Sheet metal fabrication is crucial in aerospace, where precise, lightweight parts are key. It involves cutting, bending and assembling metal structures used in aircraft, satellites and spacecraft. Aerospace sheet metal companies help production be faster and better.
In this post, we’ll discuss aerospace sheet metal details – its pros, materials used, techniques and examples.
If you are a beginner, feel free to read the guide: What is Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
Advantages of Sheet Metal Fabrication for the Aerospace Sector
Sheet metal fabrication for aerospace has major upsides for manufacturers and technicians:
- Low Production Cost – Aerospace sheet metal fabrication companies can produce aircraft parts affordably. It can save 20-30% more than other methods.
- Fast Production – Quick setup in metal stamping and forming means fast turnaround while making aircraft parts. It cuts production time by 40-50%.
- Easy Customization – Sheet metal fabrication allows precise cutting and shaping. This allows easy custom aircraft parts to meet exact design needs with tolerances as tight as ±0.005 inches.
- Maintains Material Properties – The cold forming technique keeps heat warping away. This preserves the material’s structural integrity during fabrication.
- Better Quality Control – Using custom tools and dies in stamping ensures excellent precision. It can reduce potential defect rates by 0.1%.
Best Materials for Aerospace Sheet Metal Parts
Selecting the right materials is crucial for aerospace sheet metal fabrication. The chosen materials must exhibit a combination of desirable properties. These properties include high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and the ability to withstand extreme conditions. Here are some of the most commonly used materials in sheet metal fabrication for aerospace:
| Material | Alloys | Properties | Benefits |
| Aluminum | 6061, 7075, 7475-T761 | 45-83 ksi tensile strength; Corrosion resistant; Formable | Versatile, lightweight, strong |
| Titanium | Ti-6Al-4V | 138 ksi tensile strength; Corrosion & heat resistant to 600°F | Strong, durable, high-temp |
| Stainless Steel | 17-4 PH | Up to 190 ksi tensile strength; Excellent corrosion resistance | High strength & corrosion resistance |
| Copper Alloys | Beryllium Copper, Aluminum Bronze | 110-200 ksi tensile strength; 12-60% IACS conductivity; Wear resistant | Conductive, strong, wear resistant |
| Brass Alloys | Naval Brass | 70 ksi tensile strength; 28% IACS conductivity; Corrosion resistant | Marine-suitable |
| Composites | Carbon fiber, Fiberglass, Aramids | High strength-to-weight; Excellent fatigue resistance; Tailorable | Lightweight, high-performance |
Materials for Aerospace Sheet Metal Parts.
When selecting materials for aerospace sheet metal fabrication, several key criteria must be considered:
- High strength-to-weight ratio to minimize weight while maintaining structural integrity
- Excellent corrosion resistance to withstand harsh aerospace environments
- Durability to ensure long-term performance and reduced maintenance costs
- Ability to perform under extreme conditions such as high temperatures, pressures, and fatigue loads
Aerospace Sheet Metal Making Methods
Aerospace sheet metal fabrication uses many techniques to turn metal sheets into intricate aircraft parts. These methods ensure the durability, accuracy and strength of the finished components. Let’s look at some important aerospace sheet metal fabrication processes:
Cutting Techniques
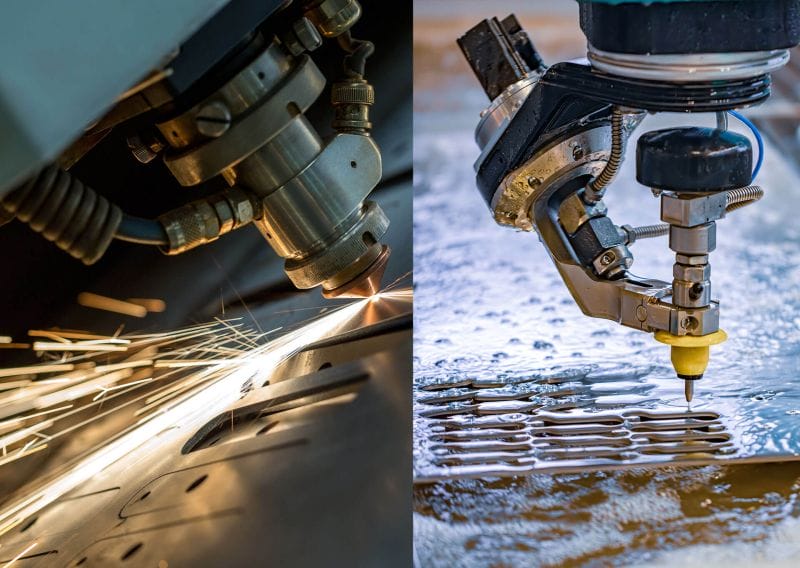

Figure 2. Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting
1. Laser Cutting
Laser cutting uses a strong laser to cut metal sheets. It is very accurate with little wasted material. It is also great for making tricky shapes in aerospace parts. Laser cutting works well with metals like titanium and aluminum. It can cut within ±0.05 mm tolerance, perfect for high-precision parts. Explore our CNC laser cutting services for high-precision applications.
