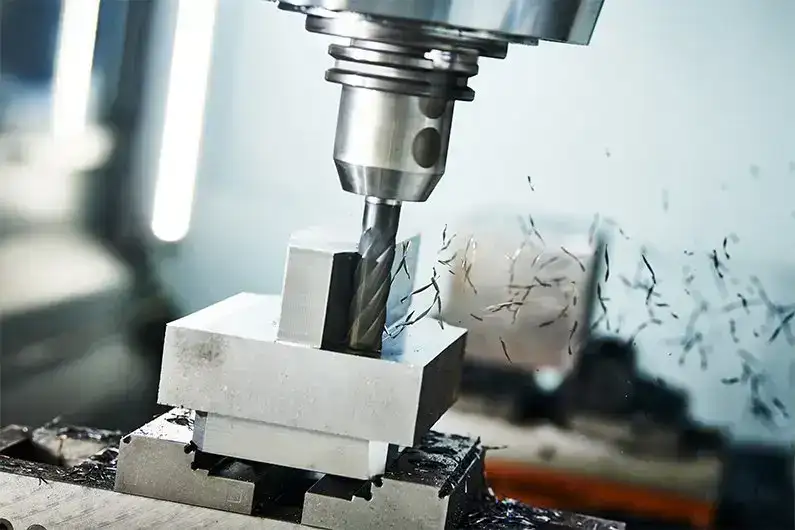

These are perhaps the most commonly used 4-axis CNC machines. They excellently create intricate parts with angled cuts and holes. The additional A-axis lets the cutting tool approach the workpiece at an angle, allowing it to mill slots and holes however needed.
Lathes
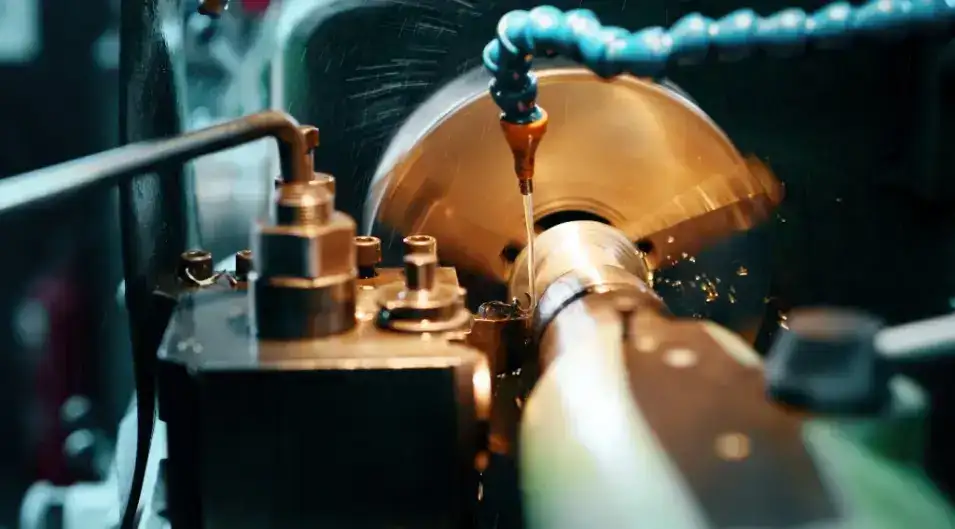

4-axis CNC lathes are used for turning operations. The added axis enables the lathe tool to approach the workpiece at any angle. It permits the manufacture of complex shapes. Lathes can work on materials like metal, wood or plastic, offering wide possibilities for manufacturing.
Router
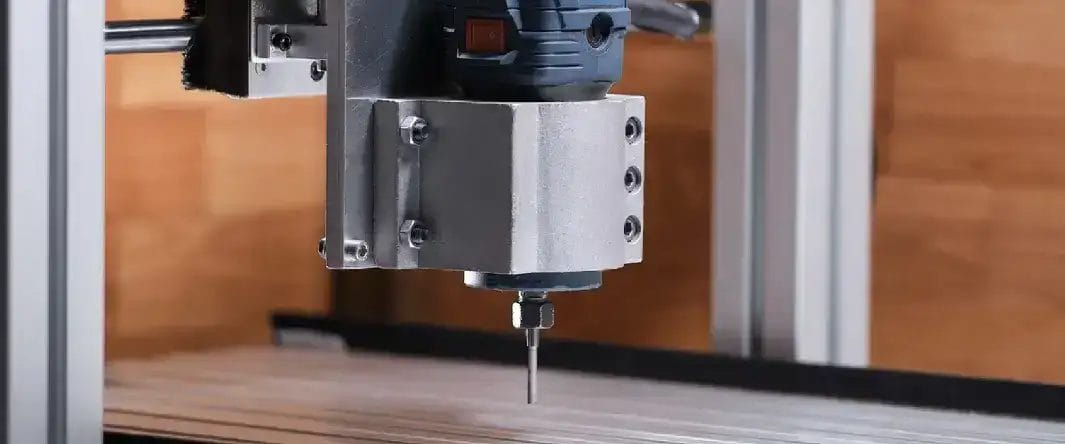

Routers are mostly used in woodworking industry. 4-axis CNC routers bring precision and ability to work on large parts. Their sturdy build and easy setup make them valuable in any production line.
