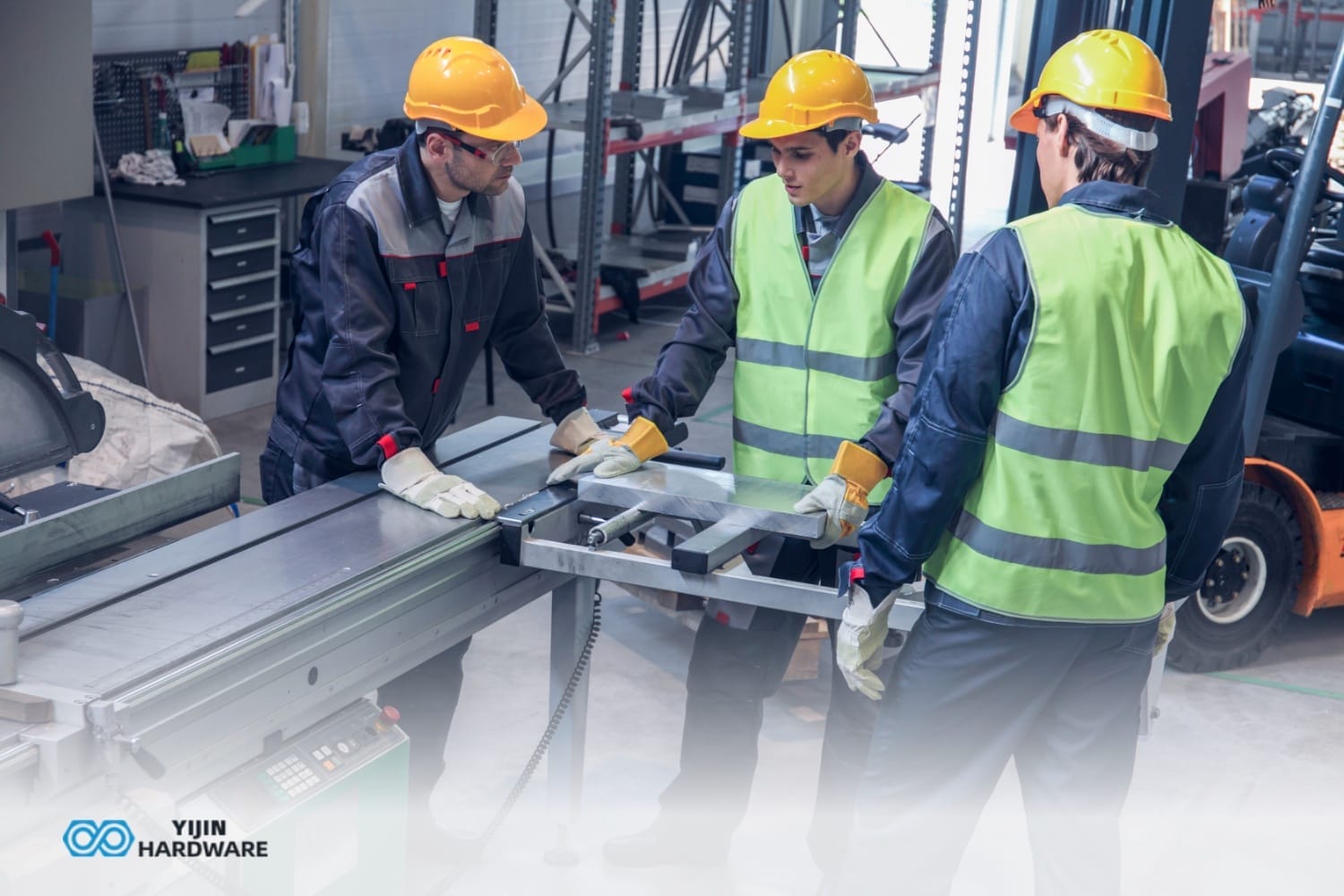
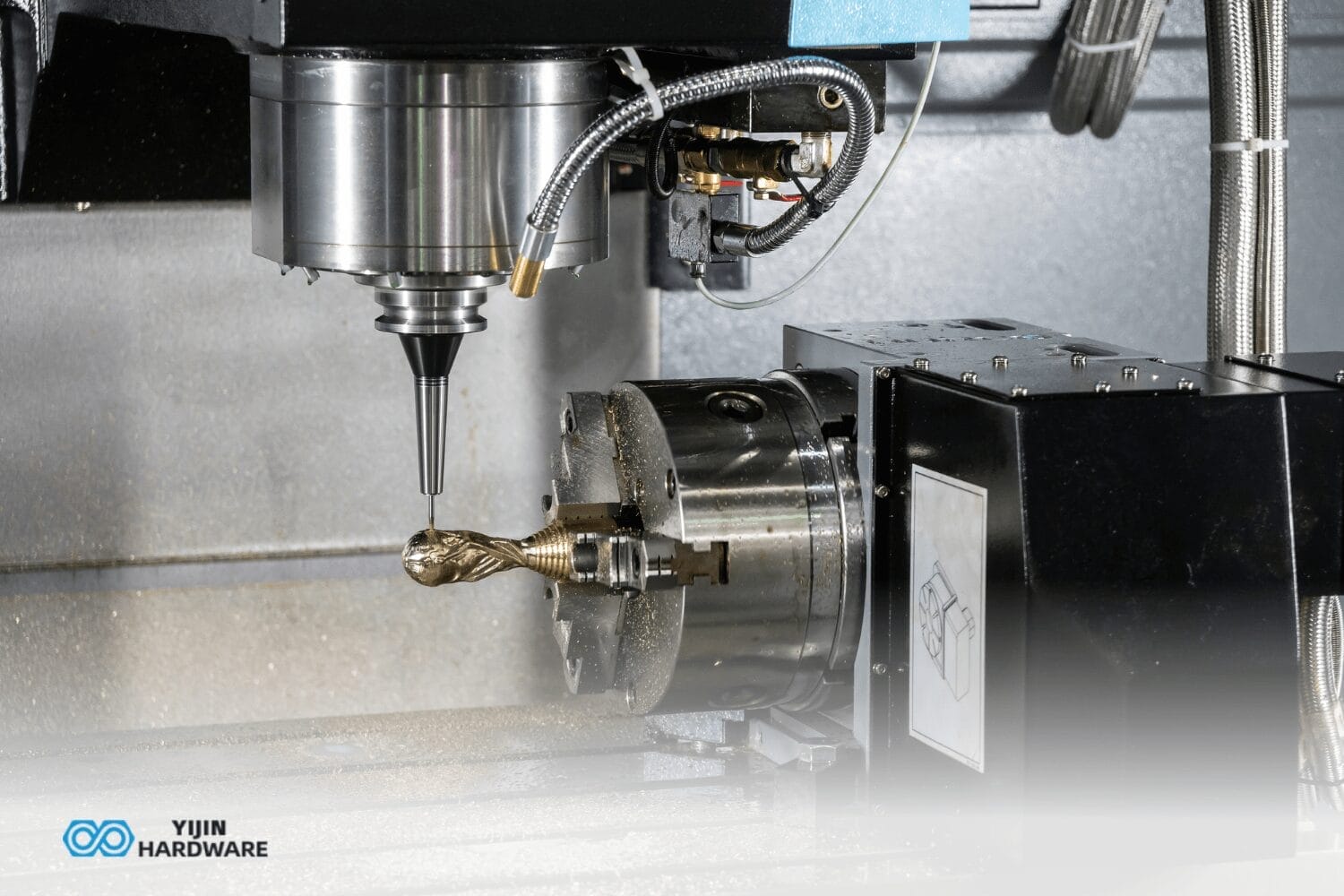
Ever wondered how machine shops make identical parts over and over? The secret is CNC machining fixtures. These specialized workholding devices secure parts during machining. At Yijin Hardware, we use fixtures daily in our factory. They’re essential for keeping parts exactly where they need to be.
Want to learn about CNC fixtures and how they can improve your manufacturing? We’re going to explain what a CNC fixture is, common uses in operations, and how your fixture material choice affects your manufacturing.
Key Takeaways
- CNC fixtures hold parts still while jigs guide tools – totally different jobs!
- Good fixtures cut setup time by 70% and reduce errors by 80%
- Proper fixture design uses the 3-2-1 principle to lock workpieces in place
- Material choice matters – steel, aluminum, or cast iron each have specific benefits
- Fixtures make automation possible through consistent positioning
What’s a CNC Fixture & How Does It Work?
A CNC fixture is basically a specialized clamp system that holds your workpiece exactly where it needs to be. These devices use locators and clamps to lock parts in place while a mill or other machine does its work.
Unlike jigs that guide the cutting tool, fixtures focus on gripping the part. Think of it this way – jigs control the tool, fixtures control the workpiece. Big difference in the machining process.
