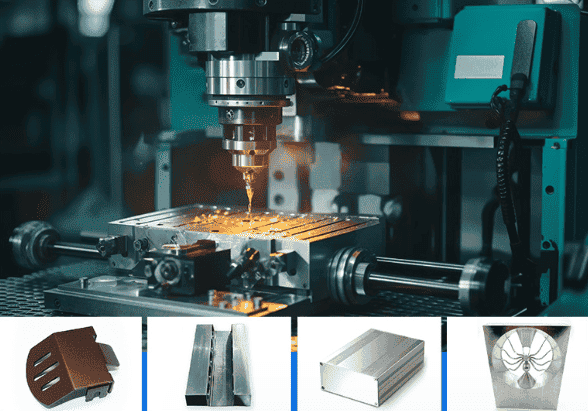
Machining aluminum requires 2-3 flute carbide end mills with high helix angles and polished surfaces, cutting at speeds 2-3 times faster than steel (200-600 m/min) with feed rates of 0.1-0.5mm per tooth. The biggest challenge is preventing built-up edge where aluminum sticks to the cutting tool, which is solved by using proper speeds, sharp tools, and never machining aluminum dry. Water-soluble coolants at 6-10% concentration with high-pressure delivery are essential for chip evacuation and preventing tool welding. 6061 aluminum offers the best machinability for general applications, while proper setup can achieve surface finishes as good as Ra 0.8 μm and tolerances of ±0.01mm.
Learning how to machine aluminum involves specific techniques that are very different from other metals. Trying aluminum CNC machining with the wrong methods causes poor surface finishes, damaged cutting tools, and wasted materials.
At Yijin Solution, our CNC experts have created the best processes for aluminum machining. Looking for CNC milling China? Our way of machining and milling consistently makes precision parts with great surface finishes, tight tolerances, and affordable production cycles.
Key Takeaways
- Aluminum’s low density (2.7 g/cm³) and high thermal conductivity demand specific cutting tools and speeds
- The optimal tool for aluminum CNC milling is a 2-3 flute carbide end mill with polished or ZrN coating
- Different aluminum grades (6061, 7075, 2024) require adjusted machining parameters for best results
- Proper coolant and lubrication prevent built-up edge formation, the most common aluminum machining problem
- CNC mill aluminum operations can achieve tolerances of ±0.01 mm for precision parts when properly optimized
What Makes Aluminum Different from Other Metals for Machining?
Aluminum has a significantly lower density (2.7 g/cm³) than steel (7.8 g/cm³), allowing faster cutting speeds and material removal rates. Its high thermal conductivity dissipates heat quickly during machining, reducing tool life issues but requiring careful spindle speed and feed management. Aluminum is extra soft. That means it can easily connect to the cutter. This can create a big problem with a built-up edge that messes with surface finishes and damages tools.
According to Nguyen et al., mathematical statistics techniques and optimization methods are applied to achieve a rational selection of process parameters in the milling of aluminum alloys. The independent variables in these studies typically include cutting speed, cutting depth, and feed per tooth, which are identified as key factors influencing both surface finish and machining efficiency. These parameters are systematically varied and optimized using statistical approaches such as the Taguchi method and regression modeling to predict and improve surface roughness and production rates during aluminum alloy milling.
Key Material Properties Affecting Machinability
- Melting point: ~660 °C (much lower than steel’s ~1370 °C) — aluminum can melt and fuse to cutting tools if machined improperly
- Non-magnetic properties: Ideal for electronic applications
- Corrosion resistance: The natural oxide layer provides excellent protection
- Thermal expansion coefficient: 2.3 × 10^-5 per °C (twice that of steel)
These unique properties make aluminum highly machinable yet demanding specific approaches. While you can cut aluminum three to four times faster than steel, its tendency to stick to tools and form long, stringy chips requires specialized tooling and techniques. The main challenge with machining aluminum is keeping friction and heat to a minimum.
What are the Best Aluminum Alloys for Machining?
The 6061 aluminum alloy offers excellent machinability, and a decent strength-to-weight ratio (290 MPa tensile strength), and is widely available for general-purpose applications. 7075 alloy provides superior strength (570 MPa) but is harder to machine due to its hardness and is primarily used for aerospace and high-performance applications. 2024 aluminum offers an excellent balance between strength and weight and machines well, but has poor corrosion resistance, requiring protective finishing for most applications.
