Automotive sheet metal fabrication is the basic foundation of the latest vehicle manufacturing. It turns flat metal sheets into parts that make up a vehicle’s structure. This metalworking skill blends normal craftsmanship with the best technology to create body panels, engine parts, and a lot more.
There is a huge need for lightweight materials and complicated designs, so custom automotive sheet metal fabrication is really quite important. Yijin Solution offers sheet metal fabrication for automotive markets.
Key Takeaways
- Sheet metal fabrication methods, including laser cutting, hydroforming, press-brake bending, and more, enable the production of both standard and highly customized automotive components.
- Advanced materials such as high-strength steels and aluminum alloys can cut vehicle weight by up to 30% while preserving crashworthiness and durability.
- CNC machining, digital process monitoring, and strict adherence to quality standards (ISO 9001:2015, AWS D8.8M:2021, AIAG CQI-15) ensure dimensional accuracy within ±0.05 mm and consistent, first-time-right production.
What is Automotive Industry Sheet Metal Fabrication?
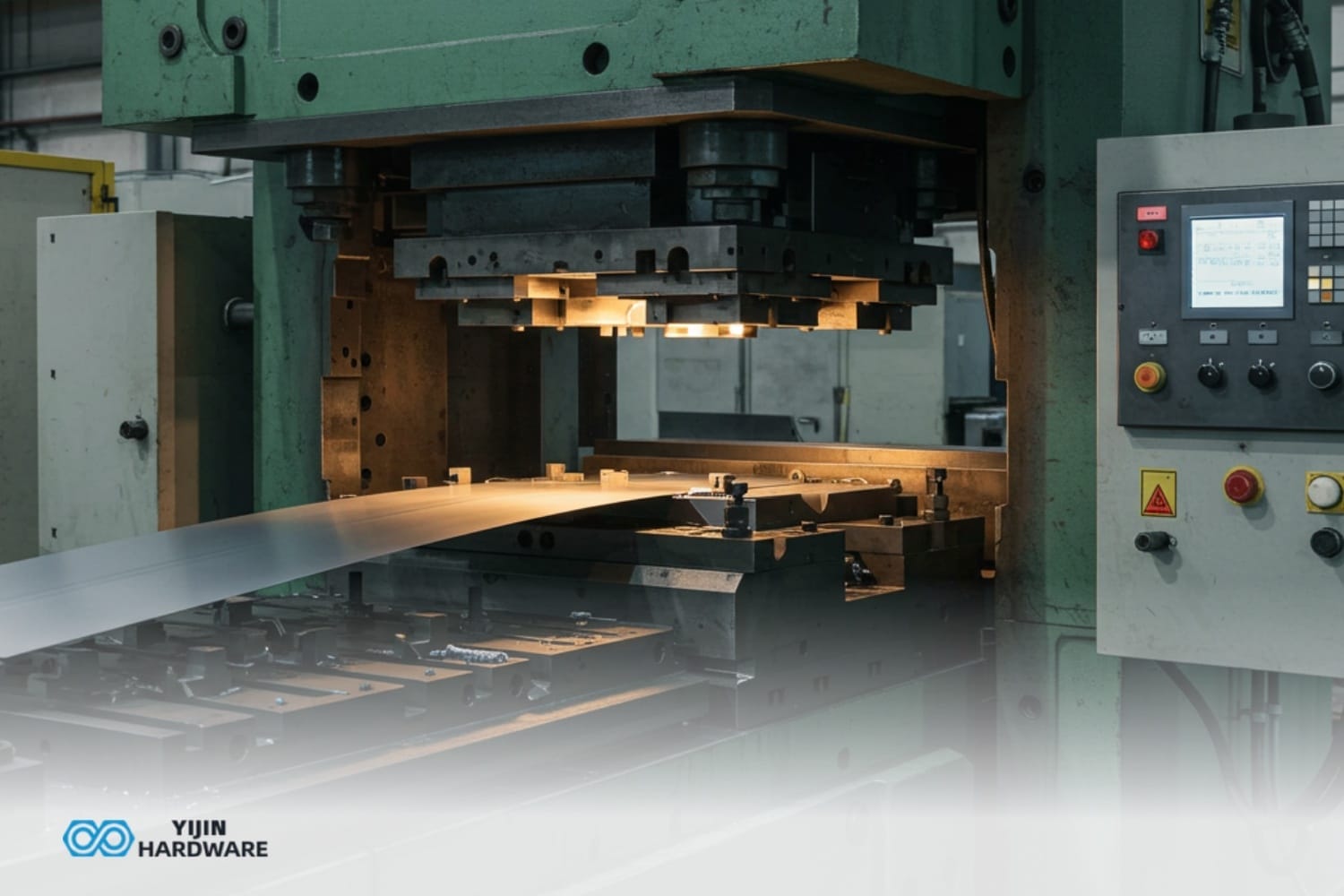

Sheet metal fabrication for automotive applications turns flat metal into vehicle components through accurate manufacturing methods. This process is all about multiple specialized operations. These include cutting, forming, and joining methods that create fenders, structural elements, and more. Automotive sheet metal fabrication blends normal metalworking with the latest design and CNC technology to get the best precision and consistency.
