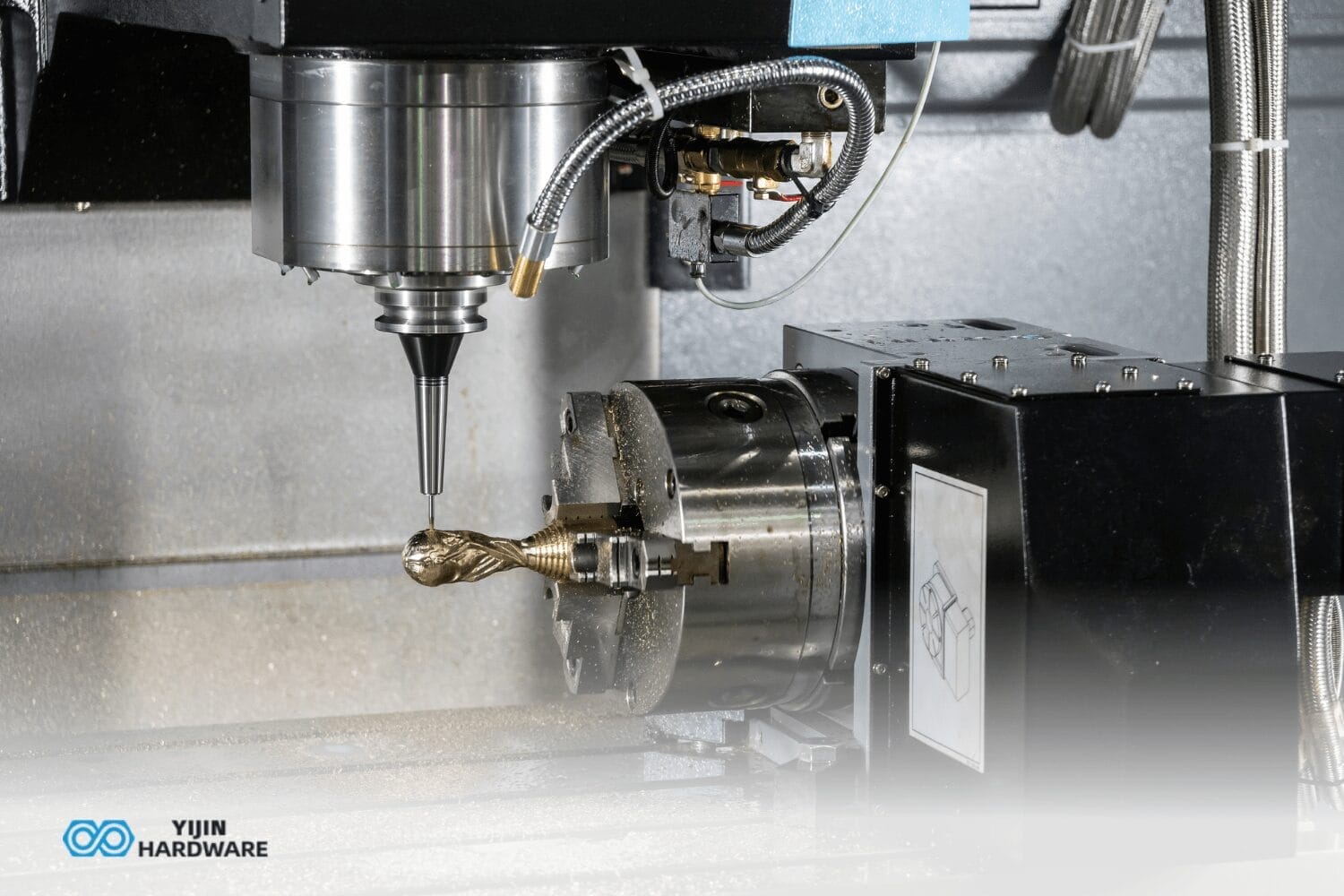
Ceramic CNC machining uses computer-controlled machines to shape ceramics. It is essential for creating parts with complicated shapes. This specialized technique employs diamond-coated cutting tools and precisely controlled machining parameters to overcome ceramics’ inherent brittleness while leveraging their exceptional properties.
