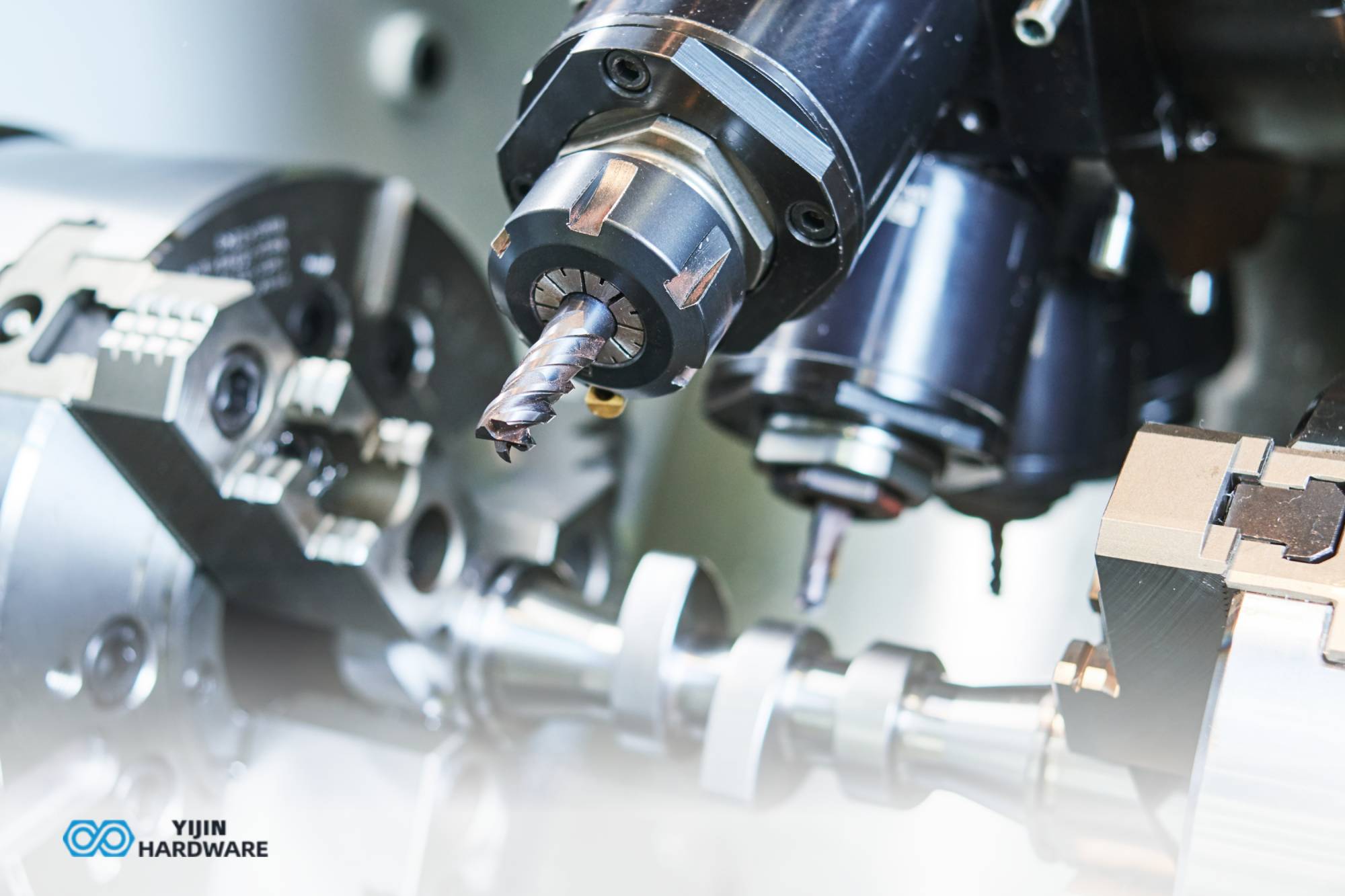
All of us know the term CNC milling. Everyone is talking about it and written some basic concepts which are already available on internet in abundance. But today, along with the fundamentals of CNC milling operations, you will read the latest developments also.