Having 4 axes instead of 3 gives enhanced abilities and efficiency for CNC machining, making the technology essential in modern manufacturing.
Applications of 4 Axis CNC Machining
The flexibility and accuracy of 4-axis CNC machining makes it super valuable. They get used in wide range of industries and applications – from aerospace and cars to medical stuff and art.
Industry Uses
Aerospace relies on it for intricate turbine blades, engine parts and structural components. Auto industry uses it for stuff like engine parts, transmissions and suspension systems. Medical device makers use it to produce precise surgical tools, implants and prosthetics.
Creative Uses
Beyond industrial stuff, 4-axis CNC machining also gets used for creative things like sculpture and jewelry. The precision and flexibility let artists and sculptors make detailed pieces with complex designs. Jewelers use it to create unique and elaborate pieces.
General Manufacturing
For general manufacturing, 4-axis CNC machining manufactures all kinds of parts like gears, brackets and complicated structural components. These machines are able to machine multiple sides in one setup, which saves a lot of time and money. That’s the reason why prototypes and custom jobs lean on it heavily.
The flexibility and accuracy make 4-axis CNC super valuable for a huge range of uses across very different industries.
Difference between 4-Axis and 5-Axis Machining
4-axis and 5-axis CNC machining can both provide advanced capabilities than regular 3-axis machining. But there are some big differences between the two when it comes to complexity, uses, and cost.
Complexity of Movements
The main difference is in how complex the movements can be. 5-axis machines can move along two extra axes (called B and C) and utilize 2 out of 3 rotation axes. This lets them make more intricate and complex shapes compared to 4-axis, which only adds one rotation axis (called A-axis) in addition to the three linear axes (X, Y, and Z).
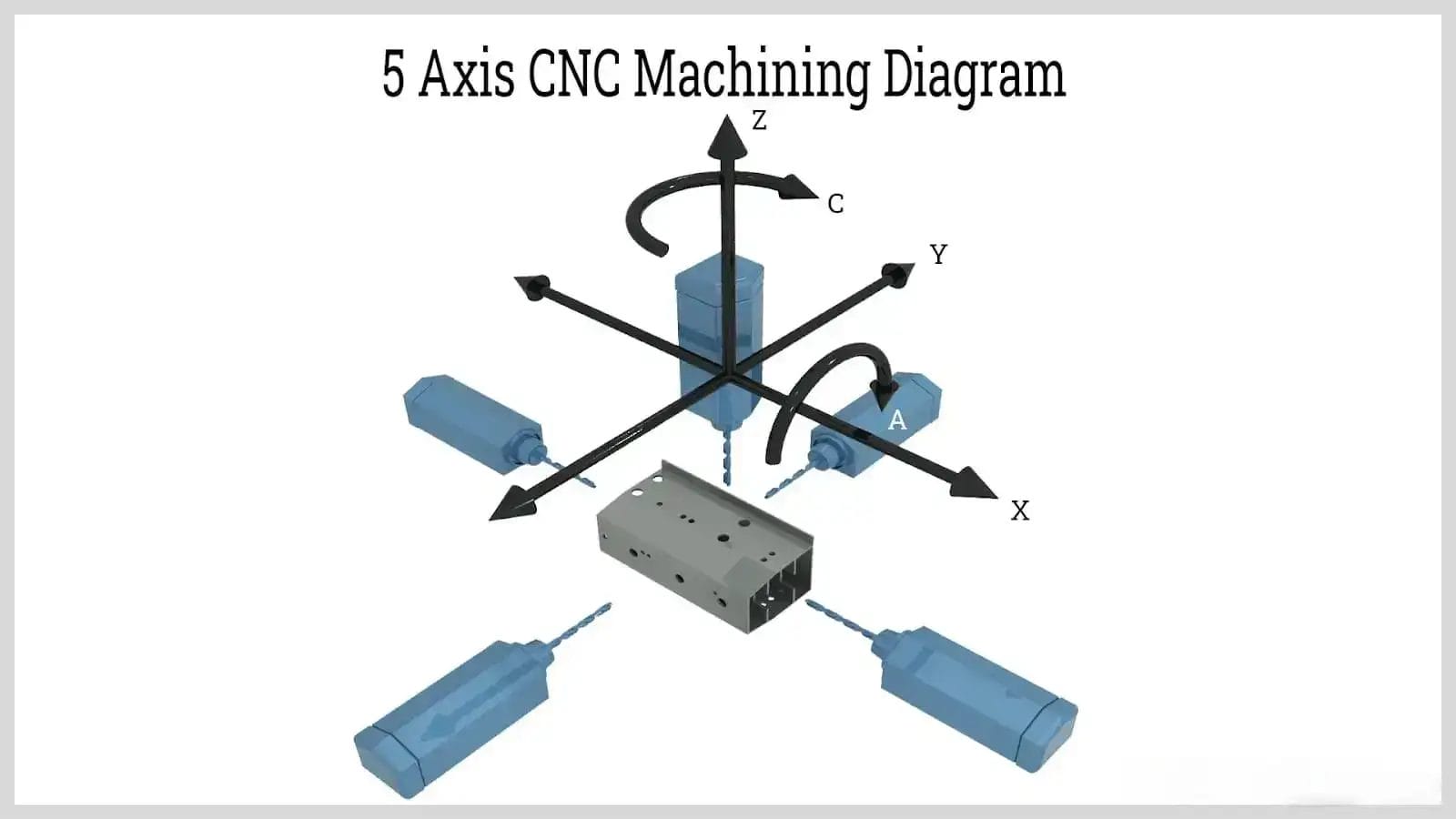
Uses and When Each Works Best
Whether 4-axis or 5-axis works better depends on what exactly you need to machine. 5-axis is great for complex curves, undercuts, and contours since it can handle the whole complicated shape in one setup. This works well when the part geometry has a lot of intricate 3D forms – like in aerospace components such as turbine blades or impellers.
But for less complex part geometries, 4-axis can be an affordable solution that still allows angled features and fewer setups.
Cost Comparison
CNC Machining Cost is a big factor. 5-axis machines tend to be more expensive given their complexity and abilities. They also need highly skilled operators and programming. The higher investment and maintenance costs may not be justified if 4-axis machining can efficiently handle the parts.
In summary – 5-axis offers maximum flexibility and complexity, but 4-axis CNC machining remains a valuable, cost-friendly choice for many applications.
Read More:
Top 10 5 Axis CNC Machining Suppliers In China
Top 10 5-Axis CNC Machining Suppliers In The World
