Computer numerical control (CNC) lathe parts manufacturing turns raw materials into really complicated parts with extremely high detailed levels of accuracy. These parts work together to achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm. We used our experience with CNC turning centers to create this full guide to the nine essential components.
They are the basic foundation of every CNC lathe machine. We want you to understand how these precision parts work together to give you the best productivity and machining precision.
Key Takeaways
- CNC lathe parts create a system where precision alignment between components is really important for accuracy
- The headstock, tailstock, and chuck create the “precision triangle” that determines machining quality
- The material composition of components (cast iron vs. metal fabrication alloys) makes a huge impact on vibration damping
- Modern control systems allow micron-level precision through advanced feedback mechanisms
- Preventative maintenance focused on bearings, ways, and alignment extends component life by 30-50%
- Understanding different types of CNC machine tools helps select the right equipment for specific applications
How do CNC Lathe Parts Work Together as a System?
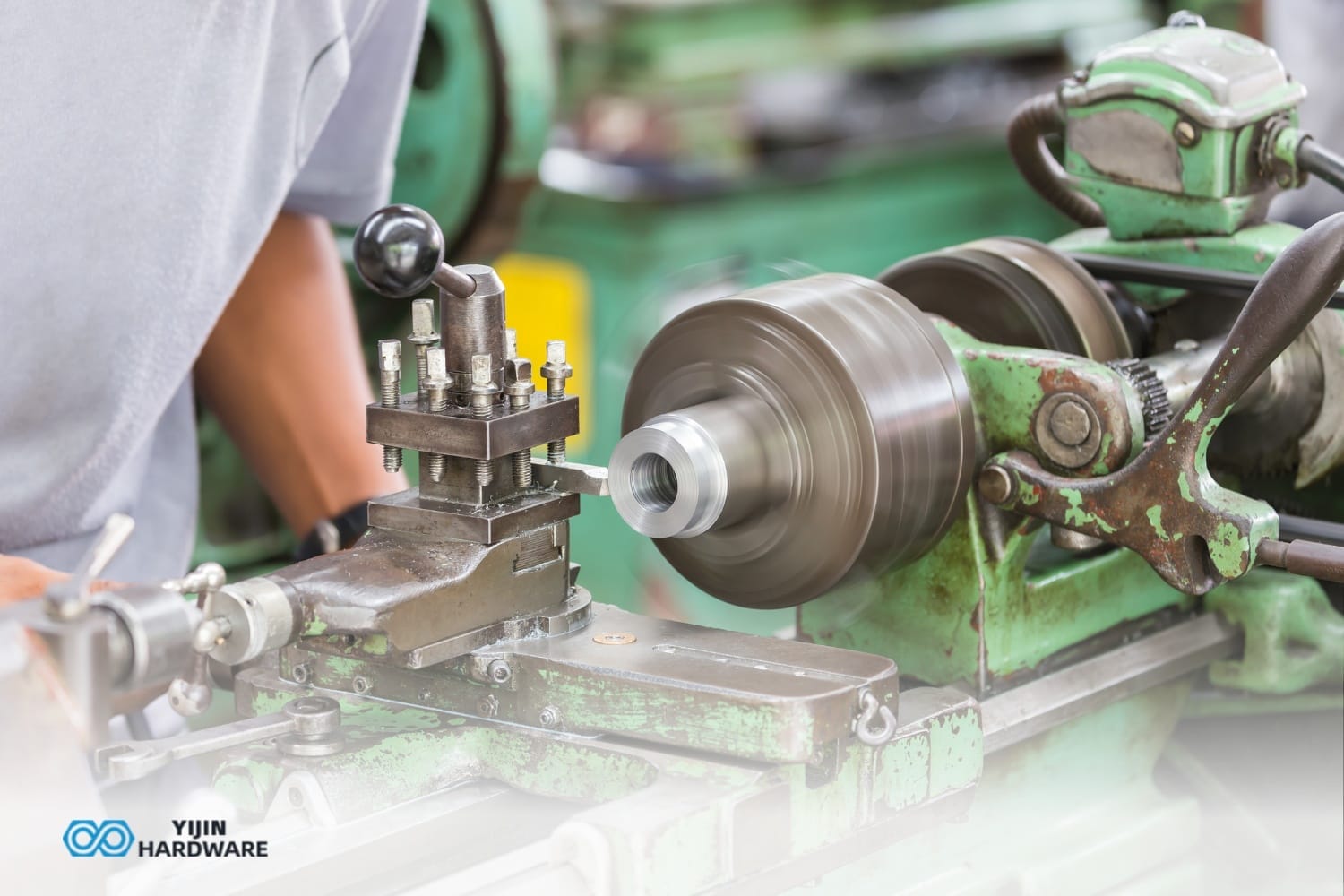

Parts of a CNC lathe create a system where each component plays a very specific role in the machining process. The headstock provides power, which is transferred to the workpiece through the main spindle and chuck. The lathe bed forms the foundation that maintains alignment between all parts of the CNC. The control panel interprets G-code instructions to coordinate the movement of the cutting tool relative to the material being machined.
