Have you ever heard of ABS plastic material but weren’t quite sure what it was? In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of ABS plastic material as well as its five key properties. Let’s dive in.
What Is ABS Plastic Material?
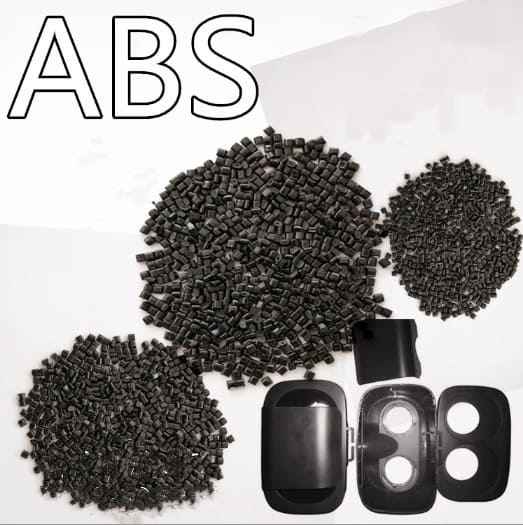
ABS plastic, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a tough and durable thermoplastic material that has been used extensively in the manufacturing of various products. It is known for its high strength, toughness, heat resistance, and electrical insulation properties.

ABS plastic is commonly used in the construction of electronic components such as computer keyboards, cameras, auto parts, medical device components, and many other items.
In addition to its versatile uses in industrial applications, this powerful thermoplastic material can also be found in everyday household items such as toys and recreational goods.
ABS plastic is created through a combination of two different polymer groups – acrylonitrile and butadiene-styrene copolymers – which are then combined through an extrusion process to form an ABS resin.

Once the resin is formed into pellets or beads, it can then be molded or thermoformed into any desired shape or size. This makes ABS plastic incredibly versatile for manufacturing just about anything from complex electronics to simple gadget accessories.
Properties of ABS Plastic Material
Due to its unique properties and durability, ABS plastic has become one of the most popular materials for manufacturers around the world. Here are five key properties that make this material so desirable:
Strength & Durability
One of the most notable features of this material is its exceptional strength and durability.
The combination of acrylonitrile’s strong backbone with styrene’s flexibility gives ABS plastics excellent impact resistance while maintaining structural integrity even under extreme temperatures.
These characteristics make it ideal for use in industries where products are expected to take heavy use or abuse over time, such as automotive parts or medical devices.

Heat-Resistance
In addition to being exceptionally durable against impact forces, ABS plastics have excellent heat-resistance capabilities too.
These properties make ABS materials suitable for a wide range of applications that require superior temperature tolerance, including cooking appliances and other products exposed to high temperatures during use or manufacturing processes such as injection molding or machining operations.
Electrical Insulation
Another advantage of using this material is its ability to provide good electrical insulation properties due to the presence of butadiene in its structure, which helps reduce conductivity between two surfaces when exposed to electricity.
This makes it particularly useful for producing electronic components like switches and connectors needed in many industrial applications where electric shock protection is a paramount safety concern.

Chemical Resistance
A further benefit of using ABS plastics is their increased resistance towards corrosive chemicals compared with other thermoplastics due to their low permeability rate, which helps prevent damage caused by liquids leaking inside them.
This makes them suitable for use in environments with harsh chemicals often used during various manufacturing processes, such as chemical etching or electroplating operations.
Cost Effectiveness
Last but not least, another major factor why so many businesses prefer this type of plastic over other alternatives on the market is its cost-effectiveness.
While more expensive than some other types, such as PETG, it provides cost savings due to higher production yields, lower tooling costs, and longer run lengths without sacrificing performance benefits.
ABS Grades for Part Prototyping and Manufacturing
ABS has a wide range of grades that differ in properties, such as density, temperature resistance, gloss level, and flame retardance.
Each grade of ABS can be used in different ways depending on the application. In this section, we will explore four of the most common grades of ABS plastic: extrusion grade, flame-retardant grade, injection molding grade, and other grades.
ABS Extrusion Grade
ABS extrusion grade is the most commonly used type of ABS plastic due to its versatility and low cost. It has good strength properties and excellent electrical insulation properties.
This grade is typically used for products such as pipes and tubes where high-impact strength and chemical resistance are required. Additionally, the glossy finish achieved with ABS extrusion can be enhanced with additives if desired.