Aluminum Alloy Designation System
- 1xxx series: 99%+ pure aluminum (minimal alloying)
- 2xxx series: Copper as primary alloying element
- 3xxx series: Manganese as primary alloying element
- 4xxx series: Silicon as the primary alloying element
- 5xxx series: Magnesium as the primary alloying element
- 6xxx series: Magnesium and silicon as primary alloying elements
- 7xxx series: Zinc as primary alloying element
| Alloy | Machinability | Tensile Strength | Best Applications | Chip Formation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061-T6 | Excellent | 290 MPa | General purpose, fixtures | Short, breaks easily |
| 7075-T6 | Good | 570 MPa | Aerospace, high-load parts | Stringy, requires breakers |
| 2024-T3 | Very Good | 470 MPa | Aircraft structures | Medium length |
| 5083-H321 | Good | 317 MPa | Marine applications | Gummy, can be difficult |
Cast aluminum alloys are more affordable, but generally more gummy and harder on cutting tools than wrought aluminum varieties. This makes wrought aluminum the preferred choice for precision machining operations in most machine shop environments.
How do you Choose the Right Tools for Machining Aluminum?
The ideal cutting tool for aluminum milling is a 2-3 flute end mill with a high helix angle and polished surface. Fewer flutes create larger chip gullets that help evacuate chips and prevent clogging with aluminum particles, which is critical for successful machining. Higher helix angle (40-45°) endmills improve chip evacuation and produce better surface finish, though a lower helix (30-35°) generates less heat in heavy rough cutting operations.
End Mill Geometry Optimization for Aluminum
- Rake angle: 10-15° positive rake (more aggressive than for steel)
- Relief angle: 10-12° (prevents rubbing and built-up edge)
- Core diameter: Slightly smaller than steel tools for larger chip gullets
- Edge preparation: Sharp edges preferred over honed edges
Tool coatings significantly impact aluminum machining success. Avoid TiN, TiAlN, and AlTiN coatings as they react poorly with aluminum. Instead, use uncoated polished carbide endmills or those with specialized ZrN, DLC, or TiB2 coatings designed specifically for aluminum. The right coating will help with chip flow and keep everything running cool during high speeds.
For specialized applications, a single flute endmill can provide maximum chip clearance in deep slot operations where chip evacuation is critical. These specialized cutters excel when cutting aluminum plates or performing deep pocket machining where standard endmills might struggle.
What are the Optimal Cutting Parameters for Aluminum?
Cutting speeds for aluminum should range between 200 and 600 meters per minute with carbide tools, 2 to 3 times faster than those used for steel. The feed rate should be set relatively high (0.1-0.5 mm per tooth) to ensure the tool cuts rather than rubs against the workpiece, which would increase heat and cause tool damage. These parameters prevent aluminum from sticking to the cutting edge and forming a built-up edge.
Parameter Optimization by Operation Type
| Operation | Cutting Speed | Feed per Tooth | Depth of Cut | Tool Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rough | 300-450 m/min | 0.1-0.25 mm | Up to 1.5× tool dia. | 2-flute endmill |
| Finishing | 400-600 m/min | 0.05-0.15 mm | 0.2-0.5 mm | 3 flute end mill |
| Slot | 250-350 m/min | 0.08-0.15 mm | Up to 1× tool dia. | 2-flute endmill |
| Drilling | 80-120 m/min | 0.1-0.3 mm/rev | – | Aluminum-specific drill |
For ipm (inches per minute) calculations, multiply your rpm by feed per tooth and number of flutes. For example, a 2-flute endmill running at 10,000 rpm with 0.003″ feed per tooth would run at 60 ipm (10,000 × 0.003 × 2 = 60).
Advanced Toolpath Strategies
- Trochoidal milling: Reduces tool engagement while maintaining material removal rates
- High-speed adaptive clearing: Maintains consistent tool load for extended tool life
- Climb milling: Preferred direction for aluminum to reduce built-up edge formation
- Ramping entry: Gradually engages the tool to prevent breakage
The machining parameters must be adjusted based on the specific aluminum alloy. Softer grades like 6061 can be cut more aggressively, while harder materials like 7075 require reduced cutting speeds and feed to prevent excessive tool wear and maintain surface quality.