Key System Interactions
- Power transmission: Motor → Headstock → Spindle → Chuck → Workpiece
- Motion control: Programming → Controller → Servo motors → Tool movement
- Structural alignment: Bed → Headstock → Tailstock → Tool turret positioning
The 9 Essential Components of CNC Lathes
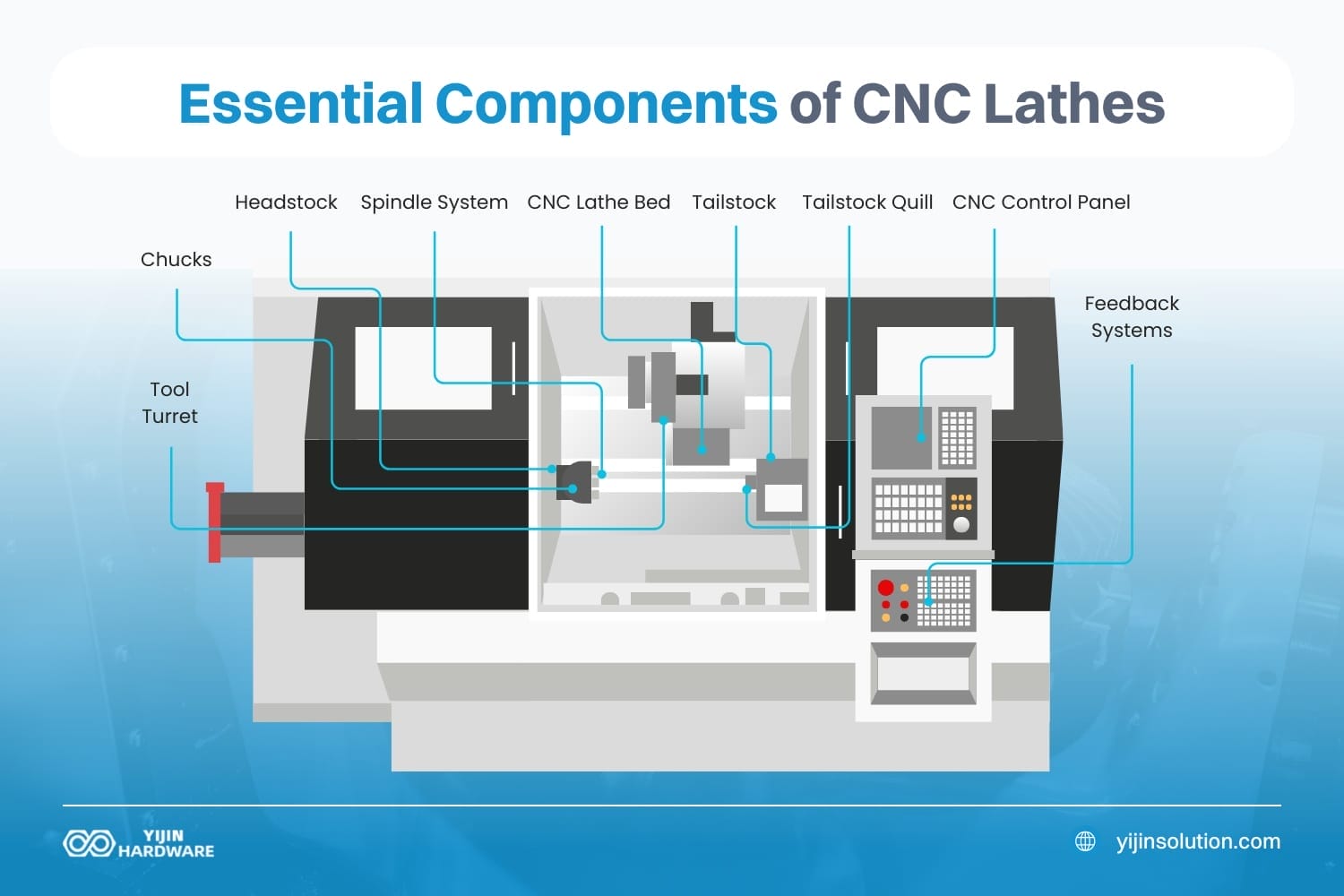
The most important lathe CNC machining parts are the headstock, CNC lathe bed, chuck, tailstock, tailstock quill, CNC control panel, tool turret, spindle system, and feedback systems. According to Coherent Market Insights, the global market for lathe machines is expected to be worth $29.65 billion in 2025 and grow to $42.88 billion by 2032, with an average yearly growth rate of 5.4% during that period.
