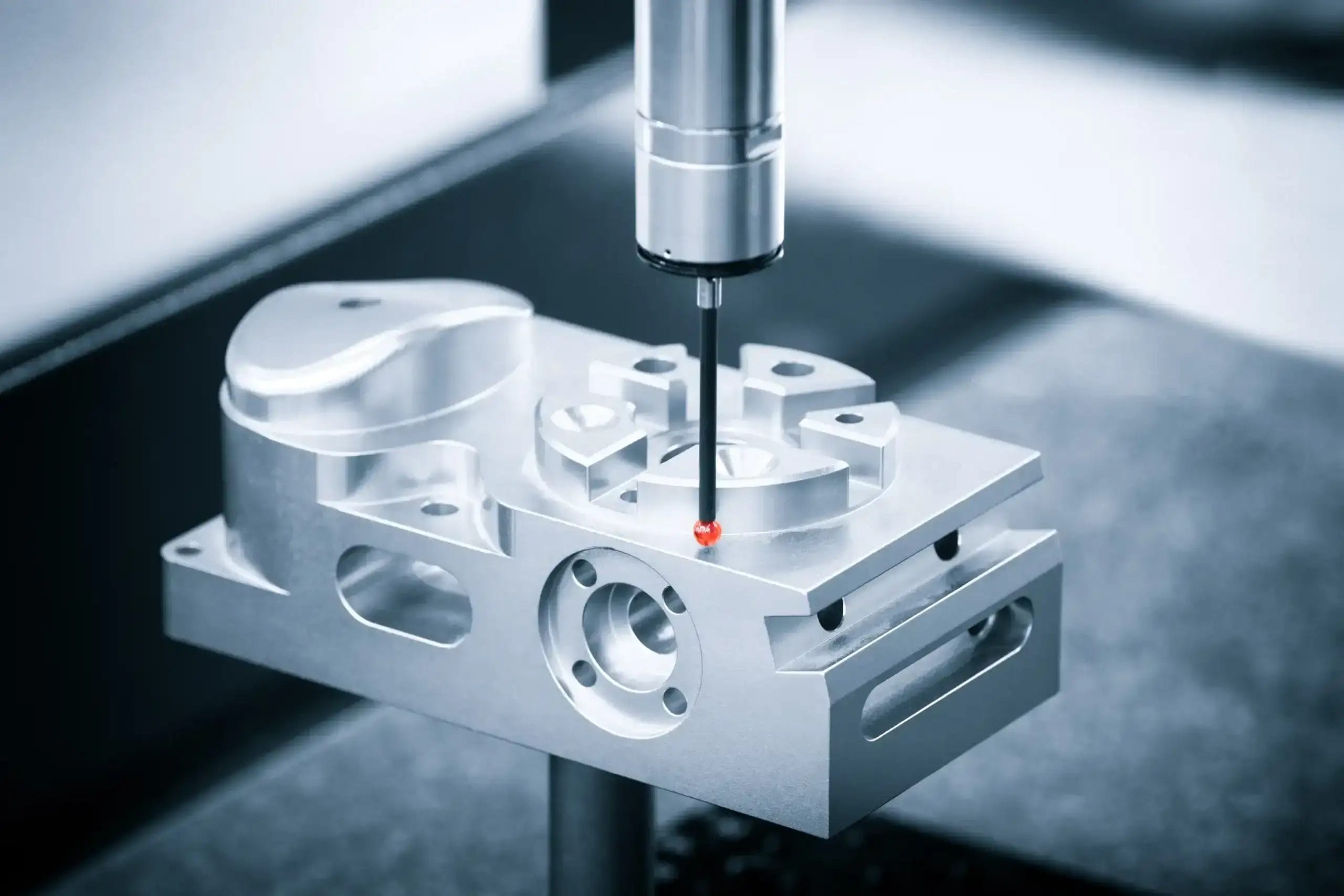
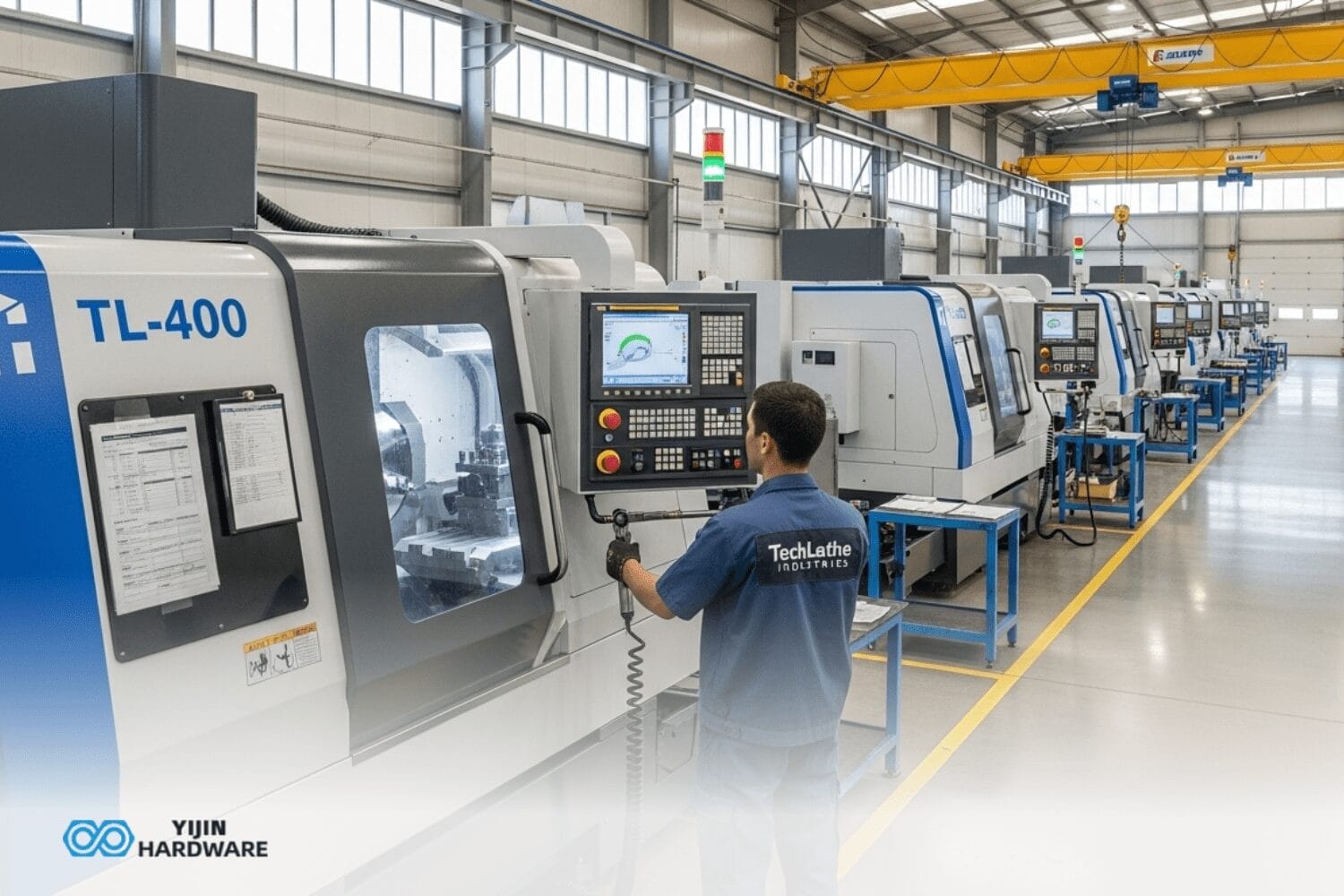
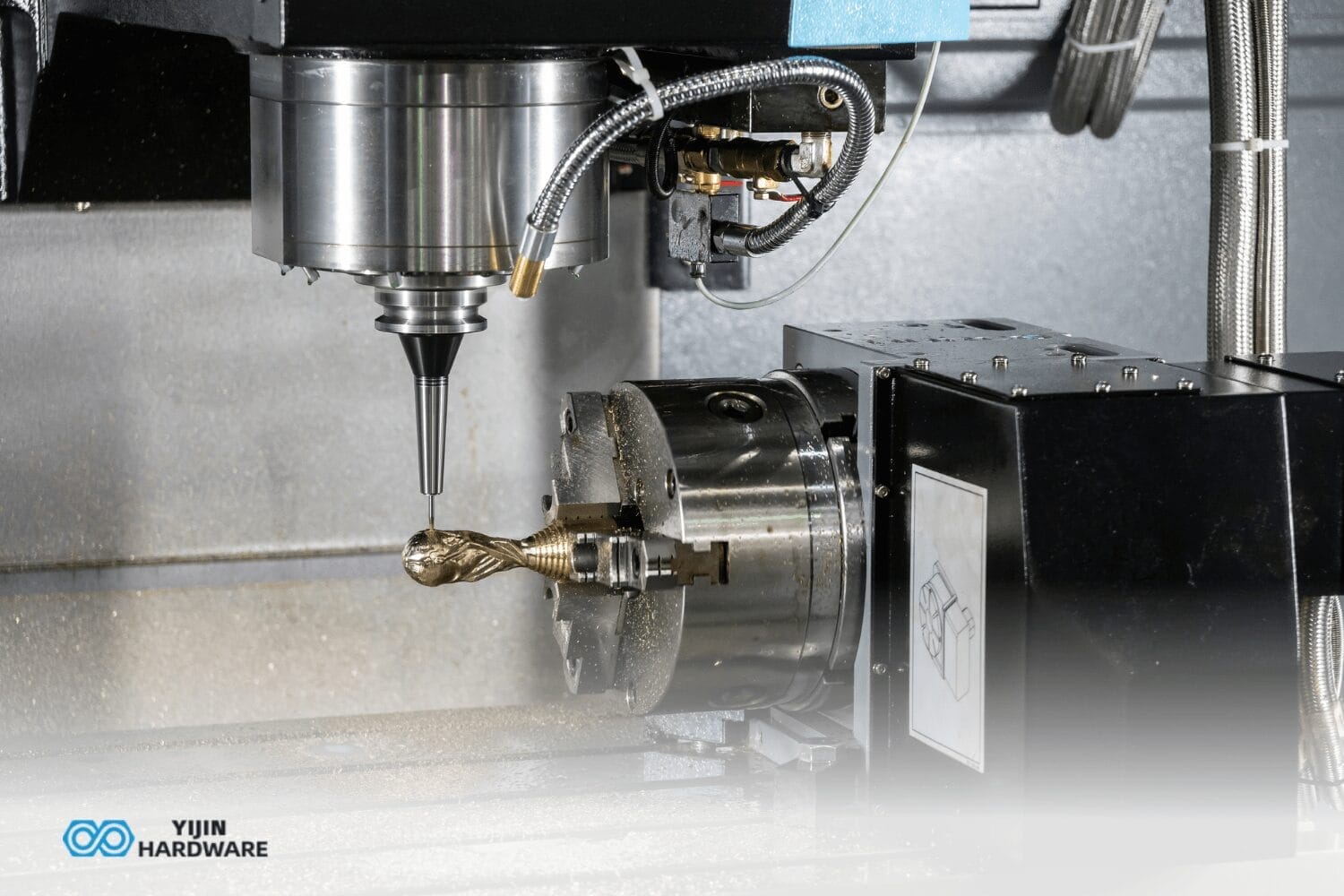
Working with titanium brings you very interesting challenges because of its special properties. At Yijin Hardware, we easily handle these challenges with our titanium CNC machining services. Our CNC mill turns this exceptionally durable metal into quality titanium parts. We take care of every grade of titanium, as our machines make parts for aerospace, medical industries, and tons more.
Key Takeaways
- Our CNC machine achieves tight tolerances of ±0.005 mm on complex titanium alloy shapes
- We use special tools with titanium aluminum nitride coating and cooling systems to prevent heat buildup
- We work with all types, from pure titanium to grade 5 titanium
- We follow ASTM B265/B348/B367 standards with full testing options
- Our special cooling and stress-relief methods keep parts in top shape
What is Titanium CNC Machining?

Titanium CNC machining is how we remove material from titanium using computer-controlled tools. This machining process needs special cutting tools and careful heat control. The CNC mill follows preset paths to cut the metal through various operations. We can make complex machined titanium parts with perfect measurements.
Technical Specifications
- Material Removal Rate: 10-30 cm³/min (depending on grade)
- Typical Cutting Speed: 40-150 m/min
- Feed Rate: 0.1-0.3 mm/tooth
- Depth of Cut: 0.2-1.5 mm
Why is Titanium Ideal for CNC Machined Parts?
Titanium offers the highest strength-to-weight ratio of any structural metal, making it perfect for lightweight applications requiring durability. At 4.5 g/cm³, titanium is 45% lighter than steel yet provides comparable high strength, with grade 5 titanium exceeding 1,000 MPa tensile strength. This alloy also forms a protective layer that delivers excellent corrosion resistance in harsh environments, while maintaining mechanical properties at extreme temperatures up to 430 °C (806 °F).