How does the CNC Aluminum Machining Process Work?
CNC aluminum milling begins with CAD modeling of the part design, which is converted to machine instructions through CAM software. The process continues with material selection and preparation, where the appropriate aluminum grade is chosen and prepared as stock material, often with allowances for fixturing. Machine setup follows, including tool selection, workpiece mounting, and machine calibration to ensure precise cutting.
Critical Process Considerations Unique to Aluminum
- Fixture design: Aluminum’s lower elastic modulus requires more support points than steel
- Tool engagement: Program smoother entries and exits to prevent chip welding
- Machine rigidity: Higher spindle speeds require balanced tooling and rigid setups
- Chip management: Evacuating long aluminum chips requires careful planning
- Thermal considerations: Account for aluminum’s thermal expansion during precision machining
The machining operation follows programmed toolpaths, removing material to create the designed part. For aluminum CNC milling machine operations, high-speed machining techniques are often employed to leverage aluminum’s high machinability while maintaining quality. The cycle time for aluminum parts is typically much shorter than comparable steel components due to faster material removal rates.
What are the Most Common Aluminum Machining Problems and Solutions?

Built-up edge (BUE) formation occurs when aluminum sticks to the cutting tool edge, degrading surface finish and reducing tool life. This problem is solved by using sharp tools with appropriate coatings, increasing cutting speeds and feeds, and applying adequate cooling during the machining process. Regular tool inspection and replacement when showing signs of BUE prevent quality issues.
Problem Detection and Prevention
| Problem | Visual Indicators | Prevention Method | Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Built-up edge | Tool edge appearance dull, material buildup | Higher speeds, proper coating | Replace or clean tool |
| Poor chip evacuation | Chips rewelding to surface | Appropriate chip breakers, air blast | Modify toolpath, increase coolant |
| Chatter | Waviness on machined surface | Increase rigidity, adjust RPM | Change toolpath, use dampening |
| Dimensional inaccuracy | Part out of tolerance | Account for thermal expansion | Adjust offsets, improve fixturing |
Chip evacuation issues arise from aluminum’s tendency to form long, stringy chips that can wrap around tools or damage finished surfaces. Effective solutions include using tools with proper chip breakers, programming appropriate chip-thinning tool paths, applying high-pressure coolant, and using air blasts to clear chips from deep pockets. Never attempt to cut aluminum dry, as this significantly increases the risk of tool failure and poor results.
How do you Properly Set Up Cooling and Lubrication for Aluminum?
Proper cooling system setup uses water-soluble coolants specifically formulated for aluminum at a 6-10% concentration with clean, filtered water. These coolants prevent aluminum chips from welding to cutting tools while providing necessary lubrication at the cutting interface. High-pressure coolant delivery systems directed precisely at the cutting zone offer superior chip evacuation and cooling efficiency.
Advanced Cooling Techniques for Aluminum
- Through-tool coolant: Delivers coolant directly to the cutting edge inside deep features
- Cryogenic cooling: Using liquid nitrogen for extremely high-speed operations
- Programmable coolant nozzles: Automatically adjust position based on tool location
- Cyclonic chip separation: Removes aluminum particles from coolant continuously
Coolant maintenance is critical for aluminum machining success. Regular concentration checks, pH monitoring (maintaining 8.5-9.5 pH), and filtration to remove suspended aluminum particles prevent coolant degradation and maintain machining quality. Clean coolant significantly extends tool life and improves surface finish quality in aluminum CNC milling operations.
What Surface Finishes can be Achieved When Machining Aluminum?
CNC milling can achieve surface roughness values as low as Ra 0.8 μm (32 μin) on aluminum parts with proper tooling and parameters. This level of finish appears smooth and slightly reflective, suitable for most mechanical interfaces and aesthetic applications. Specialized finishing techniques can further improve this to Ra 0.4 μm for critical applications.