1. Headstock
The headstock is the primary power center of a CNC machine, containing the motor and drive system that rotates the workpiece. This critical component houses precision bearings, gears, and the spindle, allowing for controlled rotational speeds from 50 to 6,000 RPM depending on the model. The headstock determines the lathe’s “swing” — the maximum diameter material that can be accommodated.
Headstock Bearings and Precision
- Angular Contact Bearings: Pre-loaded in pairs for axial/radial load management
- Hydrostatic Bearings: Use pressurized oil film to eliminate metal-to-metal contact
- Hybrid Ceramic Bearings: Silicon nitride rolling elements reduce thermal expansion
2. CNC Lathe Bed
The CNC lathe bed serves as the structural foundation that supports all other parts of the CNC lathe. This massive base component is typically made from cast iron to absorb vibrations and maintain dimensional stability during the machining process. The bed’s rigidity directly affects the machine tool’s ability to hold tight tolerances during heavy cuts.
Material Properties for Vibration Damping
| Material | Damping Capacity | Thermal Stability | Common Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | High | Good | General purpose |
| Granite Composite | Very High | Excellent | High precision CNC |
| Polymer Concrete | Excellent | Very Good | High-speed machines |
| Ductile Cast Iron | Moderate | Good | Heavy-duty cutting |
3. Chucks
Chucks are specialized devices that clamp and hold materials securely during turning operations. These critical CNC lathe parts come in several configurations including three-jaw universal chucks that self-center round stock with ±0.02 mm concentricity, four-jaw independent chucks for non-round workpieces, and collet chucks for high-precision bar work with runout as low as 0.005 mm.
Chuck Selection Criteria
- Workpiece geometry: Round (3-jaw) vs. non-round (4-jaw)
- Required precision: Standard (±0.02 mm) vs. high precision machining (≤0.005 mm)
- Material sensitivity: Hard jaws for robust materials, soft jaws for delicate surfaces
- Production volume: Manual vs. hydraulic or pneumatic actuation
4. Tailstock
The tailstock provides crucial support for longer workpieces during turning operations. This adjustable part sits opposite the headstock on the CNC lathe bed and prevents material deflection that would otherwise cause dimensional inconsistencies or chatter. The tailstock can be precisely positioned along the axis to accommodate workpieces of different lengths.
Tailstock Alignment Verification
- Position tailstock near headstock
- Mount precision test bar between centers
- Measure diameter at multiple points along test bar
- Adjust tailstock offset screws to correct any taper
- Verify alignment with dial indicator test
5. Tailstock Quill
The tailstock quill is a precision sliding cylindrical component within the tailstock that provides adjustable extension toward the workpiece. This critical element typically offers 100-300 mm of travel and houses Morse taper sockets (commonly MT3 or MT4) that accept various tooling and centers. The quill’s movement allows fine adjustment of support pressure and positioning.
Common Quill Applications
- Dead centers: Fixed support points for general turning
- Live centers: Rotating support for high-speed operations
- Drill chucks: For center drilling and hole operations
- Boring tools: For precision hole enlargement
- Reamers: For final hole size and surface finish
6. CNC Control Panel
The CNC control panel serves as the brain of the lathe, interpreting programmed instructions and converting them into precise machine movements. This sophisticated component interfaces with servo motors, encoders, and feedback systems to maintain positional accuracy as fine as 0.001 mm. The panel features a processor, memory for program storage, and a user interface for machine setup.
G-Code Programming Example
G00 X100 Z50 ; Rapid positioning
G01 X50 Z0 F0.2 ; Linear feed at 0.2 mm/rev
G02 X40 Z-10 R5 ; Circular interpolation
M03 S1200 ; Spindle on clockwise at 1200 RPM
7. Tool Turret
The tool turret holds multiple cutting tools and positions them precisely for machining operations. This automated component typically houses 8–16 tools that can be rapidly indexed into cutting position, eliminating time-consuming manual tool change procedures. Tool turrets achieve indexing accuracy of 0.001° or better, ensuring consistent tool positioning.
Tool Turret Configurations
- Standard Turrets: Static tool positions for lathe turning
- Live Tool Turrets: Include powered stations for mill operations
- BMT Turrets: Utilize modular tooling system for quick changes
- VDI Turrets: European standard for tool mounting precision
- Capto Turrets: Use a polygonal interface for maximum rigidity
8. Spindle System
The spindle system creates the precise rotational motion necessary for CNC turning. This critical component contains the main shaft, bearings, and drive connection that transfer power from the motor to the chuck. Spindle systems are rated by maximum speed (up to 6,000 RPM in standard CNC lathes) and torque capacity (typically 15-500 Nm).