Sheet metal fabrication is the basic foundation of vehicle production. It allows manufacturers like us to meet demanding needs for structural integrity, weight reduction, and design complications. The skills require engineering knowledge to balance strength, weight, and aesthetics in each part.
According to the Business Research Company, the automotive sheet metal components market is expected to grow quickly in the next few years. It was valued at around $138.84 billion in 2025 and is predicted to reach $172.26 billion by 2029. It should grow at an average rate of 5.5% per year.
Why is Sheet Metal Fabrication Critical for Automotive Manufacturing?
Sheet metal fabrication is critical in the automotive industry because it provides unmatched design flexibility and material efficiency essential for modern production needs. Manufacturers leverage sheet metal fabrication to create complex geometries and intricate shapes while maintaining tight tolerances crucial for proper assembly and performance.
The precision enabled by CNC-driven fabrication ensures metal parts fit perfectly during assembly, eliminating gaps and alignment issues that would compromise both aesthetics and functionality.
Which Cutting Techniques Deliver the Best Results for Automotive Components?
Laser cutting provides the highest precision for automotive sheet metal, with accuracy typically within 0.1 mm. This technique uses a focused laser beam to create clean, precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones, making it ideal for intricate components with complex geometries. Laser cutting excels when working with high-strength steel, aluminum alloys, and other materials used in modern vehicles.
Plasma cutting offers superior performance when working with thicker materials up to 50 mm. This technique utilizes ionized gas to create high-temperature plasma that cuts through heavy-gauge metals used in chassis and structural components, delivering excellent results for larger, more robust parts.
CNC punching provides exceptional efficiency for high-volume production with repeated patterns. This technique uses programmable tooling to create precise holes and cutouts in sheet metal, making it particularly effective for components requiring multiple identical features, such as ventilation panels and structural supports.
| Cutting Technique | Ideal Material Thickness | Precision Level | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | 0.5-20 mm | ±0.1 mm | Complex geometries, intricate details |
| Plasma Cutting | 3-50 mm | ±0.5 mm | Thicker structural components |
| CNC Punching | 0.5-6 mm | ±0.2 mm | Repeated patterns, high-volume production |
| Waterjet Cutting | 0.5-100 mm | ±0.2 mm | Heat-sensitive materials |
How do Forming and Bending Methods Shape Modern Vehicle Components?
Press brake bending creates precise angles and curves in automotive sheet metal forming with consistent repeatability. This process applies focused pressure along predetermined lines to achieve exact bends according to digital specifications, making it essential for creating structural members, brackets, and reinforcements. Modern CNC press brakes achieve bend accuracy within 0.1 degrees.
