The surface finish you select can greatly impact your product’s final looks and performance when it comes to custom CNC parts.
This article will go through 10 common aluminum finish types to help you select the ideal choice for your specific use.
From the sleek brushed aluminum visual to the robust protection of hard anodizing, you will learn how each finish can benefit your CNC projects.
Why Use Surface Finishes for Your Aluminum Parts
Surface finishes are important for increasing the life and performance of aluminum parts in custom CNC manufacturing. For example, anodized aluminum can stay in salt spray testing for up to 1000 hours while untreated aluminum lasts only 96 hours. Surface treatments also make components more visually appealing. It makes them ideal for different uses.
The most important property of surface finishes is its capability to provide a protective coating against UV light, moisture and extreme temperatures. This protective layer coating helps in preventing corrosion, wear and tear. Additionally, aluminium finishes can decrease friction, increase heat dissipation. They can also improve the part functionality as a whole.
For those looking to optimize the performance and aesthetics of your CNC parts, design and engineering services from Yijin Hardware can help guide you in selecting the best surface treatment for your specific needs. For Beginners to have a better understanding of Surface Finishes, feel free to check this guide: Surface Finishes In CNC Machining
2 Main Groups of Aluminum Finishes
Aluminum finishes improve looks, durability and performance of CNC machined components. Aluminum finishes fall into two main groups: mechanical and chemical. From mechanical to chemical finishes, each surface treatment has distinct properties.
5 Types of Mechanical Finishes
Mechanical finishing means physically changing the aluminum’s texture and look using abrasive media or tools. This process involves material removal to get the desired appearance and texture. Common mechanical techniques like brushing, polishing can impart distinct traits to the metal. Below we will discuss them briefly:
1. Brushing
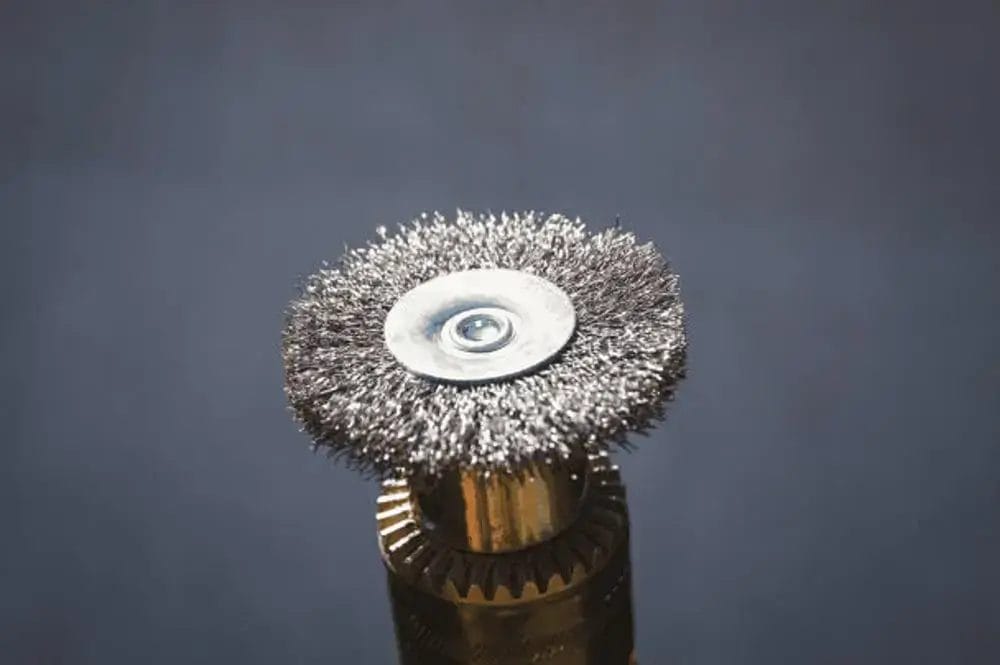