Key Takeaways:
- What is CNC milling definition?
- Applications of CNC Milling
- Process of CNC Milled Parts
Similarly, the concept of hybrid machining is here. Now, machining companies can combine CNC milling with 3d Printing technology. It helps in manufacturing custom parts with complex designs. (Research by Silva et al. 2022).
So with growing innovation in CNC milling, machining centers can develop:
- Custom-designed orthopedic implants
- Microfluidic chips for diagnostics
- Bioprinting of new tissues and organs
Simultaneously, the economical growth of CNC milling industry is also significant.
1; Grand View Research states that the global CNC machining market is projected to reach a value of over $40 billion by 2028.
What is CNC milling definition?
Just imagine, you want to make a toy car with a lump of clay. But you don’t have any tool for that. Why don’t consider a milling machine? This machine converts any raw material into a particular design. Let’s discuss further:
“CNC machining is a subtractive process. It means, you need a material to give it a specific shape.” CNC milling consists of two words:
1: CNC
2: Milling
CNC is “Computer Numerical Control”. It means computer controls the entire process.
The second term is milling. It is a cutting tool. This tool cut the material to give a particular shape. The material for CNC milling include plastics to metal.
| Material | Alloys | Tolerance Level |
| Aluminum | * 6061 (general purpose) * 7075 (high strength) * 5052 (excellent corrosion resistance) | ±0.005″ (±0.13 mm) |
| Steel | * AISI 1018 (low carbon) * AISI 4140 (chromoly, good strength) * 304 Stainless Steel (corrosion resistant) | ±0.002″ (±0.05 mm) |
| Stainless Steel | * 304 (most common, versatile) * 316 (higher molybdenum content, corrosion resistance) * 17-4 PH (high strength) | ±0.002″ (±0.05 mm) |
| Brass | * C260 (free-machining) | ±0.004″ (±0.10 mm) |
| Copper | * C110 (electrolytic tough pitch) * C170 (high conductivity) | ±0.005″ (±0.13 mm) |
| Plastics | * ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) * POM (polyoxymethylene) * Delrin (brand name for POM) | ±0.003″ (±0.08 mm) |
| Wood | * Hardwoods (oak, maple) * Softwoods (pine, cedar) | ±0.010″ (±0.25 mm) |
Ok, you must have the basic understanding of CNC milling. Yet, we have only discussed the definition. Till know, we understand that CNC milling is a process to shape any material into a specific product. Let’s move further.
CNC Milling vs. CNC Turning: What is the difference?

CNC Milling vs Turning come under CNC machining but they are different in processing materials. Sounds complicated? Let’s explore further.
- CNC Milling: A rotating cutting tool removes material from a workpiece (raw material). The tool moves along multiple axes (X, Y, and Z). Later, on the final stage, you get a complex 3D shape.
- CNC Turning: In CNC turning, the workpiece itself rotates on a spindle. CNC machining centers make cylindrical parts with it.
How does CNC Milling work?
One of the major advantage fo CNC milling is its capacity to handle a range of shapes. Since modern metalworking industries are booming, precision is in demand. Earlier, it was quite difficult to make parts with tighter tolerance. Now, with the modern 5axis milling machines, you can effortlessly meet the accurate designs.
But the question is what the whole process is?
CNC Controller: This is the control center of the operation where the computer software that interprets the digital design (CAD model) into a set of command is located.
Machine Tool: This is a mechanical system. It supports the work piece and the cutting tool. It helps them to glide smoothly along the planned axes in accordance with the controller of the CNC machine.
Cutting Tool: Cutting tools generally incorporate materials like carbide or diamond. However, its core function is removes the material. Machining companies use different types of the cutting tools. This depends on the design and tolerance level.
Workholding System: This firmly holds the work piece on to the machine bed in order to avoid movement during the cutting operation.