ABS Flame-Retardant Grade
When flame-retardant qualities are needed for an application involving ABS plastic parts or components, ABS flame-retardant grade should be considered.
This type of ABS is often used in automotive interiors due to its ability to meet stringent fire safety standards without sacrificing performance or durability.
Furthermore, since it contains flame retardants that comply with regulations like UL 94 V-0 or UL 94 5VA standards—it can provide more protection from fire than other grades of ABS plastics when properly applied in certain applications.
ABS Injection Molding Grade
ABS injection molding grade is recommended when manufacturing complex parts or components through injection molding.
Its combination of impact strength and rigidity makes it a better choice than other types of thermoplastics like polystyrene or polypropylene, which tend to lack these characteristics during high-pressure injection molding operations.
Additionally, using this type of ABS can produce higher quality parts with fewer inconsistencies due to its stiffness and heat resistance, which allow it to achieve precise detail without warping or distortion during the cooling process after the injection molding operation is complete.

The Other Grades Of ABS Plastic
Aside from the aforementioned grades of ABS plastic materials, there are several others, including FDA-approved food grading materials, anti-static electroconductive materials, glass filled materials designed for increased rigidity.
Moreover, there is rubberized soft touch material that provides flexibility combined with improved grip; UV stabilizers that protect against fading from exposure to sunlight; lubricated materials designed for reduced friction; and conductive materials created specifically for electrical insulation in electronic components.
3 Main Methods For Manufacturing ABS Plastics
The manufacturing of plastics is a complicated and intricate process that requires the use of various techniques and processes.
To ensure the quality of ABS products, manufacturers must use the right processes for producing them. Here are three of the most common types of processes for manufacturing ABS plastics:
3D Printing for ABS
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process where layers of plastic material are melted together to form an object. This form of 3D printing is suitable for producing complex shapes with precise details as well as enclosures and covers.
The layer-by-layer approach allows parts that feature intricate internal geometries, such as wall thickness variations or overhangs, to be easily produced from ABS material.
Additionally, this method allows for rapid prototyping and low-cost production when compared to other traditional forms of manufacturing.
CNC Machining for ABS
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining involves using computer software to direct cutting tools to shape a block or sheet of material into an object.
CNC machining is capable of producing high-precision parts while also offering greater control than manual machining methods. It offers flexibility when it comes to design modifications without extensive tooling costs and set-up times associated with conventional machining processes.
CNC machines are often used in the manufacturing process when working with larger pieces or batches of ABS materials due to their ability to produce complex structures quickly and accurately.

Injection Molding for ABS
Injection molding has become one of the most popular methods for mass production today due to its accuracy and cost-effectiveness at large volumes.
Injection molding involves melting a thermoplastic resin-like ABS plastic before injecting it into the cavity of a mold tool under high pressure, which then cools down, forming the desired part or product shape.
The injection molding process enables manufacturers to produce highly detailed components while maintaining tight tolerances on dimensions with minimal waste generated during production runs due to its efficient use of materials.
The 5 Most Common Applications of ABS Plastics
ABS is resistant to heat and other environmental factors as well, and it can be easily molded into many different shapes. The material also offers good electrical insulation properties and flame retardant qualities.
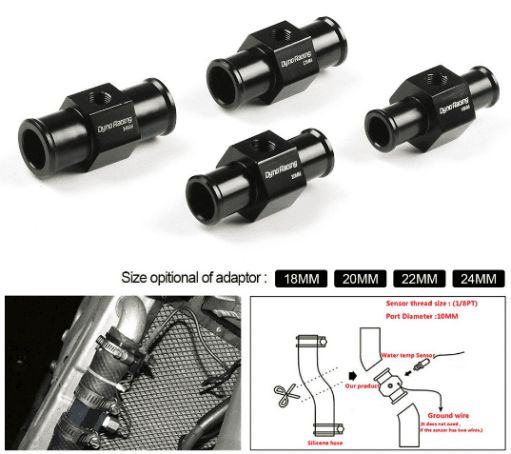
Automotive Parts
ABS plastic is widely used in the automotive industry for components such as bumpers, spoilers, dashboards, instrument panels, seats and trims, skid plates, airbag covers, door handles, mirror housings, and more.
Its durability makes it perfect for parts that are exposed to outdoor elements or need to stand up to wear from frequent use indoors or outdoors.