Unlike metals, ceramics combine high hardness with low ductility, requiring specialized approaches to machining that differ substantially from metalworking techniques. Ceramic CNC machining companies like us, here at Yijin Hardware, leverages computer-controlled precision to create components that maintain their performance. We’ve included everything you need to know about ceramic CNC’ing below.
Key Takeaways
- Ceramic CNC machining employs computer-controlled processes and diamond-coated tools to shape brittle ceramics into complex, high-performance components.
- The method follows a rigorous, multi-stage process—from material selection and design optimization to controlled rough machining and precision finishing—to overcome ceramics’ inherent brittleness while achieving tight tolerances.
- This advanced machining technique delivers high accuracy and material versatility, making it an essential solution in industries such as aerospace, medical, and electronics.
What is Ceramic CNC Machining?
Ceramic CNC machining is a precise cutting method using computer-controlled machines. The CNC process cuts ceramic material into intricate shapes. CNC machining ceramics is ideal for more nuanced and specific shapes; it is a specialized manufacturing process that creates durable parts.
Ceramics make durable parts with complex geometries and fine details. In this process, a CNC machine utilizes various cutting tools. However, the quality of ceramic relies on precise machining operations.
How does Ceramic CNC Machining Work?
Ceramic CNC machining works by creating a detailed 3D model using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, which is then converted to a machine-readable format through Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. This process generates G-code instructions that precisely control the CNC machine’s toolpaths, cutting parameters, and movement sequences. The ceramics also allow for parts with complicated designs.
What are the Stages in Ceramic CNC Machining?
The CNC machining process contains several crucial stages, from material selection to finishing and polishing. Each stage contributes to the final quality of ceramic parts.
Successful ceramic machining requires careful attention to each process stage. The unique properties of ceramic materials demand specialized approaches throughout the manufacturing workflow. The table below outlines the critical stages in order:
| Stage | Process Step | Key Requirements and Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Material Selection and Evaluation | Evaluate material properties including hardness, thermal characteristics, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength requirements. Consider how material purity and grain size affect machinability and performance in the intended application. |
| 2 | Design Optimization | Create designs that avoid stress concentrations through appropriate wall thicknesses, support structures, and gradual transitions between features. Account for ceramics’ susceptibility to cracking under mechanical or thermal stress throughout the design process. |
| 3 | Tool Selection and Preparation | Select diamond-coated or solid diamond tooling with geometries optimized to reduce fracture risk, while preparing for accelerated tool wear. Install specialized coolant delivery systems to manage the unique thermal challenges of ceramic machining. |
| 4 | Rough Machining | Remove material using conservative cutting depths, controlled feed rates, and continuous coolant application to prevent thermal and mechanical stress. Implement careful step-down approaches for deep features to maintain workpiece integrity throughout machining. |
| 5 | Precision Finishing | Apply specialized grinding and polishing techniques using ultra-precise tool control while carefully managing thermal conditions. Minimize vibration to prevent microcracking during final dimensional and surface quality refinement. |
| 6 | Quality Verification | Conduct comprehensive inspection using coordinate measuring machines for dimensional accuracy and non-destructive testing for internal integrity. Verify surface quality and material properties to ensure the component will perform as intended in its application environment. |
Each stage builds upon the previous one, creating a comprehensive process that addresses the unique challenges of ceramic machining.
What are the Key Techniques in Ceramic CNC Machining?