Thermal Properties
- High Melting Point: 1,668 °C (3,034 °F)
- Low Thermal Conductivity: 17 W/m·K (vs. 50 W/m·K for steel)
- Maximum Service Temperature: 538 °C for Ti-6Al-4V
Mechanical Properties
| Property | Commercially Pure | Ti-6Al-4V | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 434 MPa | 950-1,200 MPa | Exceeds many steels |
| Young’s Modulus | 103-107 GPa | 114 GPa | ~50% of steel |
| Fatigue Strength | 250 MPa | 510 MPa | Superior to most metals |
| Hardness | 70-90 HRB | 30-40 HRC | Less than hardened steel |
What are the Different Titanium Grades Used in CNC Machining?
Different titanium grades vary in composition, material properties, and machining characteristics. Grade 1 is the softest with the highest ductility, ideal for chemical processing equipment. Grade 2 titanium offers a good balance of strength and corrosion resistance for marine applications. Ti-6Al-4V (grade 5 titanium) combines 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium for exceptional performance in aerospace industries and medical implants. In fact, the aerospace titanium machining market was valued at USD 4.9 billion globally in 2023, according to Spherical Insights.
| Grade | Composition | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Commercially pure, the lowest oxygen | Highest ductility | Chemical processing |
| Grade 2 | Commercially pure, standard oxygen | Balanced properties | Marine equipment |
| Grade 5 | 6% Al, 4% V alloy | High strength, heat resistance | Aerospace, medical |
| Grade 23 | Extra-low interstitial | Superior biocompatibility | Medical implants |
ASTM Standards Compliance
- ASTM B265: Sheet, strip, and plate titanium specifications
- ASTM B348: Bar and billet specifications
- ASTM B367: Casting requirements
How does the Titanium CNC Machining Process Work at Yijin Hardware?
The machining process at Yijin Hardware follows a systematic workflow designed to handle the challenges of milling titanium while maximizing part quality. We begin by selecting the appropriate grade for your application, followed by programming that employs specialized cutting techniques to maintain consistent cutting forces. Our process uses rigid setups and special cutting edges with coatings designed specifically for titanium’s properties.
Specialized Machining Techniques
- Stress-Relief Treatment: 595-705 °C (1,100-1,300 °F) for 1–2 hours before cutting
- Cryogenic Cooling: Liquid nitrogen application for thermal management
- Ultrasonic Machining: Vibration-assisted cutting to reduce forces
- Minimum Quantity Lubrication: For finishing operations
Advanced Toolpath Strategies
- Trochoidal Milling: Curved toolpaths maintaining consistent engagement
- Plunge Roughing: Axial cutting to minimize lateral forces
- Climb Milling: Tool rotation matching feed direction for better chip formation
- High Feed Milling: Specialized tools with higher cutting speeds
What Challenges Must Be Overcome When Machining Titanium?
CNC machining with titanium presents several technical challenges that require special approaches for successful machining. Titanium’s low thermal conductivity concentrates heat at the cutting interface, causing rapid tool wear and potential damage. The metal’s chemical reactivity causes titanium surfaces to adhere to cutting tools above 500 °C, leading to quality issues and tool failure.
Heat Management Solutions
- High-Pressure Coolant: 70+ bar (1,000+ PSI) directed at cutting zones
- Cryogenic Cooling: Maintaining temperature below critical levels
- Thermal Analysis: Infrared monitoring during machining
- Optimized Parameters: Lower speeds with higher feed rates
Tool Wear Prevention
- Tool Materials: Carbide with cobalt binders (6-12%)
- Special Coatings: TiAlN, AlCrN for thermal and chemical barriers
- Edge Preparation: Microgeometry optimization for strength
- Tool Path Control: Maintain consistent chip thickness
What Surface Finishes Can Be Applied to Machined Titanium Parts?
Surface finish options enhance both functionality and aesthetics of CNC machined titanium parts. Mechanical polishing creates mirror-like surfaces for medical and aerospace applications, achieving smoothness as low as 0.1 μm Ra. Anodizing creates controlled oxide layers in various colors, improving wear resistance while adding visual appeal.
Available Finishes

- Mechanical Polishing: 0.1-0.4 μm Ra
- Type II Anodizing: 0.5-0.8 μm thickness, multiple colors
- Bead Blasting: Uniform matte finish, 1.6-3.2 μm Ra
- Chemical Etching: Controlled pattern creation
- Passivation: Enhanced protection layer
What Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities Set Yijin Hardware Apart?
Yijin Hardware offers hybrid manufacturing that combines additive and subtractive processes for titanium machined parts. Our electron beam technology creates near-net shapes that we then precisely machine, reducing material waste by up to 60% compared to traditional methods. This approach is valuable for complex engine components where material use is a key cost consideration.