Factors Affecting Surface Finish Quality
- Tool runout: Keep below 0.005 mm for best finish results
- Machine vibration: Minimize with proper balancing and damping
- Cutting edge radius: Sharper tools produce better finishes
- Feed per tooth: Reduce for final passes to improve surface texture
- Coolant quality: Clean, properly maintained coolant improves finish
Surface finish quality depends heavily on cutting parameters, tool selection, and machine rigidity. High spindle speeds, sharp tools with appropriate geometries, and light finishing passes produce the best results. For parts requiring extremely high-quality aesthetics, machine polishing aluminum components after CNC milling can achieve mirror-like finishes.
What Quality Standards Apply to Aluminum Machining?
ISO 9001 quality management systems provide the framework for consistent aluminum machining quality across manufacturing operations. This international standard ensures proper documentation, process control, and continuous improvement in machining operations. Many advanced manufacturing facilities implement these standards to ensure repeatability.
Critical Quality Control Techniques
- First article inspection (FAI): Complete dimensional verification of first production parts
- Statistical process control (SPC): Ongoing monitoring of critical dimensions
- Coordinate measuring machine (CMM) verification: Precision 3D measurement of complex features
- Material certification: Verification of aluminum alloy composition and properties
- In-process monitoring: Sensor systems that detect tool wear or process variation
Dimensional tolerance capabilities for aluminum CNC machined parts typically reach ±0.01 mm (0.0004”) for critical features and ±0.05 mm (0.002”) for general dimensions. These tolerances depend on part size, geometry, and the CNC machine’s capabilities. When selecting aluminum for CNC milling, consider both the machinability and the dimensional stability requirements of your application.
Yijin Solution: Advanced Aluminum CNC Machining & Milling
Successful aluminum machining requires understanding the material’s unique properties and adapting tooling, parameters, and techniques accordingly. By selecting the right alloy, using appropriate cutting tools, optimizing machining parameters, and implementing proper cooling, you can achieve excellent results with aluminum components.
At Yijin Solution, we leverage advanced multi-axis CNC machining centers, specialized aluminum-specific tooling, and expert technical knowledge to deliver precision aluminum components. Our comprehensive machining guide approach ensures every aluminum part meets the exact specifications required for your application, whether it demands tight tolerances, superior surface finishes, or optimal mechanical properties.
FAQs on How to Machine and Mill Aluminum: Complete Guide
When should you choose aluminum over other materials?
Choose aluminum when you need a lightweight component with a good strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and high thermal conductivity. Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring weight reduction while maintaining structural integrity, such as aerospace components, automotive parts, and portable devices. Its natural corrosion resistance makes it perfect for outdoor and marine applications, while its excellent thermal conductivity makes it the preferred choice for heat sinks and electronic enclosures.
Additionally, aluminum’s non-magnetic properties make it suitable for applications near sensitive electronic equipment, offering multiple benefits in a single material.
What are the cost considerations for aluminum machining?
Material costs for aluminum vary significantly by alloy type, with 6061 being the most economical while specialized alloys like 7075 command premium prices, though these material costs are often offset by faster machining times compared to steel, resulting in lower labor and machine time expenses. The overall project economics frequently favor aluminum for applications where its properties are suitable, and tool costs generally remain lower for aluminum machining operations because carbide tools last longer when cutting aluminum compared to harder materials.
Even though specialized aluminum-cutting tools may have initial price premiums, their extended life and higher possible cutting speeds deliver better overall economics, while coolant and lubricant costs remain minimal compared to the value they provide in extending tool life.
What advanced techniques are emerging for aluminum machining?
High-Speed Machining (HSM) techniques enable cutting speeds up to 10 times traditional rates on modern CNC machines, using specialized toolpaths that maintain consistent tool engagement, reducing tool load variations and allowing extremely fast material removal, while ultrasonic-assisted machining introduces high-frequency vibrations to the cutting tool, reducing cutting forces and improving surface finish on aluminum parts.
These advanced technologies are particularly effective for thin-walled aluminum components where traditional machining might cause deformation, with the ultrasonic vibration helping break chips into smaller segments and reducing built-up edge formation without additional coolant requirements, and though they require advanced CAM programming and high-rigidity machine tools, they deliver exceptional productivity for CNC milled aluminum parts.
Back to Top: How to Machine & Mill Aluminum: Full Guide