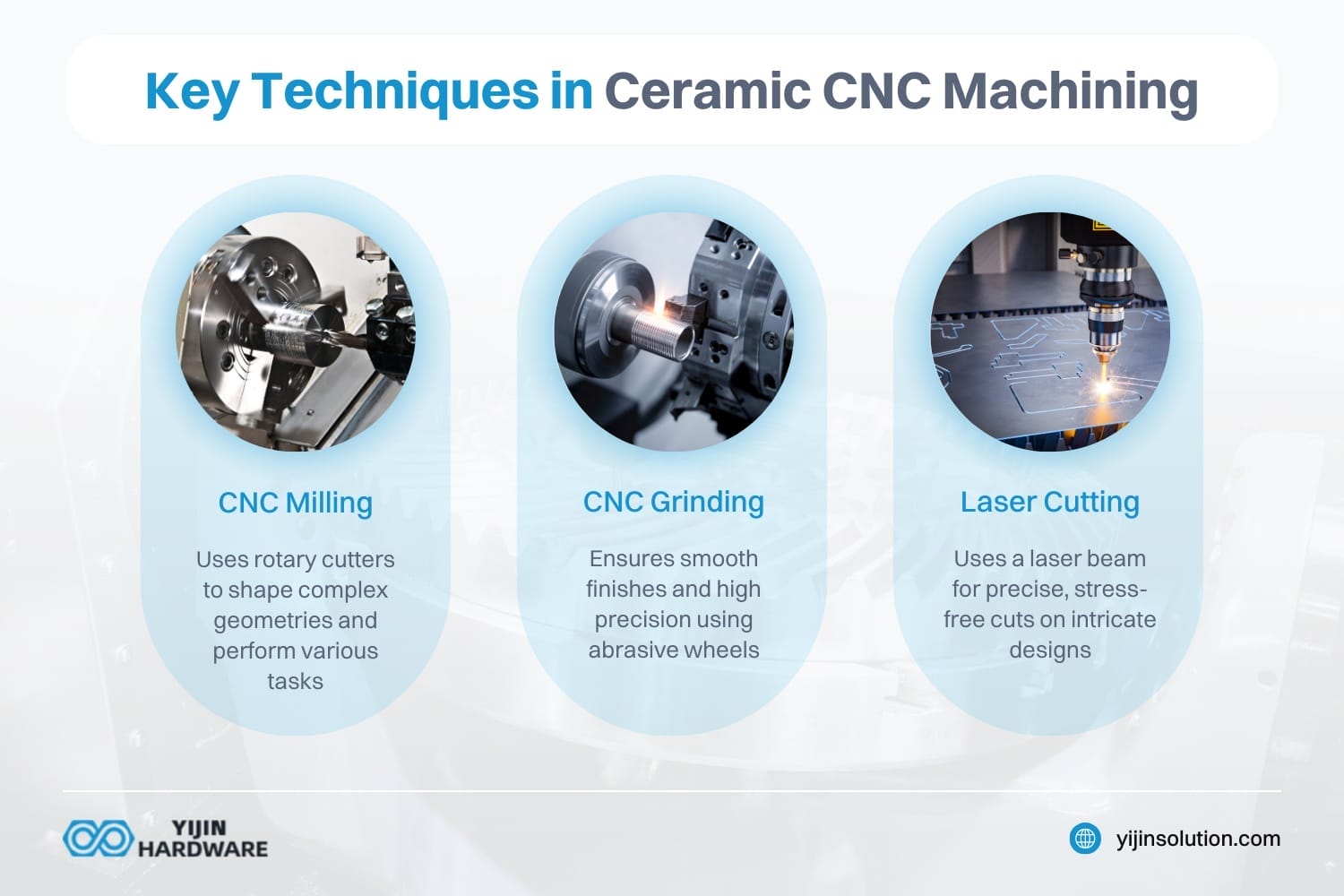
Different CNC machining techniques are essential for machining ceramics, such as milling and grinding. These techniques produce high-quality ceramic parts. The best choice is a ceramic material that fits project parameters.
- CNC Milling: CNC milling uses rotary cutters to remove material.
- It is ideal for complex geometries.
- CNC milling machines can perform various tasks.
- Used in CNC machining to remove material.
- Grinding: Grinding provides a smooth surface finish on the ceramic.