What Industries Benefit Most from Titanium CNC Machined Parts?
Titanium parts in the aerospace industry represent the largest application sector, with titanium comprising up to two-thirds of modern aircraft engine components. Jet engine manufacturers use titanium for fan blades, compressor discs, and structural frames due to its performance at extreme temperatures and excellent fatigue resistance. The weight reduction directly translates to fuel savings, making titanium alloy parts economically viable despite higher material costs.
Medical industries benefit from titanium’s biocompatibility, with the metal forming the foundation for implants, surgical instruments, and prosthetics. Grade 23 titanium (ELI Ti-6Al-4V) is particularly valuable for implantable devices due to its exceptional purity and biocompatibility. Dental implants, bone screws, hip replacements, and pacemaker casings all rely on precisely machined titanium components.
Key Applications
- Automotive: Racing components, valve systems, connecting rods for high-performance engines
- Marine: Propeller shafts, pumps, and underwater equipment that resist saltwater corrosion
- Chemical Processing: Reactors, heat exchangers, and storage vessels for aggressive chemicals
- Energy: Components for geothermal, nuclear, and offshore installations
- Sports Equipment: High-end bicycle frames, golf clubs, and tennis rackets
Each industry leverages titanium’s unique combination of high strength, low weight, and corrosion resistance to solve specific engineering challenges where conventional materials fall short.
How to Evaluate Cost-Effectiveness When Using Titanium
Cost considerations for titanium CNC machining projects require balancing material expenses against long-term performance benefits. Raw titanium typically costs 5–10 times more than steel, with grade 5 titanium commanding premium prices due to its superior properties. However, proper analysis must account for the entire lifecycle, not just initial manufacturing costs.
Titanium Vs Alternative Metals
| Cost Factor | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Price | 30-50% of total project cost | Design optimization to reduce material waste |
| Tool Wear | 15-25% higher than with steel | Specialized tooling with longer service life |
| Machining Time | 30-40% longer processing times | Optimized cutting parameters and tool paths |
| Lifecycle Value | Extended service life (often 3x) | Calculate cost-per-year rather than initial investment |
Successful machining of titanium requires strategic approaches to minimize these cost factors. Using hybrid manufacturing techniques reduces material waste by up to 60% compared to traditional methods. Near-net-shape forming before final machining significantly lowers the amount of titanium removed through expensive cutting operations.
The key to cost-effective titanium use lies in design optimization. Parts designed specifically for titanium’s properties often require less material while maintaining performance targets. Additionally, titanium’s excellent corrosion resistance eliminates costly protective treatments and extends service life, creating substantial long-term value despite higher initial investment.