Difference between 4-Axis and 3-Axis Machining
Going to 4 axes for CNC brings big advantages over old 3-axis machining, mostly because of the added A rotation axis.
Capability Enhancement
The A axis rotation lets 4-axis machines create way more complex geometries and features that 3-axis machines would struggle with or can’t handle. 3-axis is typically used where features are parallel or perpendicular to X, Y, and Z. But sometimes the designed feature cannot be physically manufactured by a 3-axis machine, or it may be more cost effective to machine with a 4-axis machine.
Anything at an angle to the X/Y/Z coordinate system won’t happen with 3-axis, even if the feature itself is flat. There are two angled feature types: angled planar faces and angled features that are non-planar. Features like angled holes, undercuts, and contours are simple to produce with 4-axis machining.
Operational Differences
4-axis machining can seriously cut production times and simplify setups versus 3-axis. By rotating the workpiece, 4-axis accesses multiple sides without manual repositioning. This will ultimately reduce the number of steps. Because of this feature, 4-axis machining is especially useful for parts like complex brackets and cylinders that have features on multiple sides.
Also, 4-axis eliminates human error risk when repositioning and can hold tighter tolerances between features on different sides of the part. Complex profiles such as cam lobes can be machined on a 4-axis machine.
There are two 4-axis CNC types: indexing and continuous. Indexing 4-axis machines can only rotate the A-axis into a fixed position. On the other hand, when cutting, continuous 4-axis machines can rotate the A-axis along with the other axes simultaneously.
Cost and Complexity
Although 4-axis CNC machines cost more, they can save money for some uses. The expanded capabilities avoid expensive special fixtures and tooling that 3-axis would need to produce similar results. However, running 4-axis CNC machine requires more operator skills and training than 3-axis.
Conclusion
Using 4 axis CNC machining has shown big advantages for precision, efficiency, and flexibility in all kinds of industries. This technology lets complex parts get made in fewer setups and with better accuracy. That makes it superior for intricate designs needing detailed machining from multiple angles.
The future looks bright for 4-axis CNC machining as the technology keeps advancing. As CNC improves even more on precision and capabilities, the demand will grow for complex, super accurate machined parts. That will drive more innovations in 4-axis CNC machining methods.
For expertise in multi-axis CNC, Yijin Hardware stays a leader in the field. As multi axis CNC machining specialists, they provide cutting-edge solutions for diverse manufacturing needs. Their commitment to quality and precision makes them an ideal partner for any project needing advanced multi axis CNC machining.
Contact Yijin Hardware today. Their expert team is ready to help you with your needs.

 info@yijinsolution.com
info@yijinsolution.com (+86) 188-2253-7569
(+86) 188-2253-7569