2. Waterjet Cutting
A cold cutting method using high-pressure water mixed with abrasive particles to cut metal sheets. It is good for sensitive materials since it doesn’t create heat affected areas. It can make complex shapes with great edge quality. Waterjet Cutting can also handle up to 300 mm thick and 3000 x 6000 mm sized materials. It is ideal for large aerospace components.
3. Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting employs a plasma torch to slice through conductive metals, making it ideal for thicker aerospace parts. With its cost-effectiveness and ability to handle heavy-duty projects, our plasma cutting service ensures excellent results for even the most demanding components.
Forming Methods
1. Hydroforming
Hydroforming uses high-pressure fluid to shape sheet metal. It can create intricate shapes with uniform thickness. Good for aircraft engine casings. Saves material, needs less joining.
2. Stretch Forming
Stretches and bends sheet metal over a die. Used for big curved panels on wings and planes. Gives smooth curves without wrinkles. Works on up to 50 mm sheets, 4000 x 6000 mm in size.
3. CNC Brake Press Bending
CNC brake press bending shapes sheet metal into precise angles and curves. This process is essential for creating components like brackets and frames. Learn more about our metal bending service for custom aerospace solutions.
Joining Methods
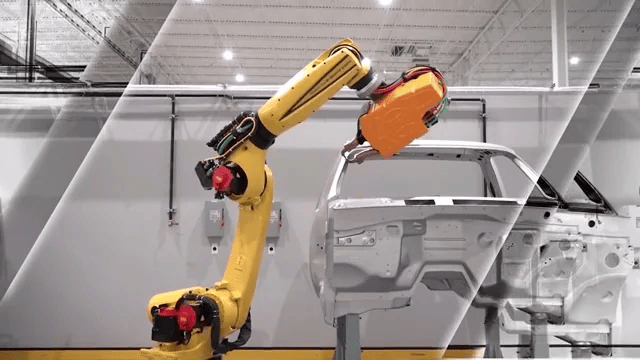
Figure 3. Robotic Welding
1. Robotic Welding
Robotic welding automatically joins metal sheets when building aircraft. It makes very precise, consistent welds. Robotic systems follow programmed paths and settings. This results in top quality welds with minimal flaws. Works well for joining critical structural sections that need to be robust with high integrity. Can join materials up to 50 mm thick.
2. Riveting
Riveting is the conventional way to join sheet metal aircraft parts. Rivets are mechanical fasteners put through pre-drilled holes then deformed. This makes a permanent joint. Riveting creates a sturdy, reliable connection between sheets. Good for assembling plane fuselages, wings, other structures. Handles shear loads to 90 kN and tensile loads to 45 kN.
Finishing Methods
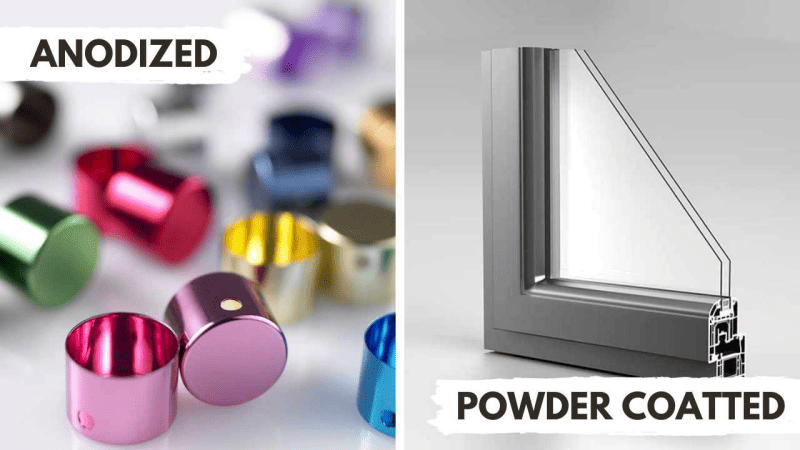
Figure 4. Anodizing & Powder Coating
1. Anodizing
Anodizing creates a protective layer on aluminum parts. It makes aluminum more corrosion-resistant (up to 30 times). Anodizing is also used to create different textures.