How Can You Optimize Designs for Titanium CNC Machining?
Design optimization for titanium balances performance with manufacturing efficiency to control costs. Wall thickness should be minimum 0.8 mm (preferably 1.2 mm or greater) to prevent deflection during cutting, as titanium’s properties can cause thin walls to vibrate. Internal corner radii should be designed at 1/3 the diameter of the smallest tool used, typically 0.5 mm minimum.
Design Guidelines
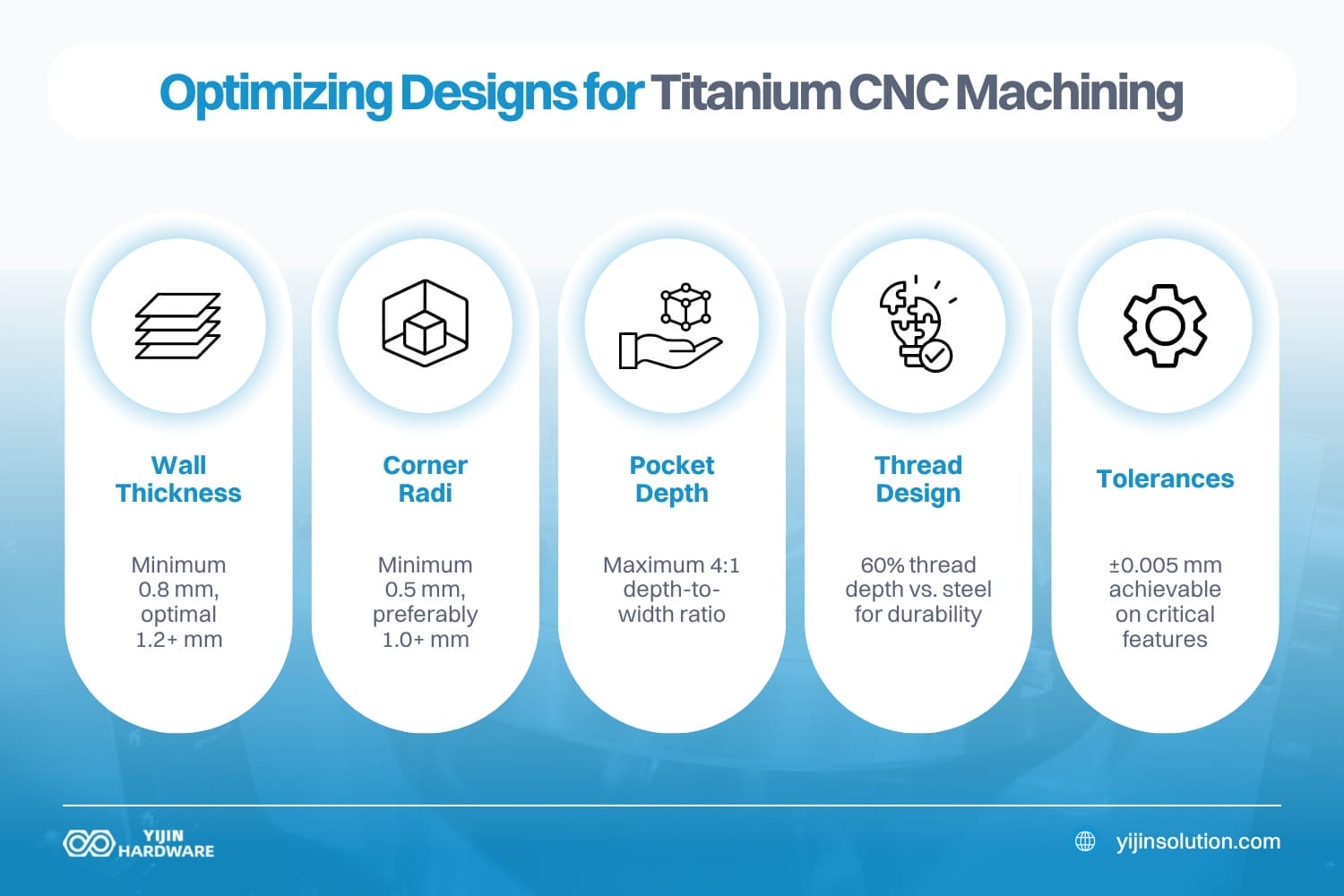
- Wall Thickness: Minimum 0.8 mm, optimal 1.2+ mm
- Corner Radii: Minimum 0.5 mm, preferably 1.0+ mm
- Pocket Depth: Maximum 4:1 depth-to-width ratio
- Thread Design: 60% thread depth vs. steel for durability
- Tolerances: ±0.005 mm achievable on critical features
Ready for Expert Titanium CNC Machining?
At Yijin Hardware, we combine advanced equipment, specialized tooling, and extensive experience to deliver exceptional titanium CNC machined parts. Our capabilities ensure your components meet the most demanding requirements for applications in aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors.
Contact us today for a consultation on your titanium machining project and discover how our advanced techniques and materials expertise can transform your designs into reality. With our focus on quality and precision, we’re your ideal partner for all titanium CNC machining needs.
Titanium CNC Machining FAQs
Why is titanium hard to machine?
Titanium is difficult to cut because it combines low thermal properties, high chemical reactivity, and unique mechanical characteristics. Its poor heat transfer concentrates cutting temperatures at the tool edge, causing rapid wear. Additionally, titanium’s elasticity causes workpiece deflection undercutting pressure, creating vibration issues during machining operations.
What cutting tools work best for titanium CNC machining?
The most effective tools for machining titanium are sharp carbide cutters with specialized coatings designed specifically for this challenging metal. Tools with TiAlN or AlTiN coatings resist the high heat generated when cutting titanium, while variable helix designs reduce vibration. For best results, tools should have positive rake angles (5-15°) and reinforced edges to handle the shock when cutting this material.
How does titanium compare to steel for machined parts?
Titanium and steel offer different performance profiles, with titanium providing 45% weight reduction while maintaining comparable strength. Titanium shows superior resistance to corrosion, particularly in saltwater, where it outperforms even high-grade stainless. However, titanium typically costs 5-10 times more than steel and requires more specialized processing, making it best for applications where its unique properties justify the investment.
Back to Top: Titanium CNC Machining | Custom Titanium Machining Parts