CNC fixtures use two main parts:
- Locators – pins and stops that position the part correctly
- Clamps – devices that hold the workpiece tightly
What CNC Fixtures Do

- Positioning: Puts your part exactly where it should be
- Stabilizing: Prevents movement during cutting
- Referencing: Creates consistent starting points for multiple parts
- Supporting: Stops the workpiece from bending while cutting
Common Types of Fixtures Used in CNC Operations
Jigs and fixtures come in many varieties based on what they need to do. Milling fixtures are probably the most common types you’ll see in shops. They’re designed to hold parts while the machine tool removes material using rotating cutters.
Drilling fixtures are specialized for making holes. They position the workpiece perfectly so drill bits hit exactly the right spots. Boring fixtures help enlarge and finish existing holes with precision. Each type can be classified by how they work and what they’re designed to do.
Turning fixtures like chucks and collets are used when the workpiece itself rotates, like on a lathe. Indexing fixtures are common types that allow you to rotate the part to specific angles for machining multiple sides. For shops that need flexibility, CNC vise setups remain one of the best ways to fixture simple parts.
Applications of CNC Fixtures by Industry
| Industry | Common Fixture Types | Key Benefits | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Custom jigs, multi-axis fixtures | Extreme precision, complex geometries | Aluminum, steel |
| Automotive | Modular systems, hydraulic fixtures | High volume, quick changeover | Cast iron, steel |
| Medical | Custom workholding fixture, vacuum systems | Biocompatible, complex shapes | Stainless steel, aluminum |
| Electronics | Small precision fixtures, vacuum plates | Miniature features, thin materials | Aluminum, plastic |
How to Choose the Right Fixture for Your Manufacturing Process
Picking the right fixture dramatically improves your CNC workflow. The manufacturing process determines which fixture will work best. For simple parts, a standard CNC vise might be perfect. For complex jobs, custom fixtures provide the best solution.
When deciding between a jig or fixture, remember their fundamental difference. Fixtures hold the workpiece in place while the machine does the work. CNC jigs, while less common nowadays, guide the cutting tool itself. In modern CNC operations, fixtures are often the better choice since G-code controls tool movement.
Start by analyzing your part: What surfaces need machining? How will you clamp without distorting the workpiece? How many parts will you make? For one-offs, simple setups work fine. For production runs, investing in proper fixture design pays off huge. Fixtures provide consistency that’s impossible to achieve with manual setups.
Fixture Selection Checklist
- Part geometry: Complex shapes need specialized holding strategies
- Material properties: Soft materials need gentle clamping
- Batch size: Higher volumes justify more sophisticated fixtures
- Required accuracy: Tighter tolerances demand better workholding
- Machine access: Fixture must allow tool paths without interference
- Setup time: Consider how quickly operators can load/unload parts
Different Types of CNC Fixtures for Various Machining Jobs
Not all fixtures are the same. Different jobs need specific fixture types. For CNC milling, you’ll see vise fixtures, angle fixtures, and fixture plates that hold parts against cutting forces.
In CNC turning, the setup is totally different. Chuck fixtures, collets, and mandrels grip round parts during spinning operations. The workholding needs to change completely when the part rotates!
For grinding, we use special fixtures to stop vibration. Magnetic chucks, sine bars, and centerless fixtures keep parts steady during finishing. And for boring operations, we need fixtures that keep everything perfectly aligned.
For precision work, many engineers rely on CNC turning parts Manufacturer and CNC milling China solutions from trusted brands like Yijin Hardware to ensure accuracy, consistency, and durability.
Special Fixture Types
| Fixture Type | What It’s For | Key Parts | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Table Fixtures | Cutting multiple sides | Indexing system, dividing head | Tool steel, cast iron |
| Modular Fixtures | Flexible manufacturing | Tooling plates, locators, clamps | Aluminum, steel |
| Vacuum Fixture | Holding thin materials | Vacuum pump, seals | Various materials |
| Custom Fixtures | Complex part shapes | Application-specific parts | Multiple materials |
Main Parts of a CNC Fixture
Every fixture starts with a solid foundation – the base plate. Think of it as the backbone of your setup. These modular fixture plates provide a sturdy mounting surface. They come in cast iron, steel, or aluminum. Most have T-slots or grid patterns for attaching other components.
Locating elements, position your workpiece. They touch specific surfaces on your part using pins, stops, and V-blocks. Good fixtures use the 3-2-1 principle – three points control the first plane, two points control the second, and one point controls the third. This locks your part completely.
The experts say that the CNC workholding market is going to be worth around $2.8 billion by 2033.