- It is vital for precise applications.
- Abrasive wheels refine dimensions to reduce errors.
- Grinding is used for machining to make quality parts.
- Laser Cutting: A laser beam cuts the ceramic workpiece.
- It is suitable for intricate designs and thin sections.
- This ensures clean, precise edges without material stress.
- Laser cutting to cut ceramic improves exactness.
Choosing the Right Ceramic for CNC Machining
The type of ceramic influences the machining and performance. Different ceramics used exhibit distinct properties, such as zirconia and silicon carbide ceramics. Ceramics are ideal materials when performance matters, but precision machining of ceramics requires the right ceramic.
| Ceramic Type | Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina Ceramics | High hardness, wear resistance | Electrical insulators, wear parts |
| Zirconia | High strength, fracture toughness | Medical implants, high-stress components |
| Silicon Carbide | Extreme hardness, high-temperature strength | Abrasives, semiconductor components |
| Aluminum Nitride | High thermal conductivity | Heat sinks, electronic substrates |
| Machinable Ceramic | Ease of machining | Prototypes, small-scale production |
Advantages of Ceramic CNC Machining
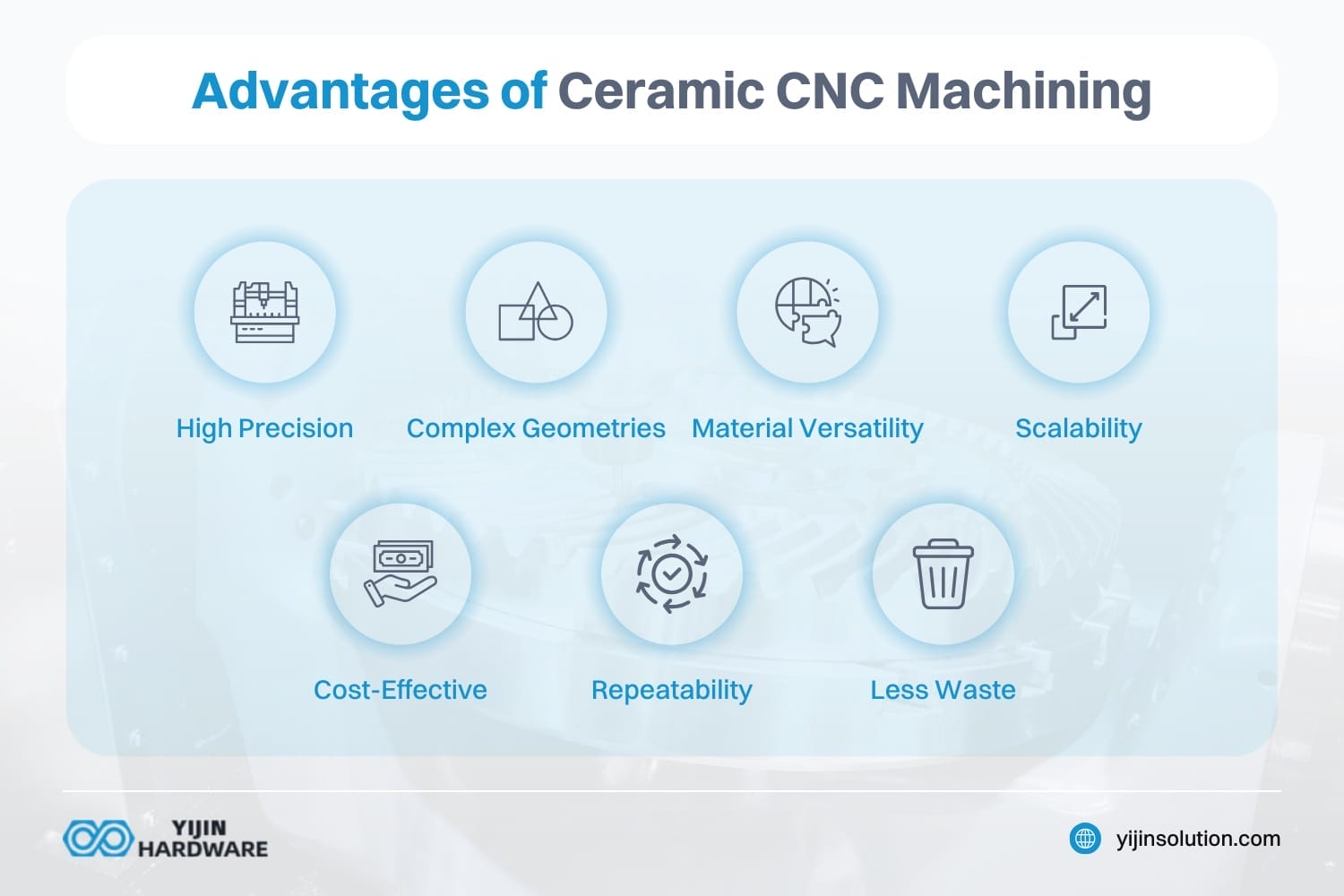
The advantages of ceramic machining, such as high precision and material versatility, are significant for various industries. Ceramic CNC machining offers many benefits over traditional machining methods.
- High Precision: Achieves tight tolerances for critical applications
- Complex Geometries: Creates intricate shapes otherwise impossible
- Material Versatility: Machines with a range of different types of ceramics
- Scalability: Adapts to varying production volumes efficiently
- Cost-Effective: Reduces material waste and improves production rates
- Repeatability: Ceramic parts are made consistently
- Less Waste: The process reduces waste.
Applications of Ceramic CNC Machining
Applications of ceramic machining span numerous industries, such as aerospace and medical devices. Ceramic CNC machining due to its unique qualities is versatile. According to the Journal of Materials Processing Technology, ceramic matrix composites are enabling materials, unlocking new thermo-mechanical properties for engineers.
- Aerospace: Heat shields, engine components