Brushing is a mechanical surface treatment that gives a uniform, satin-like finish. It uses abrasive brushes or pads to produce fine and parallel lines on the metal. This method also removes minor surface blemishes and creates a consistent, directional pattern that diffuses light for a matte look.
The two main brushing methods are wheel brushing and belt brushing. Wheel brushing uses nylon or rotating wire wheels to make circular patterns, while belt brushing uses abrasive belts for linear patterns. Wheel brushing works better for curved areas while belt brushing is suitable for flat surfaces. It is used to improve visual appeal and create a decorative look. However, it may slightly reduce corrosion resistance.
Brushed aluminum finishes are generally used for architectural parts, appliances, and electronics casings.
2. Polishing
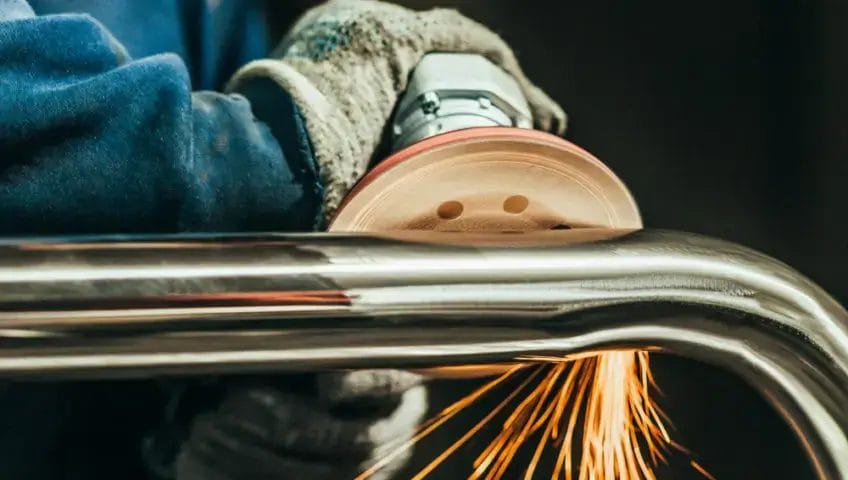

Polishing is a finishing method that produces a smooth and reflective surface on aluminum parts. It progressively uses finer abrasives to eliminate microscopic surface irregularities.
Two main types of polishing are mechanical polishing and electrolytic polishing.
Mechanical polishing utilizes rotating wheels with abrasive compounds. Electrolytic polishing uses an electrolyte solution to dissolve surface material. Mechanical polishing creates high gloss finishes while electrolytic polishing works better for intricate shapes.
Polishing gives maximum reflectivity up to 95% and a luxurious look but needs more maintenance to preserve the shine. Also, polished surfaces are more vulnerable to visible scratches and fingerprints.
Polished aluminum surface finish are often used in automotive trim, boat parts, and high-end consumer goods.
3. Grinding
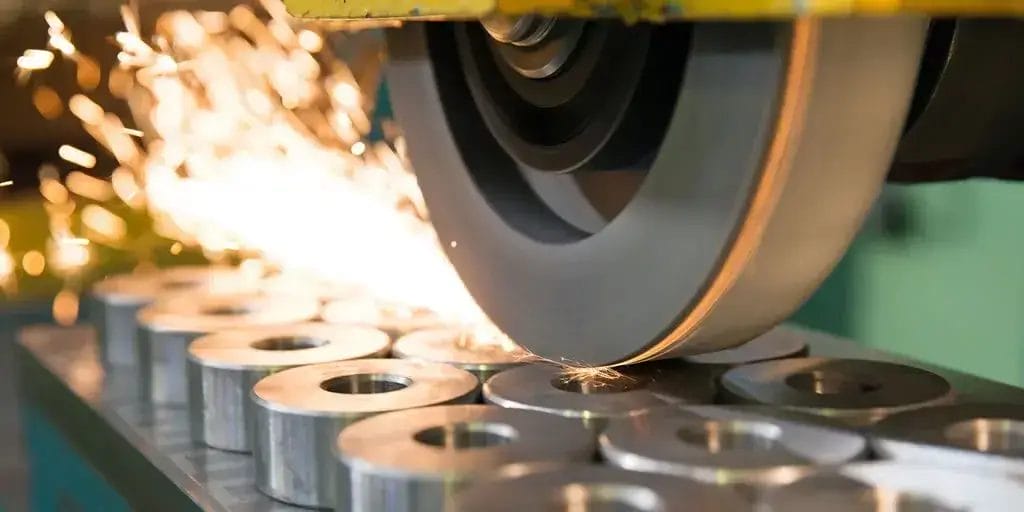