Types of Clamps
- Mechanical clamps: Toggle clamps, cam clamps, strap clamps, toe clamps
- Power clamps: Air cylinders, hydraulic units, electric motors
- Specialty clamps: Magnetic chucks, vacuum workholding systems
How Fixtures Make Manufacturing Better and Faster
Here’s the thing about manufacturing – consistency is everything. CNC fixtures make every part the same. Your first part matches your last, even after thousands of cycles. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, good fixtures can reduce errors by up to 80% compared to manual setups.
They’re also huge time-savers. Once you set up a fixture, operators can swap parts quickly. No more spending half an hour aligning each part! The Society of Manufacturing Engineers says fixtures typically cut setup time by up to 70%.
Main Benefits
- Better parts through consistent positioning
- Less scrap from positioning errors
- Longer tool life because cutting conditions stay stable
- More machine uptime from faster setups
- Safer operation with less manual handling
How Material Choice Affects Fixture Performance
Material choice makes a huge difference in how fixtures perform. For high-volume production, tool steel (A2, D2, O1) works best. These tough materials stay accurate even after thousands of uses. They resist wear where they contact the workpiece.
For lighter jobs or bigger fixtures, aluminum alloys (6061-T6, 7075-T6) are great. They’re lighter, easier to machine, and cheaper than steel. We use them often for prototype fixtures. Some shops even 3D print fixtures for quick one-off projects or weird shapes.
Material Comparison
| Material | Wear Resistance | Stability | Weight | Cost | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tool Steel | Excellent | Excellent | Heavy | High | High-volume jobs |
| Cast Iron | Very Good | Excellent | Very Heavy | Medium | Vibration-sensitive work |
| Aluminum | Fair | Good | Light | Low | Prototypes, low volume |
| 3D Print Materials | Varies | Good | Very Light | Medium | Custom prototypes |
Smart Design Tips for Better Fixtures
Good fixture design isn’t just about holding a part – it’s clever engineering. The foundation is the 3-2-1 locating principle we mentioned earlier. It ensures your workpiece is properly secured without distorting it.
Smart designers also analyze cutting forces. They figure out where the tool will push or pull and place clamps to counteract those forces. Using computer-aided design, we can simulate these forces before making anything. This ensures our fixtures hold parts securely without damaging them.
Important Design Considerations
- Tool access: Make sure nothing blocks the cutting tool
- Quick loading: Design for fast part swapping
- Chip clearing: Leave space for chips and coolant
- Crash prevention: Avoid tool/fixture collisions
- Operator comfort: Consider how people will use the fixture all day
How Yijin Hardware Can Help With Your Fixture Needs
At Yijin Hardware, we specialize in creating custom fixtures for tricky machining challenges. Our engineering team uses advanced software to test fixture designs before we make them. We simulate real machining conditions to catch problems early.
Our in-house CNC mill and turning centers are staffed by skilled machinists who understand workholding inside and out. We make fixtures in hardened steel, aluminum, and cast iron to match your exact needs. Every fixture gets thoroughly checked before delivery.
Top CNC Fixtures
CNC fixtures are workhorses in modern manufacturing. They hold workpieces exactly in place, making sure every part comes out identical. They slash setup times, reduce errors, and enable automation. The right fixture balances technical needs with practical considerations like quick loading and operator comfort.
Yijin Hardware brings years of expertise in fixture design to your manufacturing challenges. Need help with custom workholding solutions? Our team is ready to boost your production efficiency. Email us at info@yijinhardware.com or call +86-123-4567 to get started. Let’s make your next project faster, more accurate, and more profitable!
FAQs on What is a CNC Fixture?
How are fixtures different from jigs?
Fixtures and jigs do completely different jobs in the shop, though people mix them up all the time. Fixtures hold your workpiece in position, while jigs guide the cutting tool through bushings or templates. Modern CNC machines use G-code to control tool paths automatically, so jigs aren’t really needed anymore – fixtures are what you want for CNC work.
What’s the best way to hold small or complex parts?
For tiny parts, vacuum workholding works great on flat pieces, while 3D printed fixtures can create perfect nests for odd shapes. Another good option is using toe clamps with small contact points or vise jaws with custom pockets. These methods prevent distortion while keeping small parts exactly where they need to be during machining.
Do I need custom fixtures for my CNC project?
Look at your part shape, production volume, and accuracy needs compared to standard workholding options. If your parts have complex shapes, need machining from multiple sides, or if you’re making hundreds of identical pieces, custom fixtures make sense. When standard vises force compromises, investing in custom fixture design will pay off quickly in better parts and faster production.
Back to Top: What Is a CNC Fixture? Simple Guide to Workholding