- Medical: Implants, dental prosthetics
- Electronics: Substrates, insulators
- Defense: Armor, high-performance parts
- Automotive: Sensors, wear parts
- Chemical: Chemical-resistant parts
Yijin Hardware delivers top-quality CNC ceramic services. We combine CNC machining with advanced techniques, and our expertise ensures precision ceramic components. Contact us today for reliable machining services and exceptional results.
Ceramic CNC Machining FAQs
What materials cannot be CNC machined?
Some materials, such as glass ceramics, rubber, and certain composites, cannot be easily CNC machined. CNC machining services work best with rigid, stable materials that hold precise cuts. Ceramics aren’t impossible to machine, but their hardness and brittleness require specialized tools. Non-machinable materials often lack structural integrity or produce excessive tool wear.
How to select the right ceramic for CNC machining?
Selecting the right ceramic for CNC machining depends on hardness, thermal stability, and application needs. Technical ceramic materials like alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide are ideal for CNC machining. The use of ceramics in CNC depends on whether the part requires extraordinary precision or extreme durability. Ceramics are commonly used in aerospace, medical, and electronics industries for high-performance components.
What are some common CNC machining ceramic problems?
Common CNC machining problems with ceramics include chipping, cracking, and excessive tool wear after creating machined parts. Disadvantages of ceramic CNC machining arise from material brittleness and high cutting tool costs. Machining can be used to process ceramics, but specialized techniques reduce material damage. Ceramic substrates require slow feed rates and diamond-coated tools for best results.
Are ceramics difficult to machine?
Ceramics are used in CNC machining, but they are challenging due to their hardness and brittleness. Using a CNC machine, manufacturers must carefully control speeds and tool pressures to prevent fractures. Multi-axis CNC machines help by enabling complex cuts while reducing stress on the material. Despite challenges, CNC machining makes it possible to achieve precise ceramic parts for demanding applications.
Back to Top: What is Ceramic CNC Machining?