Grinding is an accurate abrasive process for removing material from aluminum surfaces using rotating wheels or belts.
Two main techniques are surface grinding and cylindrical grinding.
Surface grinding is used to make flat surfaces. While, cylindrical grinding is for cylindrical or conical shapes. The grinding wheel of bonded abrasive grains rotates at high speeds (typically 3000-6000 RPM) for accurate material removal rates of 0.0001-0.001 inches per pass.
Grinding can achieve tight tolerances of ±0.0001 inches which is great for high-precision parts. It’s good for removing surface defects, preparing surfaces for finishing or making a uniform matte appearance. It typically improves surface roughness by 70-80% compared to milling.
Grinding is widely used in industries like automotive and aerospace where tight tolerances are important.
4. Blasting
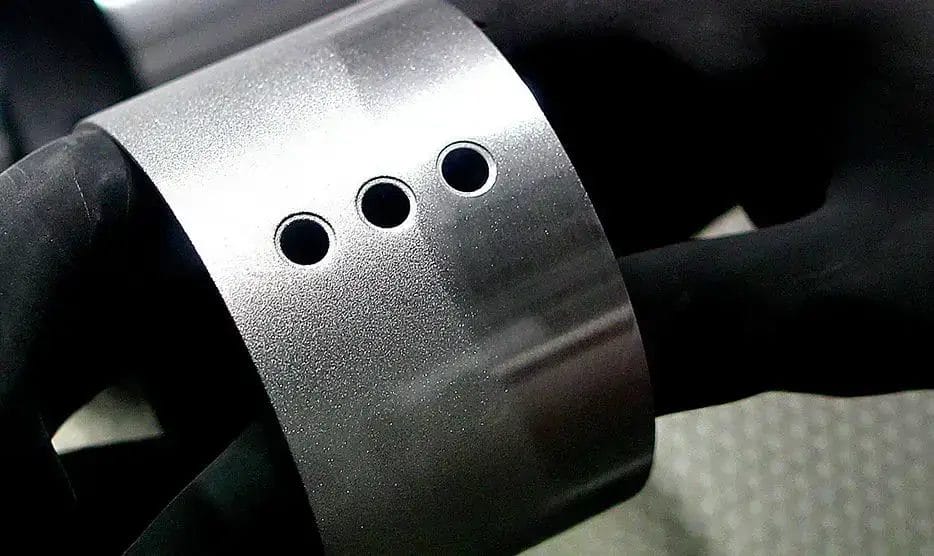

Blasting is a surface finishing process that throw abrasive materials at high speeds (50-130 m/s) against aluminum surfaces. Common blasting media are sand, glass beads, steel shot, and aluminum oxide. These particles remove surface contaminants, create texture, and alter the surface profile.
The process usually uses air pressure of 60-100 PSI and can achieve surface roughness (Ra) between 0.8-6.3 μm. It depends on media size (20-120 mesh) and blasting settings. The process gives a uniform matte finish and the final surface texture depending on the media size and blast pressure used.
Benefits of blasting include fast processing and great surface preparation for subsequent coatings. Blasting aluminum finishes are commonly used in automotive, aerospace and architecture. There they are mainly used for paint removal, surface preparation and matte textures.
5. Tumbling

Tumbling is a mass finishing method that uses a rotating barrel or vibrating container with abrasive media to smooth aluminum parts.
It has two types: vibratory tumbling and rotary tumbling. Vibratory tumbling uses high-frequency vibrations. While rotary tumbling relies on barrel rotation. Both types create friction between parts and media which results in smoothing surfaces and removing burrs. The process often uses ceramic, plastic or steel media, along with compounds to improve finishing.
Tumbling is economical for high volume production. This technique is ideal for parts that need deburring and surface smoothing.
Tumbling aluminum finishes are used in consumer electronics, automotive parts and decorative hardware.
5 Types of Chemical Finishes
Chemical finishes mean changing the aluminum surface through reactions with certain chemicals or electrochemical processes. These types change the surface properties of aluminum. It increases its hardness, corrosion protection and appeal.
1. Anodizing