The CNC controller meticulously coordinates these elements. It transmits instructions to the motors that govern the movement of the axes, dictating the cutting tool’s path and depth. This controlled removal of material transforms the raw block into the envisioned final product.
Types of CNC Milling Operations

1. Face Milling
- Function:Creates a flat and even surface on the top of a workpiece.
- Technical Details:
- Cutting Tool: A flat-faced end mill with multiple cutting edges is undertaken. However, the number of cutting edges impacts machining capacity.
- Toolpath: The cutting tool traverses a back-and-forth path across the entire top surface of the workpiece. It gradually removes material to get a flat plane.
2. Peripheral Milling:
- Function:Makes slots, pockets & grooves along the periphery (edge) of the workpiece.
- Technical Details:
- Cutting Tool: End mills with various diameters. Similarly, machinists incorporate cutting edge geometries. It depends on the desired slot width and profile. Ball nose end mills can create curved features.
- Toolpath: The cutting tool follows a programmed path along the designated edge of the workpiece, precisely removing material to create the required slot, pocket, or groove.
3. Slotting:
- Function:Creates elongated, narrow channels within the body of the workpiece. Imagine digging internal trenches or pathways within the material.
- Technical Details:
- Cutting Tool: Narrow-diameter end mills are specifically chosen for slotting due to their ability to access and remove material from confined spaces.
- Toolpath: The cutting tool follows a programmed path along the designated location within the workpiece, typically in a straight line or a defined curve for specific features.
4. Pocketing:
- Function:Removes material from a designated area within the workpiece, creating a recessed pocket. Think of scooping out a specific region to create a cavity.
- Technical Details:
- Cutting Tool: Same as in peripheral milling, various size of end mills are incorporated for milling the pocket. Simultaneously, it depends on the size and shape of the pocket. Ball nose end mills can produce a cove cut or rounded corner pockets.
- Toolpath: The cutting tool moves along the path that is pre-set for the pocket’s shape. The tool follows a raster pattern whereby the passes made are in a back-and-forth manner. Its job is to trim the unwanted material in the last stage of designing.
5. Contour Milling:
- Function:Creates complex and intricate two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) shapes on the surface of the workpiece.
- Technical Details:
- Cutting Tool: In this scenario, all nose end mills are standard tools for contour milling. They can effortlessly bring smooth curves.
- Toolpath: The cutting tool follows a highly precise path. This design comes from CAD model. It dictates the tool’s movement along multiple axes. At the end, you get the final shape.
6. Thread Milling:
- Function:Develops high-precision internal /external threads on the workpiece.
- Technical Details:
- Cutting Tool: Machinists undertake specialized thread milling tools with a specific thread profile. These tools typically have multiple cutting inserts.
Types of CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines have various configurations. Each is used to manufacture specific product. For example;
There can be three to five axes in a CNC machine. This number depends on the:
- Machining center
- Operating capacity
- Type of log entry
- Cutting Machines
- Part design.
There are:
- Left to right (X-axis)
- Front to back (Y-axis)
- Up and down (Z-axis)
- 180 degrees in X-plane
3 Types of CNC Machines
- 3-Axis CNC Machines: X, Y, and Z. The workpiece sustain a solid position. Simultaneously, the cutting tool operates along the X, Y, and Z planes. It is used at this stage where there is a lot of detail and complex features. Machinists use it in automatic operations to mill slots and cut sharp edges.
- 4-Axis CNC Machines: X, Y, Z, and one additional rotational axis. It allows cutting on an additional axis and is used when a hole has to be made on the side or a cut has to be made there. This rotary movement can clip and remove material from both sides.
- 5-Axis CNC Machines: Machining can be performed from all five directions using two of the three rotational axes. 5-axis machining allows 180° rotation through the X, Y, and Z axes. It takes more time to program such a machine because it is used to make very complex parts.
For further reading, feel free to read their comparisons:
3-Axis vs 5 Axis CNC Machining
How much does CNC Milling cost?