Metal Spinning for Cylindrical Components
Metal spinning transforms flat circular discs into axially symmetrical shapes through rotational forming. This specialized technique creates components with exceptional dimensional accuracy (within 0.001 inches) while maintaining consistent wall thickness. Metal fabrication equipment for spinning excels in producing:
- Cylindrical components like bearing housings
- Symmetrical cones for fluid systems
- Domes and hemispheres for decorative elements
- Circular flanges and wheel components
Stretch-Forming for Complex Curves
Stretch-forming produces permanently curved components by stretching metal under tension around a contoured die. This technique creates smooth, consistent curvatures without wrinkling, particularly valuable for large exterior panels. Stretch-forming:
- Eliminates “spring-back” common in traditional forming
- Creates complex multi-axis curves impossible with press braking
- Maintains consistent material thickness across curved surfaces
- Achieves high-quality Class A surfaces for visible components
Hydroforming for Complex Geometries
Hydroforming utilizes hydraulic pressure to shape metal into complex forms with superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional methods. This technique forces sheet metal into a die using pressurized fluid, creating components with uniform material thickness and exceptional structural integrity, particularly valuable for creating complex components like exhaust systems and structural frames.
What Joining Technologies Ensure Structural Integrity in Automotive Assembly?
Resistance spot welding creates strong, durable joints in automotive sheet metal by applying electric current and pressure at specific points. This technique forms the foundation of Body-in-White (BIW) assembly, creating fusion points that maintain structural integrity while allowing efficient production. Modern automotive BIWs typically contain 2,000-5,000 spot welds that form the vehicle’s safety cage.
TIG welding produces high-precision seams with minimal heat-affected zones, preserving material properties around the joint. This advanced weld technique creates consistent, narrow welds ideal for visible areas and components requiring water-tight or gas-tight seams, while allowing better design flexibility than traditional joining methods.
Magnetically Impelled Arc Butt (MIAB) Welding
MIAB welding joins tubular components with exceptional efficiency and consistency. This specialized technique uses electromagnetic forces to rotate the arc around the tube circumference, creating perfectly uniform welds in a single operation. MIAB welding achieves:
- Consistent penetration around the entire tube circumference
- Minimal heat-affected zone compared to conventional methods
- Superior joint strength for critical safety components
- Higher production rates than manual or conventional automated welding
Which Materials Optimize Performance in Automotive Sheet Metal Components?
Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) deliver exceptional strength-to-weight ratios essential for modern vehicle structural components. These specialized steel variants offer yield strengths between 550-1200 MPa while maintaining formability necessary for complex automotive geometries. AHSS enables critical safety structures in impact zones while reducing overall vehicle weight.
Aluminum alloys provide significant weight reduction (typically 30-40% compared to steel) while maintaining adequate strength for many automotive applications. The 5000-series (with magnesium) and 6000-series (with magnesium and silicon) aluminum alloys specifically designed for automotive use deliver excellent formability, corrosion resistance, and finish quality for body panels and closure panels.
| Material Type | Density (g/cm³) | Yield Strength Range | Primary Automotive Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AHSS | 7.85 | 550-1200 MPa | Safety cage, impact structures |
| Aluminum 5000-series | 2.7 | 125-350 MPa | Body panels, hood, trunk |
| Aluminum 6000-series | 2.7 | 200-400 MPa | Structural components, extrusions |
| Magnesium Alloys | 1.8 | 150-275 MPa | Steering wheels, instrument panels |
| Titanium | 4.5 | 800-1100 MPa | Exhaust systems, springs |
Tailor-Welded Blanks (TWBs)
Tailor-welded blanks combine different thicknesses or materials into a single component before forming. This advanced approach places specific material properties exactly where needed, optimizing performance while minimizing weight. TWBs allow:
- Strength reinforcement only where structurally necessary
- Weight reduction in non-critical areas
- Optimized crash energy absorption
- Material-specific properties in different component zones
How does CNC Machining Revolutionize Automotive Sheet Metal Fabrication?
CNC machining achieves exceptional dimensional accuracy in automotive components, typically within ±0.05 mm. This precision ensures a perfect fit and function of complex assemblies while minimizing tolerance stack-up issues that could compromise vehicle performance. Modern 5-axis CNC systems can machine complex geometries impossible with conventional fabrication methods.