Anodizing uses an electrochemical process to create a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer on aluminum surfaces.
It involves submerging aluminum in an electrolyte bath and passing an electric current through it. When current goes through the solution, oxygen ions are discharged. These ions then combine with aluminum atoms at the surface to form a hard, porous aluminum oxide layer.
The thickness of the oxide layer can be controlled by adjusting anodizing duration and current, typically ranging from 5 to 25 microns.
The three main anodizing types are:
- Sulfuric acid anodizing (Type II) – Most common, makes clear or colored finishes.
- Chromic acid anodizing (Type I) – Thinner coatings, often used in aerospace.
- Hard anodizing (Type III)- Creates thick, wear-resistant coatings.
Anodized aluminum offers many benefits like better hardness, electrical insulation. it also offers a range of aesthetic finishes from matte to high gloss. This finishing method is widely used in places where both functional performance and visual appeal are important. For example architecture, aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods industries.
2. Chemical Conversion Coatings

Chemical conversion coating makes a protective layer on metal surfaces. It does so through a chemical reaction between the metal and a special solution. It is achieved by dipping metal part in a chemical solution that reacts with the surface to form protective coating.
The main types of chemical conversion coatings are chromate conversion coatings and phosphate conversion coatings. Chromate uses chromic acid to make a layer with excellent corrosion protection. Phosphate uses phosphoric acid to form a crystalline coating for good paint adhesion.
These coatings are typically between 0.00001″ to 0.00003″ thick and can be clear, colored or iridescent. The process increases corrosion resistance and improves paint adhesion.
Chemical conversion coating is usually used for applications like automotive parts, aerospace parts and as pre-treatment for painting or powder coating processes.
3. Electroplating

Electroplating is a process that deposits a thin layer of metal on aluminum surfaces which changes its surface qualities. The aluminum part gets immersed in an electrolyte solution with metal ions and electric current passing through it.
Electroplating can increase aluminum’s conductivity, wear resistance, and corrosion defense. It is commonly used in automotive, electronics, and jewelry industries.
4. Etching

Etching is defined as the removal of material from aluminum surfaces by using chemicals or physical means.
It has two types which are chemical etching and laser etching. Chemical etching employs acidic or alkaline solutions to dissolve targeted areas. While laser etching vaporizes surface material with focused light beams. Both methods can make complex patterns, textures, or markings on aluminum components with high accuracy.
The etching depth ranges from 0.0001” to 0.020” which depends on the methods and parameters used. Etching allows excellent design flexibility, supports intricate patterns, and is economical for high volume manufacturing.
It is used to create decorative effects on architectural parts and print circuit boards.
5. Powder Coating
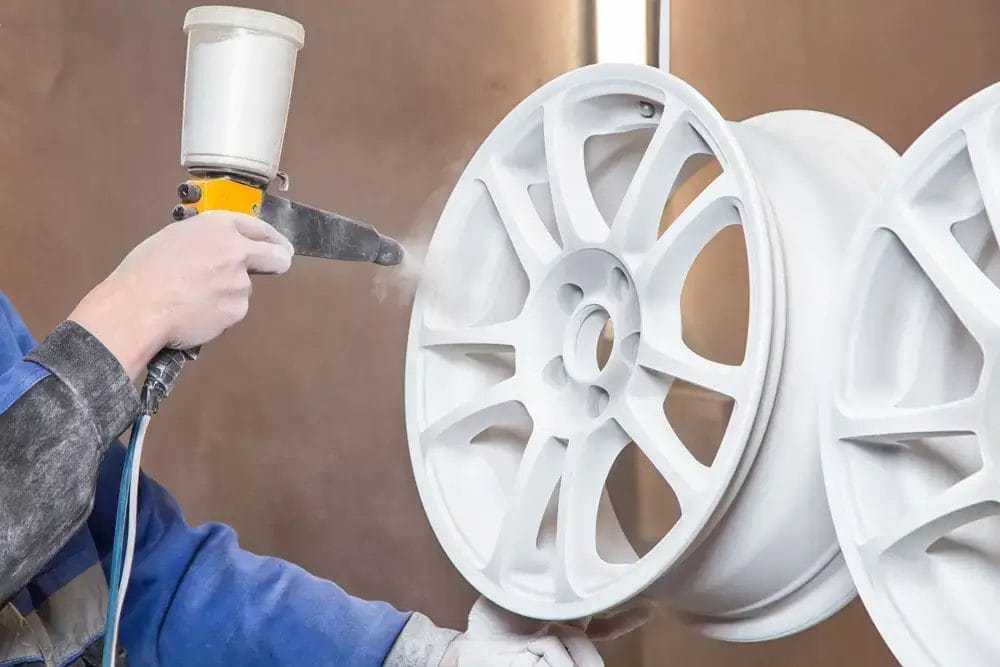