CNC milling involves variable costs, and various factors can affect it. The material you will use is significant as the more rigid the material is, the more it will cost the machine. Also, designs with many features and close tolerances are time-consuming to code and incorporate frequent tool changes, increasing costs.
Also, the production volume is critical because large orders reduce the cost per unit, whereas small orders, such as prototypes, can be costly. It also takes more time to machine complex shapes or parts with deeper cavities, which is expensive. Last, the price of a machine shop may also differ, and it is recommended to seek a quotation from a number of shops to get the most reasonable one.
CNC Milling Cost Table According to Materials
Sure, here is the table with a 1px solid black border for the contents:
| Factor | Aluminum | Brass | Stainless Steel | Titanium | Plastics |
| Material | Lower | Moderate | High | Highest | Moderate (depends on type) |
| Order Size | * Single prototype: $50-$100 * Batch of 10 parts: $30-$50 | * Single prototype: $75-$125 * Batch of 10 parts: $40-$60 | * Single prototype: $125-$200 * Batch of 10 parts: $75-$100 | * Single prototype: $200-$300+ * Batch of 10 parts: $100-$150 | * Single prototype: $40-$80 * Batch of 10 parts: $20-$40 |
| Surface Finishing | As-machined (lowest) | Minor increase for deburring/cleaning | $15-$40+ per part for sanding/polishing, anodizing adds additional cost | $20-$50+ per part for sanding/polishing | $5-$20+ per part |
| Part Complexity | Lower for simple 2.5D parts | Moderate for moderately complex 3D parts | High for complex 3D parts with tight tolerances | Highest for highly complex 3D parts with tight tolerances | Increases for complex designs |
What Custom Parts Can You Make With CNC Milling?
Aerospace:
In CNC milling, machining companies are making parts like:
- Engine parts
- landing gear components
- And airframe structures.
These all parts require high-strength alloys.
Automotive:
As discussed above, the engine parts are high in demand. Latest developments are EV machining. Hybrid vehicles require custom automotive parts with tighter tolerance. Some of the major examples of automotive parts are:
- Engine blocks
- Transmission housings
- Custom car parts
Medical Devices:
With each passing day, medical industry is evolving. Big machines have reduced in size. However, they have improved results. Since medical field is complex, it needs high-precision metal milling parts. Some of the major medical milled parts are:
- Surgical instruments
- Prosthetics
- Implants
Consumer Electronics:
A significant shift in technology is ahead in electronics industry. Electronic companies are looking for more durable and smarter ways to access their customers. Hence, the competition is also high in making more efficient parts.
- Housings for laptops
- Smartphones
- General purpose electronic devices
Prototyping:
Prototyping is a common practice in CNC machining shop. It reduces time and cost of the manufacturer before the product goes into massive manufacturing. CNC milling is addressing this technology in the following ways:
- Functional prototypes
- Design validation
- Testing before mass production.
Advantages of CNC Milling
- CNC Milling machines are fully automated. Previously, manual machining methods were not accurate. Moreover, the chances of mistakes were higher. And it was time consuming also.
- You can get maximum accuracy of complex designed parts
- Waste is almost minimum. Since it is automated, material waste had reduced significantly in CNC milling.
- Rapid turnaround ensures maximum production. You can produce parts in bulk orders.
Get the Most of CNC Milling with Yijin Hardware
 At Yijin Hardware, we have state-of-the-art CNC milling machines. Our machining center is equipped with latest 3-axis and 5-axis CNC milling machines. Simultaneously, we can execute a range of materials and offer full-range of surface finishing.
At Yijin Hardware, we have state-of-the-art CNC milling machines. Our machining center is equipped with latest 3-axis and 5-axis CNC milling machines. Simultaneously, we can execute a range of materials and offer full-range of surface finishing.
Yijin Hardware collaborates closely with its clients to meet their design requirements. Therefore, we ensure higher precision, and rapid turnaround time.

 info@yijinsolution.com
info@yijinsolution.com (+86) 188-2253-7569
(+86) 188-2253-7569