Digital manufacturing integration connects design directly to production, eliminating interpretation errors. CAD models transfer seamlessly to CNC controllers, ensuring the manufactured component precisely matches the engineer’s intent and specifications. This digital continuity also enables rapid design iterations and prototyping.
Digital Process Monitoring Systems
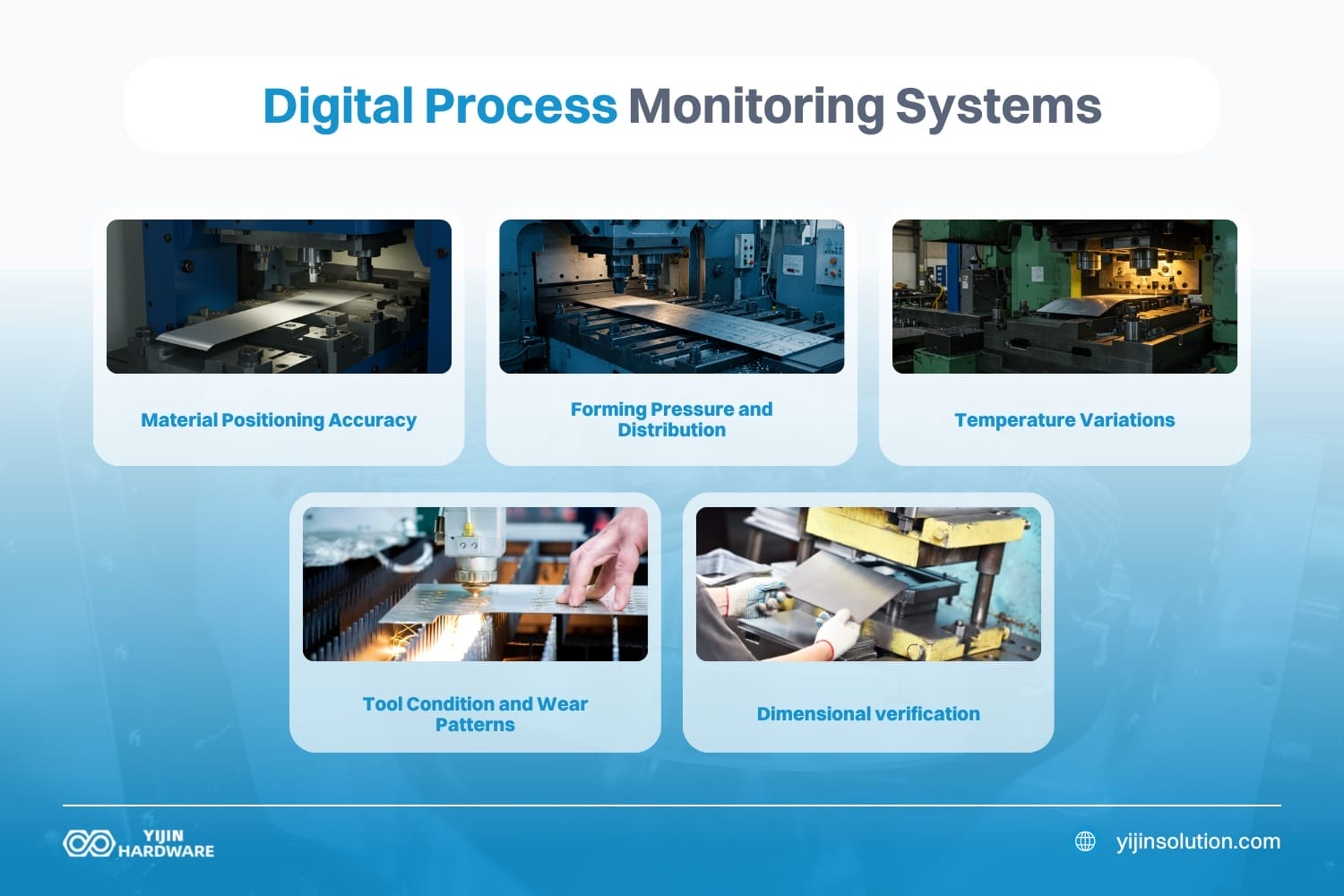
Advanced sensor integration provides real-time feedback during fabrication processes. These systems continuously monitor critical parameters, including:
- Material positioning accuracy (within 0.01 mm)
- Forming pressure and distribution for consistent results
- Temperature variations during processing
- Tool condition and wear patterns
- Dimensional verification against CAD specifications
What Quality Standards Govern Automotive Sheet Metal Manufacturing?