Powder coating is an electrostatic dry finishing technique in which finely ground pigment and resin particles are sprayed onto aluminum surfaces. The coated part then cures in an oven which melts the powder into a uniform film.
Types of powder coating include polyester and epoxy coating. Polyester coating is suitable for outdoor use. While epoxy coating provides superior chemical resistance.
Coating thickness ranges from 1.5-3 mils for decorative to 6-12 mils for functional coatings. Powder coating gives great durability, corrosion protection, and color options.
It is widely used in outdoor furniture, architectural components and automotive parts where chip resistance and weather resistance matter.
Factors To Consider When Choosing An Aluminum Finish:
Choosing the best aluminum surface finish requires careful thinking about a variety of factors. These factors are important to guarantee best performance and value for your specific application. Some of them them are given below:
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is important for parts that are exposed to harsh conditions. Hard anodizing method is a good choice for protecting against temperature changes, humidity, chemicals, and severe weather patterns.
Visual Appeal
Visual appeal is important once functional needs are met. Anodizing provides more vibrant colors while maintaining metal texture. For a modern look, consider brushed or polished aluminum finishes.
Performance
Performance requirements further narrow down the choice of finish options. Hard anodizing technique allows superior durability for high-wear parts. Chemical coatings are suitable for applications that need good electrical conductivity.
Industry rules
Industry rulesmay authorize or ban certain finishes. For example medical devices often need easily sterilized surfaces, so electro polishing works well there. Always check that the finish you chose abide with relevant standards.
Cost considerations
Cost Considerations mean balancing quality and budget. While some finishes like hard anodizing have higher initial costs, they often provide better long-term value due to increased durability. For mass production, automated processes like chemical coating can be more cost-effective.
Looking for Surface Finishes for Your Aluminium Parts?
For top-notch aluminum finishing for your CNC parts, look no further than Yijin Hardware.
With over 20 years under our belt and a state-of-the-art 25,000 square meter facility, Yijin Hardware provides a wide range of aluminum finishing options. These include anodizing, powder coating, and plating.
Our dedication to quality and innovation shows through our ISO/TS 16949 certification. We have over 99% customer satisfaction rate. Our experts have worked across different industries. We guarantee that your specific needs will be met precisely.
Want to take your aluminum parts to the next level? Reach out to us today for unmatched surface treatment solutions.
FAQs
Q1: What’s anodizing?
A: Anodizing uses an electrochemical process to create a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer on aluminum. It improves its durability and enables color addition.
Q2: How’s powder coating different from wet painting?
A: Powder coating uses dry powder electrostatically charged powder and is cured under heat. while wet painting uses liquid paints. Powder coating is more durable and environmentally friendly.
Q3: Can you weld anodized aluminum?
A: Yes, but first remove the anodized layer from the weld area to make sure proper fusion.

 info@yijinsolution.com
info@yijinsolution.com (+86) 188-2253-7569
(+86) 188-2253-7569