Computer Cases
ABS plastic is often used in the manufacturing of computer cases due to its shock-resistant properties. It provides excellent protection for sensitive technology components inside the case while still being lightweight enough for easy portability.
Printing
3D printing filaments made from ABS plastic are becoming increasingly popular among hobbyists who want reliable results when creating one-of-a-kind pieces or prototypes of products they’d like to manufacture commercially someday.
In addition to its strong mechanical properties and good surface finish quality, 3D printed objects made with ABS offer great visual appeal because they come out smooth with no visible layer lines present on their surface after printing has been completed.
Household Items
Not only is ABS suited for commercial purposes, but it also finds application in everyday items around the home, such as toys as well as hardware components like nuts & bolts found on TVs or furniture pieces like bed frames or chairs with metal joints, etc.
The material’s ability to resist shock makes it an ideal choice for children’s play toys that need to withstand multiple drops onto hard surfaces without sustaining any damage themselves nor resulting in injury if part of the toy becomes detached during playtime accidents.

Medical Devices
Due to its high shatter resistance and temperature stability properties, among other features explained above, ABS plastic is often employed in medical instruments such as syringes used in laboratories or non-invasive surgery tools employed by dermatologists during skin treatments, etc.
Its non-reactive nature allows instruments made with this material not to react with biological fluids ensuring better patient safety when these instruments are utilized during medical procedures.
However, its low weight ensures less fatigue for physicians using them over extended periods of time, allowing them better precision during their work compared with heavier instruments.
Those heavier instruments could lead to mistakes if handled sloppily due to doctor fatigue caused by their sheer weight alone over long hours spent performing operations on patients at the hospital ward etc.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Using ABS Plastic for Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a process that enables manufacturers and engineers to quickly create a physical representation of their product or component from a 3D CAD model.
It is widely used in the product development process due to its ability to quickly and accurately produce parts with complex geometries.
One of the most commonly used materials for rapid prototyping is acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). In this article, we’ll explore some of the pros and cons of using ABS material in rapid prototyping.
Advantages Of Using ABS In Rapid Prototyping
One of the major advantages of using ABS in rapid prototyping is its strength and durability. ABS has excellent mechanical properties, making it ideal for creating durable, functional prototypes that can withstand rigorous testing and use.
Additionally, ABS has good dimensional stability, meaning it retains its shape and size during long periods of use or exposure to heat or cold temperatures. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where accuracy and precision are critical.
Another advantage of using ABS in rapid prototyping is its cost-effectiveness. Compared to other materials, such as aluminum or stainless steel, ABS is relatively inexpensive and offers greater cost savings when producing larger quantities of parts or components.
Additionally, because ABS can be melted down and reused multiple times for different prototypes, manufacturers can maximize their investments by reusing materials instead of purchasing new ones every time a prototype needs to be made.
Disadvantages Of Using ABS In Rapid Prototyping
One major disadvantage of using ABS in rapid prototyping is its tendency to warp over time if exposed to certain environmental conditions, such as high temperatures or humidity levels.
This warping can lead to inaccurate parts that don’t meet specifications or aren’t suitable for final production purposes. As such, manufacturers should take steps to ensure that the environment where the prototype will be created is properly controlled prior to starting the process.
Additionally, while ABS offers greater cost savings compared to other materials such as aluminum alloys or stainless steel, it still requires more post-processing than these alternatives due to its relatively low surface hardness rating (Shore D scale).
This means that additional machining may be necessary before parts are ready for use; otherwise, they may not be able to withstand heavy loads or extreme temperatures without cracking or breaking down over time.
Conclusion
ABS plastics are widely used in many different applications due to their favorable mechanical properties and durability – making them ideal for engineering applications such as automotive parts, healthcare products, and electronics casing, among others.
Manufacturers have multiple options when it comes to producing ABS materials, including 3D printing, Small Batch CNC machining, and injection molding, which each offer distinct advantages depending on requirements such as volume, geometry complexity, accuracy tolerance levels, etc.

 info@yijinsolution.com
info@yijinsolution.com (+86) 188-2253-7569
(+86) 188-2253-7569