ISO 9001:2015 certification establishes comprehensive quality management systems essential for automotive component manufacturing. This standard requires documented procedures, regular audits, and continuous improvement processes that ensure consistent product quality. Manufacturers must demonstrate systematic approaches to quality control throughout their operations.
AWS D8.8M:2021 provides specific requirements for automotive weld quality, defining inspection criteria and acceptable parameters. This standard covers various welding methods including resistance spot welding, arc welding, and laser welding, specifying test methods and acceptance criteria for each. Compliance ensures structural welds meet safety and performance requirements.
Non-Destructive Testing Methods
Advanced inspection technologies verify internal and surface quality without damaging components:
Ultrasonic testing detects internal defects in welds and material
- Magnetic particle inspection identifies surface and near-surface discontinuities
- Dye penetrant testing reveals microscopic surface cracks
- X-ray and computed tomography provide three-dimensional defect visualization
- Laser scanning verifies dimensional accuracy against CAD models
How do you Choose the Right Sheet Metal Fabrication Partner for Automotive Projects?
Choosing the right sheet metal fabrication involves partnering with a company that offers quality service, meets your production standards, and offers reliable support through and through. Yijin Solution provides comprehensive sheet metal fabrication for automotive markets with advanced equipment and specialized expertise. Our extensive experience with automotive-grade materials and components ensures exceptional quality, precision, and corrosion resistance. We maintain all relevant automotive certifications while offering competitive pricing for both prototype and mass-production volumes.
Yijin Solution | Advanced Automotive Sheet Metal Parts
Yijin Solution delivers exceptional technical capabilities in automotive sheet metal fabrication through our advanced CNC machining systems, specialized forming equipment, and comprehensive quality control processes.
Our expertise encompasses the full spectrum of automotive components, from body panels to engine components, ensuring optimal results even under harsh conditions for both production vehicles and custom automotive applications. Contact us for our advanced sheet metal part services.
Automotive Sheet Metal Fabrication FAQs
How does electrohydraulic forming differ from conventional hydroforming?
Electrohydraulic forming uses electrodes to explosively vaporize fluid that deforms the working material. This high-energy process creates significantly more forming pressure than conventional hydroforming (up to 10× higher), enabling the formation of extremely complex geometries and sharper features. Electrohydraulic forming also achieves results in microseconds rather than seconds, dramatically reducing cycle times while allowing the formation of materials with limited ductility.
What special considerations apply when fabricating sheet metal for electric vehicles?
Electric vehicle sheet metal fabrication requires specialized approaches to battery enclosure shielding, thermal management, and electromagnetic interference protection. Battery enclosures demand exceptional precision with leak-tight joining methods to prevent thermal runaway situations. Weight reduction becomes even more critical, driving the use of aluminum-intensive structures and multi-material designs. Additionally, EV-specific components require specialized electromagnetic shielding properties not typically considered in conventional vehicle fabrication.
How do digital twins enhance automotive sheet metal fabrication?
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical fabrication processes that simulate actual production in real-time. These digital models predict potential forming issues like springback and material thinning before physical production begins, reducing costly tooling iterations. During production, digital twins continuously compare actual measurements with virtual predictions, automatically adjusting process parameters to maintain quality. This technology reduces development time by up to 40% while increasing first-time-right production rates by identifying process optimization opportunities impossible to detect with conventional methods.
Back to Top: Automotive Sheet Metal Fabrication: Methods, Materials & Applications