2. Powder Coating
Powder coating is a dry finishing process. It involves applying a powdered coating and heating it. Gives aerospace parts a strong, even, attractive finish. Very resistant to corrosion, impact, fading. Good for both inside and outside use. Can make metal up to 10 times more wear-resistant than uncoated.
3. Plating
Plating puts a thin layer of another metal like nickel, chrome, or cadmium. Makes aerospace parts more resistant to corrosion and wear. Also improves appearance. Different plating methods to be used are based on the need of part. For example, nickel plating can make steel up to 5 times more wear-resistant and 10 times more corrosion-resistant.
Examples of Aerospace Sheet Metal Parts
Figure 5. Different Aircraft Sheet Metal Parts
Aerospace sheet metal fabrication makes many critical aircraft components. Here are some sheet metal parts made for aerospace:
- Exterior Skins– Body and wing panels use aluminum alloys like 2024-T3 and 7075-T6. These are usually 0.040″ to 0.063″ thick.
- Cockpit Parts– Instrument and control panels employ aluminum alloys and sometimes stainless steel. Thickness of metal sheet depends on the part and stress.
- Rotor Pylon Parts– Helicopter transmission housings and tail boom skins uses aluminum and titanium alloys, usually 0.020″ to 0.125″ thick based on the part.
- Enclosures andPanels – Avionics boxes use 0.040″ to 0.090″ aluminum alloys to block electromagnetic interference.
- Miscellaneous Parts– Brackets, supports and other structural parts use various aerospace materials. Thickness and tolerance depend on use and stresses.
Sheet Metal Parts Examples
Sheet metal fabrication is widely used across various industries to produce a diverse range of parts and components. Here are some examples of sheet metal parts in certain industry sectors.
- Automotive Industry: Body panels, frames, engine covers, exhaust systems, fuel tanks, heat shields, brackets, and mounts.
- Construction Industry: Roofing sheets, wall cladding, flashing, gutters, downspouts, ductwork, vents, and structural components.
- Medical Industry: Equipment housings, brackets, bases, trays, tables, carts, and enclosures for medical devices.
- Electronics Industry: Enclosures, chassis, brackets, heat sinks, shields, and mounting plates for electronic components.
- Household Appliances: Enclosures, frames, structural components, shelves, drawers, and panels for appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens.
Sheet Metal Work at Yijin Solution
Yijin Solution is one of leading sheet metal fabrication companies in china. We have more than 20 years of precision sheet metal and CNC machining experience. Our sheet metal services include:
- Water Jet Cutting: Up to 300 mm thick, 3000 x 6000 mm max area
- Bending: Up to 50 mm thick, 4000 x 6000 mm max area
- Laser cutting: Up to 50 mm thick, 4000 x 6000 mm max area
- Plasma cutting: Up to 50 mm thick, 4000 x 6000 mm max area
We also offer extra services like stamping, welding, rolling and punching for your custom projects. Our custom services also include finishing treatments like powder coating and plating. We use best quality equipment imported from Switzerland, Japan, Germany, and Sweden to make sure of excellent quality.
Yijin is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We maintain strict quality control throughout the fabrication process. We have 25,000+ square meter facility and can produce over 8 million parts in a month. For rush orders, we can deliver high-precision samples within 24 hours.
Yijin specializes in aerospace sheet metal parts, and we work with many materials. These include titanium alloys (Ti-6Al-4V), aluminum alloys (6061, 7075), and stainless steel alloys (SS304, SS316). We adhere to the aerospace industry’s strict standards to get optimal results.
Are you interested in having custom sheet metal parts made? Contact our team today for expert guidance