Spindle Precision Factors
- Bearing Class: P4 bearings deliver 2-4 μm runout, P2 bearings under 1 μm
- Thermal Stability: Temperature-controlled bearing housings maintain alignment
- Balance Grade: G2.5 or better for high-speed operations
- Drive Type: Belt-driven vs. direct-drive affects vibration patterns
9. Feedback Systems
Feedback systems provide real-time position and speed information to the controller, enabling closed-loop control and exceptional machining precision. These critical components include linear scales with resolution down to 0.1 μm and rotary encoders that monitor how parts rotate with 0.001° precision. Feedback systems constantly compare the commanded position with the actual position.
Types of Feedback Systems
- Optical Linear Scales: Glass or metal scales read by optical sensors
- Magnetic Encoders: Resistant to coolant/contaminants
- Rotary Encoders: Monitor spindle speed and positioning
- Inductive Sensors: Detect tool presence and position
What Auxiliary Systems Support CNC Lathe Operations?
Auxiliary systems enhance CNC functionality through supporting capabilities like cooling, lubrication, and chip management. Coolant systems deliver cutting fluid directly to the tool-workpiece interface, reducing friction and extending tool life. These systems are vital for aerospace and aluminum parts production, where heat management is critical.
Advanced Auxiliary Technologies
- Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL): Reduces environmental impact
- Mist Collection Systems: Improve air quality and visibility
- Thermal Stabilization: Maintains consistent temperatures across components
- Auto Parts Catchers: Collect finished parts in sequential order
How to Select the Right CNC Lathe Components for Your Application?
Selecting appropriate CNC turning and milling equipment requires matching specifications to your specific manufacturing requirements. The introduction to CNC turning centers should begin with understanding whether you need to produce simple or complex parts. Material considerations affect component selection, with brass CNC and aluminum parts requiring different machining parameters than steel.
| Application Need | Critical Components | Key Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| High Precision CNC | Spindle, Bearings | Runout < 0.005 mm |
| Heavy Cutting | Headstock, Bed | Motor power, Rigidity |
| Long Workpieces | Tailstock, Bed | Support capacity, Length |
| Complex Parts | Control Panel, Turret | Program capacity, Tool positions |
Essential Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guidelines
Regular maintenance significantly extends CNC lathe life and maintains precision. Implement daily checks of coolant levels and cutting tool condition. Weekly tasks should include lubrication verification and chip accumulation removal. Monthly maintenance requires tailstock and headstock alignment verification using dial indicators.
For troubleshooting, implement a sequential approach: first check mechanical systems (loose bolts, worn bearings), then electrical connections, and finally control systems. Document all maintenance activities and create a component replacement schedule based on operating hours rather than waiting for failures. Listen for unusual sounds during operation—they’re often the earliest warning signs of impending component issues.
Yijin Hardware | Professional CNC Lathe Machine Work
Understanding the essential parts of a CNC lathe enables better machine selection, operation, and maintenance in the world of CNC manufacturing. Each component contributes to the system’s overall precision and capabilities, from the power-generating headstock to the carefully designed lathe bed and versatile tool turret. For custom CNC lathe applications, understanding these interconnections is crucial.
At Yijin Hardware, we provide customized CNC machining services including CNC turning and milling, sheet metal fabrication, and precision CNC machining. Our technical expertise with CNC lathe parts from China ensures we select and maintain the optimal machine configurations for your specific requirements. Contact us today for precision-turned parts that meet your exact specifications.
CNC Lathe Machine Parts FAQs
How do you properly align a CNC lathe for optimal precision turning?
Proper CNC lathe alignment requires a systematic approach to measuring multiple precision factors. First, check bed level using precision levels accurate to 0.02 mm/m along and across the ways. Next, verify headstock alignment using a test bar and dial indicator, adjusting until runout measures less than 0.005 mm. Finally, align the tailstock using the two-collar method, measuring diameters at both ends of a test piece to detect and correct any taper.
What are the signs of spindle bearing failure in a CNC lathe?
Spindle bearing failure in CNC machines manifests through several detectable signs. Unusual noise patterns, particularly high-pitched whining or rhythmic knocking, indicate bearing cage damage or roller defects. Excessive vibration measured with accelerometers shows frequencies corresponding to bearing elements. Temperature increases beyond the normal operating range (typically >5 °C above baseline) suggest lubrication breakdown. Finally, dimensional inconsistencies in machined components, especially with varying diameter measurements, indicate bearing wear affecting spindle rigidity.
How do IT technologies enhance modern CNC lathe performance?
IoT technologies transform CNC machine performance through real-time monitoring and predictive capabilities. Vibration sensors detect slight changes in bearing or drive conditions before they cause quality issues. Production monitoring systems track cycle times, tool life, and part counts to optimize scheduling. Remote connectivity allows programmers to update G-code or troubleshoot issues without machine downtime. Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze operational data to forecast component failures before they occur, reducing unplanned downtime by up to 45%.
Back to Top: CNC Lathe Machine Parts